
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
In the Friedel-craft alkylation reaction alkyl chloride and benzene reacts to form alkylated benzene compound. The Lewis acid AlCl3 reacts with
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
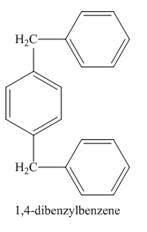
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
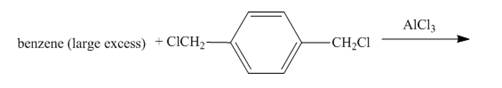
Figure 1
The benzene ring in the presence of AlCl3 reacts with 1, 4-bis(chloromethyl)benzene to form benzyl benzene. The benzene is present in excess amount so the compound formed will again react with one molecule of benzene to form 1, 4-dibenzylbenzene. The complete reaction is shown below.
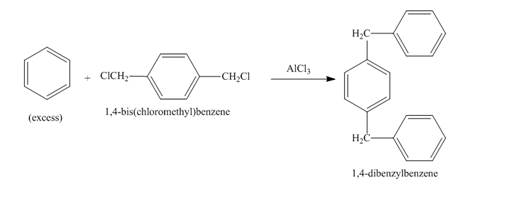
Figure 2
The structure of compound formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
In the Friedel craft alkylation reaction alkyl chloride and benzene reacts to form alkylated benzene compound. The Lewis acid AlCl3 reacts with alkyl halide to generate the carbocation. The carbocation intermediate undergoes rearrangement to form more stable carbocation, and then reacts with benzene to form alkyl benzene. Alkyl benzene formed is very reactive and further undergo alkylation reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
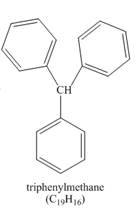
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
benzene(large excess)+CHCl3AlCl3→(a hydrocarbon C19H16)
The benzene reacts with chloroform to form dichloromethyl benzene. Aluminium chloride acts as catalyst in this reaction. As benzene is present in excess amount, it will again react with the dichloromethyl benzene to form triphenyl methane. The complete reaction is shown below.
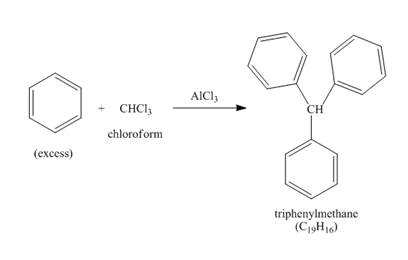
Figure 3
The structure of compound formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
In the Friedel craft alkylation reaction alkyl chloride and benzene reacts to form alkylated benzene compound. The Lewis acid AlCl3 reacts with alkyl halide to generate the carbocation. The carbocation intermediate undergoes rearrangement to form more stable carbocation, and then reacts with benzene to form alkyl benzene. Alkyl benzene formed is very reactive and further undergo alkylation reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
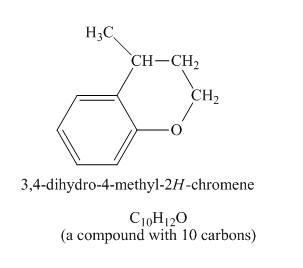
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
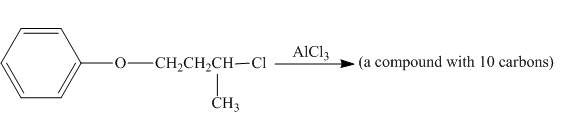
Figure 4
The given compound undergoes Friedel craft alkylation reaction to form the cyclic compound. The product formed in the given reaction is 3, 4-dihydro-4-methyl-2H-chromene. The complete reaction is shown below.
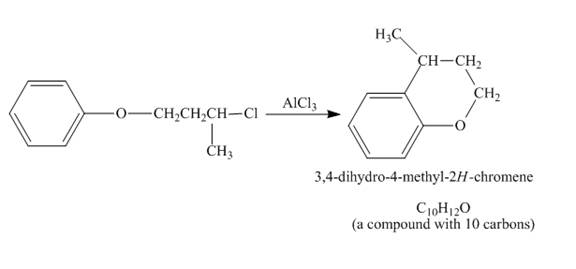
Figure 5
The structure of compound formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 5.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Reaction of benzene with acyl chloride in presence of Lewis acid like aluminium tricloride takes place to form acylated benzene. This reaction is known as Friedel-crafts acylation reaction. The electrophile in this reaction is a carbocation, known as acylium ion. This ion is formed when acid chloride reacts with Lewis acid.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
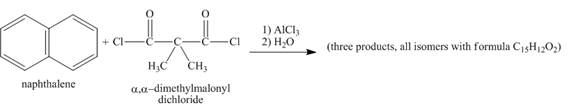
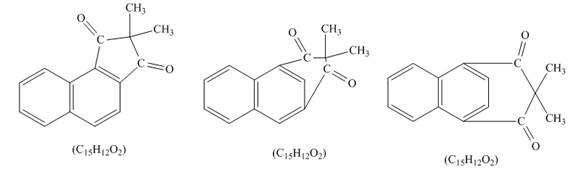
Figure 6
Naphthalene reacts with α,α-dimethylmalonyldichloride to form three different products. Lewis acid removes the chloride atom from α,α-dimethylmalonyldichloride. Then, carbocation formed will react with naphthalene ring to form three products. All the three products formed have molecular formula C15H22O2. The complete given reaction is shown below.
