
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the ester formed when ethanoic acid and propyl alcohol react has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Esters are prepared by condensation of
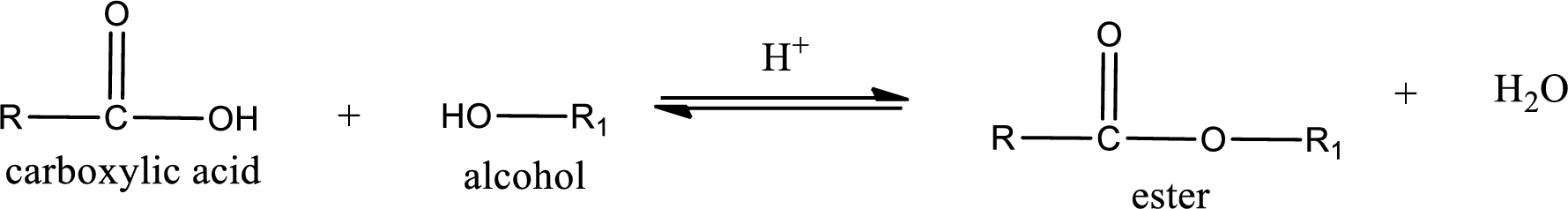
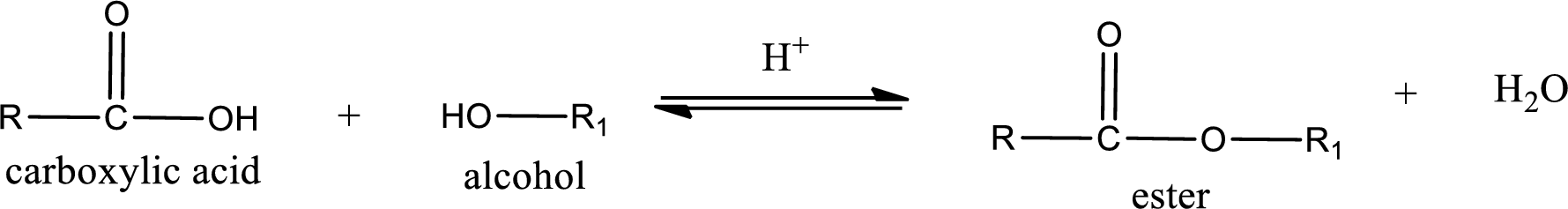
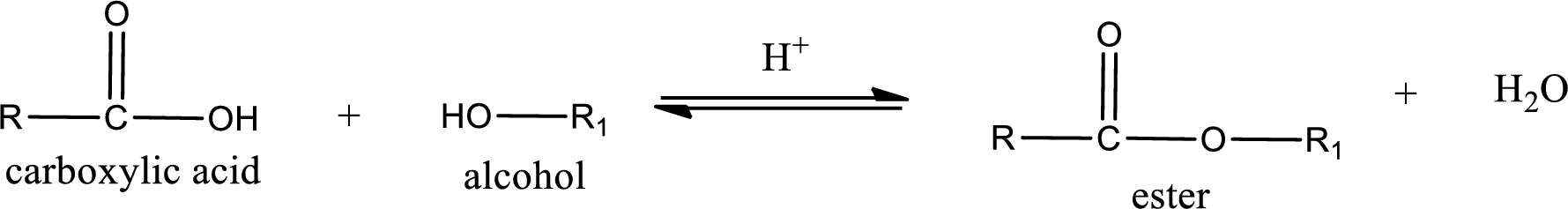
Esterification reaction is the one in which the carboxylic acid is condensed with an alcohol (or phenol) in presence of strong acid catalyst to produce ester. The general reaction scheme can be given as,
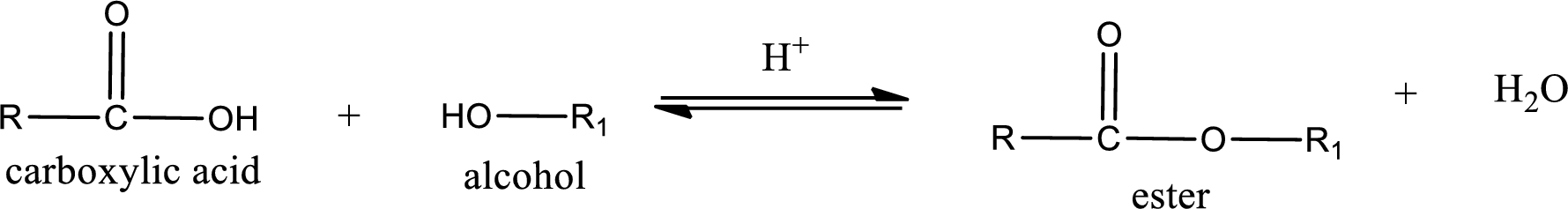
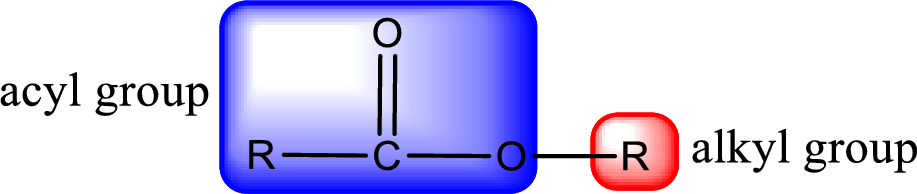
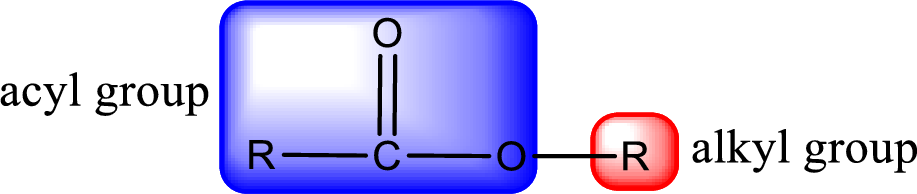
For naming an ester, it can be structurally viewed in a way that contains an acyl group and an alkyl group.
