
Concept explainers
Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are connected by a slider block P of negligible mass. The rod attached at A has a mass of 0.8 kg and a length of 160 mm. Rod BP has a mass of 1 kg and is 200 mm long and the friction between block P and AE is negligible. The motion of the system is controlled by a couple M applied to bar BP. Knowing that at the instant shown rod BP has an angular velocity of 20 rad/s clockwise and an angular acceleration of 80 rad/s2 clockwise, determine (a) the couple M, (b) the components of the force exerted on AE by block P.
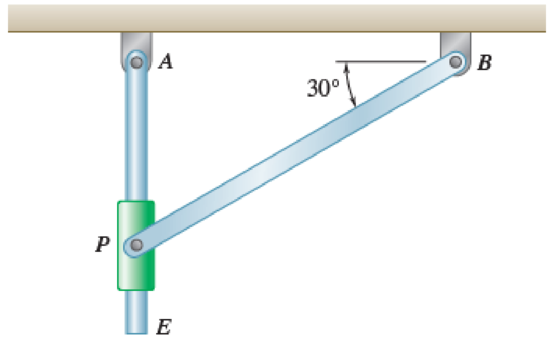
Fig. P16.141 and Fig. P16.142
(a)
Find the value of couple M.
Answer to Problem 16.142P
The value of couple M is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the rod AE is
The mass of the rod BP is
The length of the rod AE is
The length of the rod BP is
The angular velocity is
The angular acceleration is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Calculate the position vector
The position of P with respect to A.
The position of P with respect to B.
The position of P with respect to E.
The angular velocity of rod BP in vector form is
The angular acceleration of rod BP in vector form is
Calculate the velocity of rod BP
Substitute
Consider the relative angular velocity of rod AE as
Calculate the velocity of point P
Substitute
Resolving i and j components as shown below.
Calculate the acceleration of rod BP
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point P with respect to point E
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point P
Substitute
Resolving i and j components as shown below.
Calculate the weight of
For rod AE.
Substitute
For rod BP.
Substitute
Calculate the mass moment of inertia
For rod AE.
Substitute
For rod BP.
Substitute
Calculate the position vector
The position of mass center G with respect to the rod AE.
The position of mass center H with respect to the rod BP.
Calculate the acceleration of point G
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point H
Substitute
Calculate the inertial terms of the mass center
For rod AE.
For rod BP.
Calculate the effective couples at mass center
For rod AE.
For rod BP.
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of rod AE as shown in Figure 1.
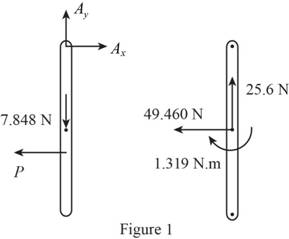
Refer to Figure 1.
Apply the Equilibrium of moment about A as shown below.
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of rod BP as shown in Figure 2.
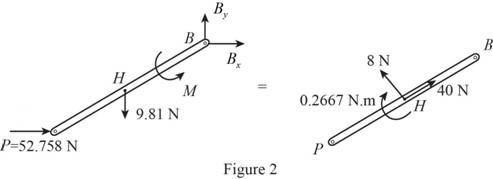
Refer to Figure 2.
Apply the Equilibrium of moment about A as shown below.
Hence, the couple M is
(b)
Find the components of the force exerted on AE by block.
Answer to Problem 16.142P
The components of the force exerted on AE by block is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the rod AE is
The mass of the rod BP is
The length of the rod AE is
The length of the rod BP is
The angular velocity is
The angular acceleration is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
The components of the force exerted on AE by block
Therefore, the components of the force exerted on AE by block is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANIC
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Experiencing MIS
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Using properties of a saturated water, explain how you would determine the mole fraction of water vapor at the surface of a lake when the temp of the lake surface and the atmospheric pressure are specified.arrow_forwardConsider a glass of water in a room at 15 degrees C and 97 kPa. If the relative humidity in the room is 100 percent and the water and the air are in thermal and phase equilibrium, determine the mole fraction of the water vapor in the air and the mole fraction of air in the water.arrow_forwardStaring with an energy balance on a cylindirical shell volume element, derive the steady one dimensional heat conduction equation for a long cylinder with constant thermal conductivity in which heat is generated at a rate of egen.arrow_forward
- Consider a round potato being baked in an oven. Would you model the heat transfer to the potato as one, two, or three dimensional? Would the heat transfer be steady or transient? Also, which coordinate system would you use to solve this problem, and where would you place the origin? Explain.arrow_forward0 = 6 a = 25 t = 3 Y b = 30 xarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardreading is 0.4 mas SHOWN. Assume h₁ = 0.4 m, h₂ = 0.5 m. (a) Do you know the specific weight of mercury? (b) Do you know the specific weight of gasoline? (c) Do you know the specific weight of oil? (a) YHg = 133,000 (b) Ygas = 6867 (c) Yoil = 8829 eTextbook and Media Part 2 N/m³ N/m³ N/m³ A+ Gasoline t +B Oil -Mercury Attempts: unlimited Did you calculate the pressure difference between two locations using the correct specific weight? Did you assume that the pressures in fluid are the same in a horizontal plane even though they are in different tubes? Are the calculated pressures in a column of fluid always higher at lower elevations? Did you account for the fact that the two horizontal tubes of the U-tube are above the ground? Concepts: The pressure in a fluid is a function of the specific weight of the fluid and the height relative to a reference. Pressure is constant in a horizontal plane of a continuous mass of fluid. (a) What is the initial pressure difference? (PA-PB) (b) What is…arrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) "-4y+3y=0 3) "+16y=0 2) y"-16y=0 4) y"-y-6y=0 5) y"+2y=0 7) y"+y=0, (#0) 9) y"-y=0, y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -4 11) y"-4y+3y=0, y(0)=-1, 13) y'(0) = -5 "+2y+2y=0 15) y"-9y=0 17) y"-4y=0 6) y"-2y+2y=0 8) "+4y+5y=0 10) y"-9y=0, y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 0 12) y"-3y+2y= 0, y(0)=-1, y'(0) = 0 14) 4y+4y+y=0 16) "+6y+12y=0 18) 4y+4y+17y=0arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