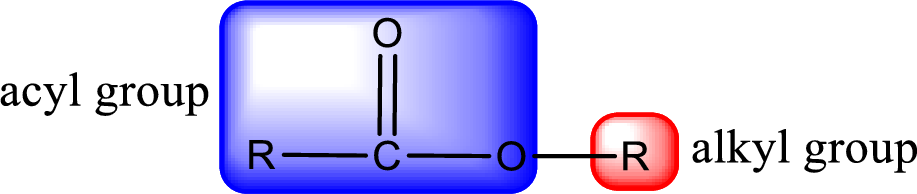
Rules to obtain IUPAC name and common name for an ester:
- Alkyl part appears first in the IUPAC name and it is followed by the acyl part of ester as a separate word.
- Name of the alkyl part in the ester is just a name of R group. It can be alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl group.
- Acyl part present in the ester is named by considering the acid name and replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
- To obtain the common name the alkyl part name is the same while the acyl part name is derived from the common name of the acid by replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
(a)
Answer to Problem 16.98EP
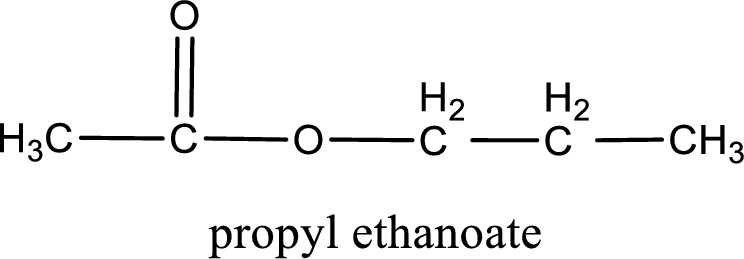
IUPAC name of the ester formed is propyl ethanoate.
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid and alcohol structure is,

The reaction between two compounds that are shown above, result in the formation of ester. The structure of the ester formed and the complete reaction can be given as shown below,
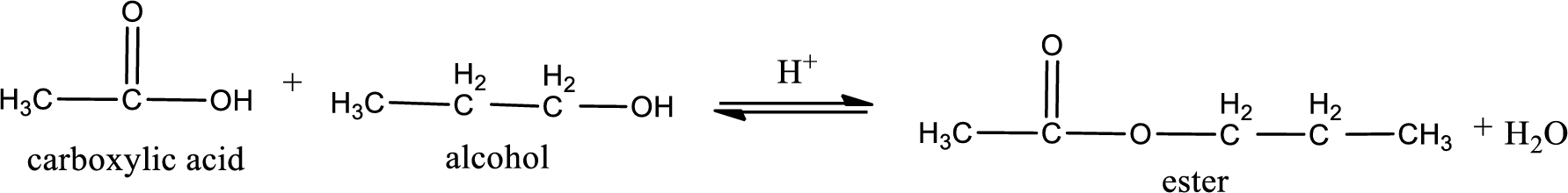
The structure of ester is,
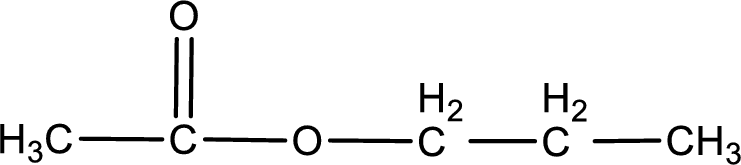
The alkyl and acyl group is identified as shown below,
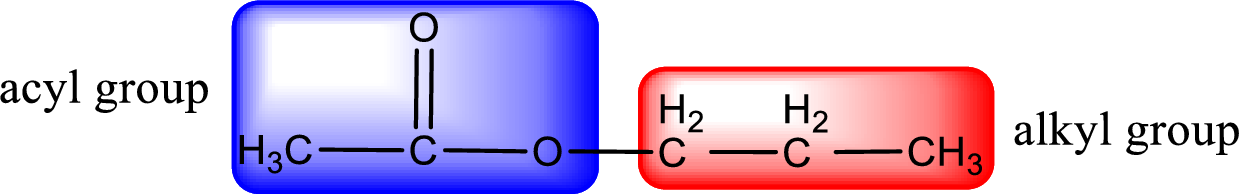
Alkyl group contains three carbon atoms. Hence alkyl group is named as propyl. The acyl group contains two carbon atoms. The IUPAC name of carboxylic acid that contains three carbon atoms is ethanoic acid. For naming acyl group in ester the suffix “-ic acid” is converted into “-ate”. This gives the name of acyl part as ethanoate. Therefore IUPAC name of the given ester is propyl ethanoate.
IUPAC name of the formed ester is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the ester formed when acetic acid and 1-pentanol react has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Esters are prepared by condensation of carboxylic acid with an alcohol. A molecule of water is lost on this reaction. The reaction that takes place in producing esters is known as esterification reaction.
Esterification reaction is the one in which the carboxylic acid is condensed with an alcohol (or phenol) in presence of strong acid catalyst to produce ester. The general reaction scheme can be given as,
For naming an ester, it can be structurally viewed in a way that contains an acyl group and an alkyl group.
Rules to obtain IUPAC name and common name for an ester:
- Alkyl part appears first in the IUPAC name and it is followed by the acyl part of ester as a separate word.
- Name of the alkyl part in the ester is just a name of R group. It can be alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl group.
- Acyl part present in the ester is named by considering the acid name and replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
- To obtain the common name the alkyl part name is the same while the acyl part name is derived from the common name of the acid by replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
(b)
Answer to Problem 16.98EP
IUPAC name of the ester formed is pentyl ethanoate.
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid and alcohol structure is,
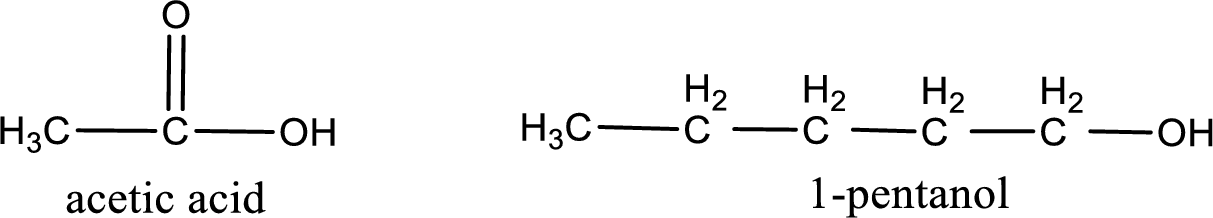
The reaction between two compounds that are shown above, result in the formation of ester. The structure of the ester formed and the complete reaction can be given as shown below,

The structure of ester is,
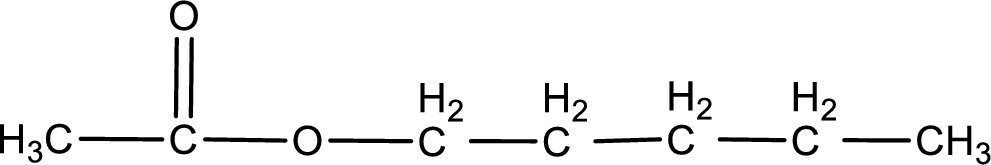
The alkyl and acyl group is identified as shown below,
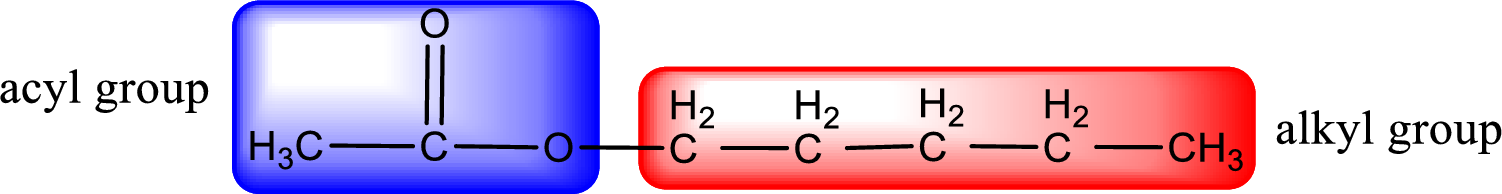
Alkyl group contains five carbon atoms. Hence alkyl group is named as pentyl. The acyl group contains two carbon atoms. The IUPAC name of carboxylic acid that contains three carbon atoms is ethanoic acid. For naming acyl group in ester the suffix “-ic acid” is converted into “-ate”. This gives the name of acyl part as ethanoate. Therefore IUPAC name of the given ester is pentyl ethanoate.
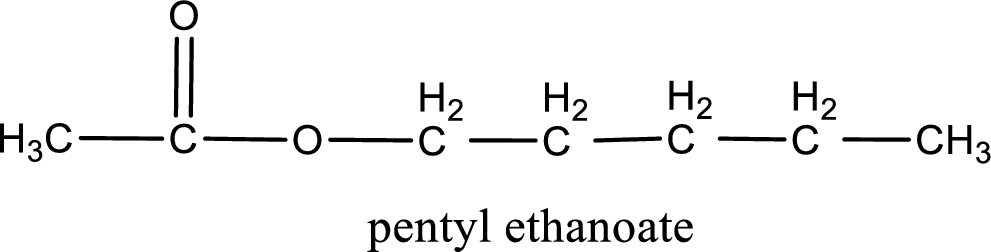
IUPAC name of the formed ester is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the ester formed when acetic acid and 2-pentanol react has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Esters are prepared by condensation of carboxylic acid with an alcohol. A molecule of water is lost on this reaction. The reaction that takes place in producing esters is known as esterification reaction.
Esterification reaction is the one in which the carboxylic acid is condensed with an alcohol (or phenol) in presence of strong acid catalyst to produce ester. The general reaction scheme can be given as,
For naming an ester, it can be structurally viewed in a way that contains an acyl group and an alkyl group.
Rules to obtain IUPAC name and common name for an ester:
- Alkyl part appears first in the IUPAC name and it is followed by the acyl part of ester as a separate word.
- Name of the alkyl part in the ester is just a name of R group. It can be alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl group.
- Acyl part present in the ester is named by considering the acid name and replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
- To obtain the common name the alkyl part name is the same while the acyl part name is derived from the common name of the acid by replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
(c)
Answer to Problem 16.98EP
IUPAC name of the ester formed is 1-methylbutyl ethanoate.
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid and alcohol structure is,
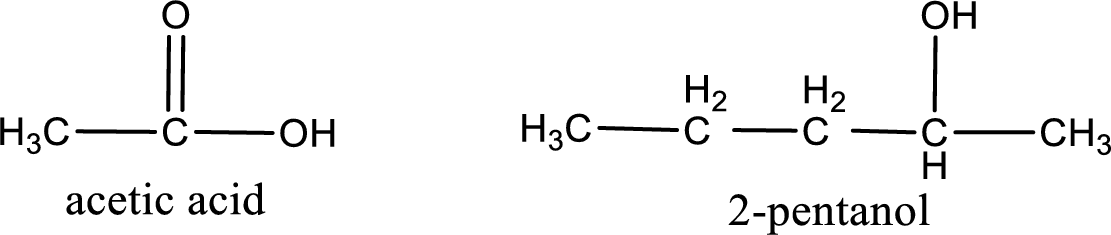
The reaction between two compounds that are shown above, result in the formation of ester. The structure of the ester formed and the complete reaction can be given as shown below,

The structure of ester is,
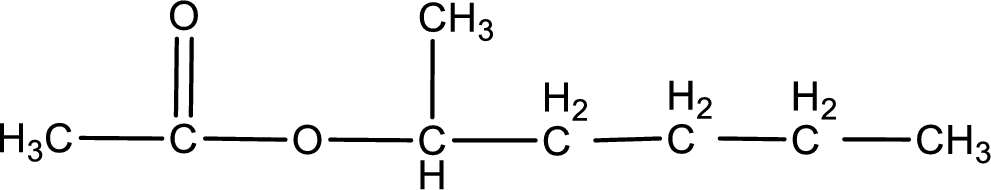
The alkyl and acyl group is identified as shown below,
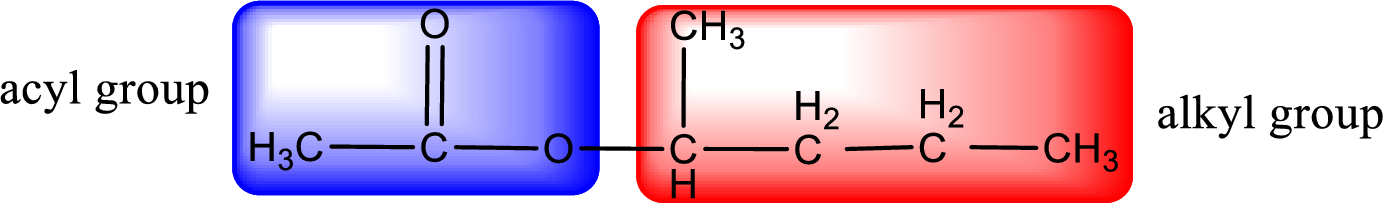
Alkyl group contains five carbon atoms. Four carbon in a long chain with a methyl group substituted in the first carbon atom. Hence alkyl group is named as 1-methylbutyl. The acyl group contains two carbon atoms. The IUPAC name of carboxylic acid that contains three carbon atoms is ethanoic acid. For naming acyl group in ester the suffix “-ic acid” is converted into “-ate”. This gives the name of acyl part as ethanoate. Therefore IUPAC name of the given ester is 1-methylbutyl ethanoate.
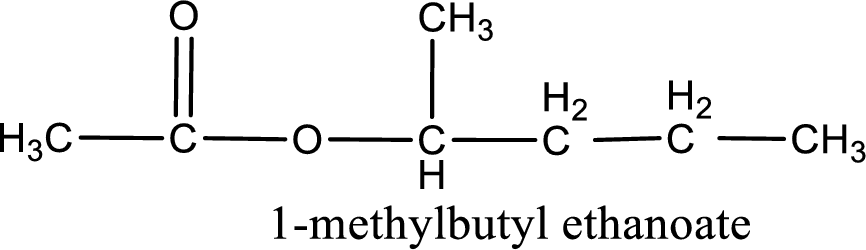
IUPAC name of the formed ester is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the ester formed when ethanol and benzoic acid react has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Esters are prepared by condensation of carboxylic acid with an alcohol. A molecule of water is lost on this reaction. The reaction that takes place in producing esters is known as esterification reaction.
Esterification reaction is the one in which the carboxylic acid is condensed with an alcohol (or phenol) in presence of strong acid catalyst to produce ester. The general reaction scheme can be given as,
For naming an ester, it can be structurally viewed in a way that contains an acyl group and an alkyl group.
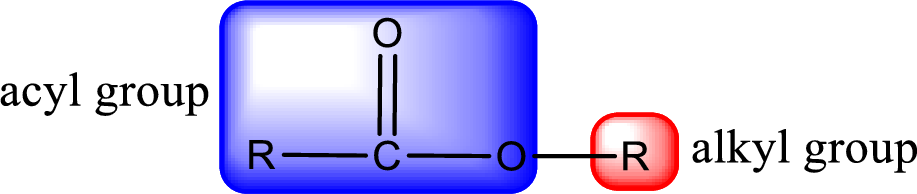
Rules to obtain IUPAC name and common name for an ester:
- Alkyl part appears first in the IUPAC name and it is followed by the acyl part of ester as a separate word.
- Name of the alkyl part in the ester is just a name of R group. It can be alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl group.
- Acyl part present in the ester is named by considering the acid name and replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
- To obtain the common name the alkyl part name is the same while the acyl part name is derived from the common name of the acid by replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
(d)
Answer to Problem 16.98EP
IUPAC name of the ester formed is ethyl benzoate.
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid and alcohol structure is,
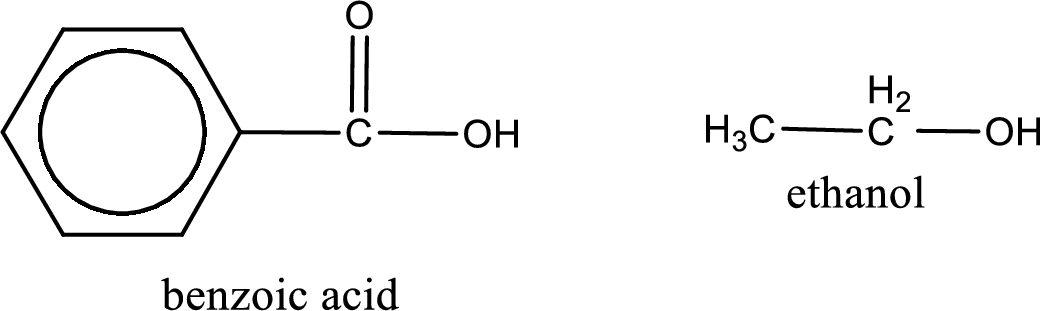
The reaction between two compounds that are shown above, result in the formation of ester. The structure of the ester formed and the complete reaction can be given as shown below,
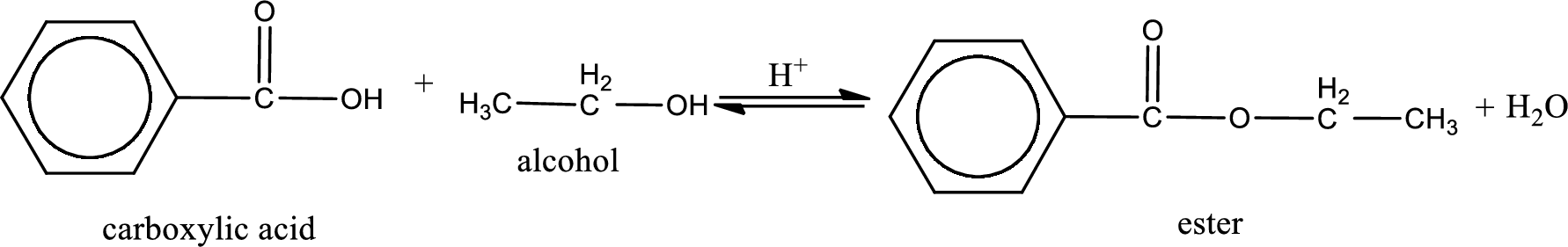
The structure of ester is,
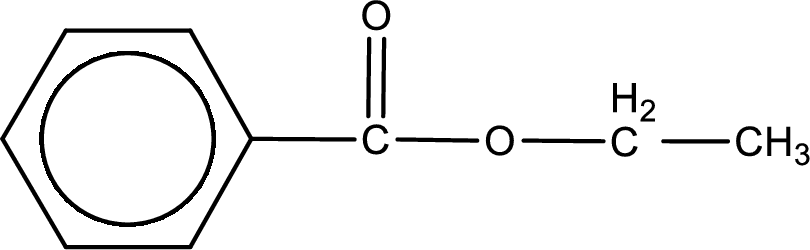
The alkyl and acyl group is identified as shown below,
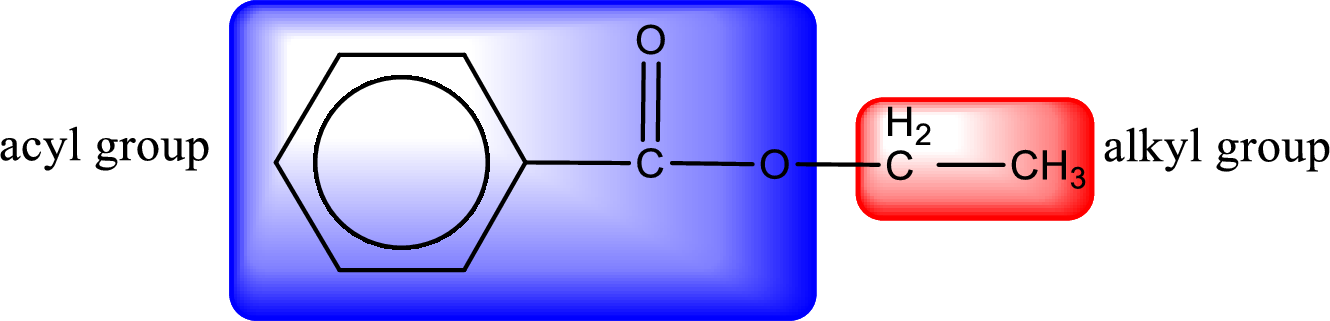
Alkyl group contains only two carbon atoms. Hence alkyl group is named as ethyl. The acyl group contains a benzene ring structure. The IUPAC name of carboxylic acid that contains benzene ring is benzoic acid. For naming acyl group in ester the suffix “-ic acid” is converted into “-ate”. This gives the name of acyl part as benzoate. Therefore IUPAC name of the given ester is ethyl benzoate.
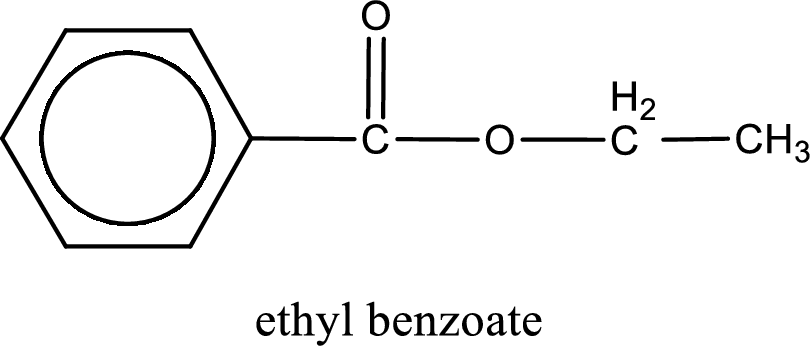
IUPAC name of the formed ester is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- For the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. arrow_forwardHow to draw the reaction mechasnism belowarrow_forwardName the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forward
- What is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forwardHow to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forward
- Please help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forwardProvide solutionsarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