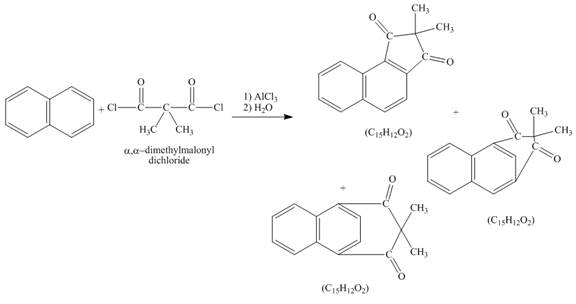
Figure 7
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 7.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
The substituted benzene ring when undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction, then it will form ortho, meta or para compounds. If the substituent present on the ring is directing the electrophile at ortho-para position, then it an ortho-para directing group. If the already present substituents direct the incoming electrophile to meta position, then it is a meta directing group. Hydroxyl group is ortho-para directing group.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
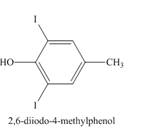
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
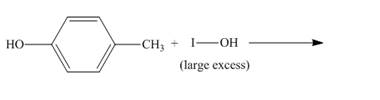
Figure 8
The compound p-cresol reacts with the hypoiodous acid to form the 2-iodo-4-methylphenol. The iodide ion is electrophilic in nature and it attacks the ortho position of the p-cresol. The hypoiodous acid is present in excess so the product formed again reacts with it to give ortho substitution product 2, 6-diiodo-4-methylphenol.
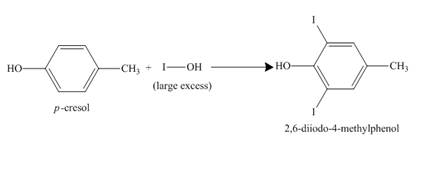
Figure 9
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 9.
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
The substituted benzene ring when further undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction, and then it will form ortho, meta or para compounds. If the substituent present on the ring is directing the electrophile at ortho-para position, then it an ortho-para directing group. If the already present substituent directs the incoming electrophile to meta position then it is a meta directing group. Cyclohexyl group is ortho-para directing group.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
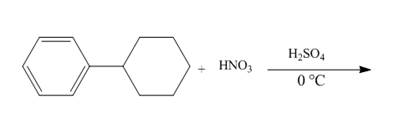
Figure 10
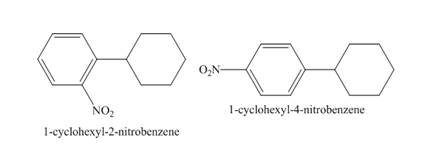
The compound 1-cyclohexylbenzene undergoes nitration reaction. The mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid is the nitrating mixture. The nitronium ion is generated which is an electrophile. The cyclohexyl ring is electron donating group, therefore ortho and para products will be formed. The products formed are 1-cyclohexyl-2-nitrobenzene and 1-cyclohexyl-4-nitrobenzene. The complete reaction is shown below.
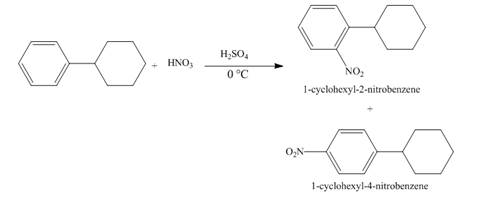
Figure 11
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 11.
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Reaction of benzene with acyl chloride in presence of Lewis acid like aluminium tricloride to form acylated benzene is known as Friedel-crafts acylation reaction. The electrophile in the reaction is a carbocation, known as acylium ion. This ion is formed when acid chloride reacts with Lewis acid.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
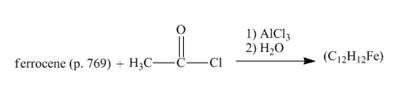
Figure 12
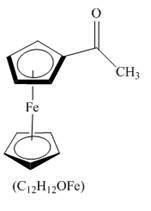
The compound ferrocene reacts with acyl chloride to form acylated ferrocene ring. The acetyl group is an electrophile. The electrophilic substitution reaction of ferrocene takes place to form acylated ferrocene. The 1,2− disubstituted product can also be formed but in very small amount. The complete given reaction is shown below.
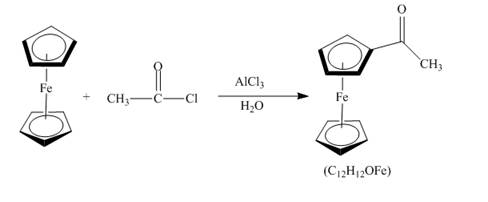
Figure 13
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 13.
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Nitration reaction takes place in the presence of nitric acid. It is an electrophilic substitution reaction. Nitronium ion is formed as electrophile in nitration reaction. The methoxy group is an activating group, it is ortho-para directing group. The nitro group is strongly deactivating group and it is meta directing group.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
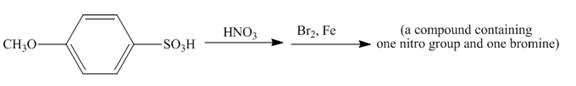
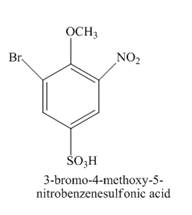
Figure 14
The reaction of 4-methoxybenzenesulfonic acid with nitric acid forms ortho nitration product. The methoxy group is strong activating group so it will form ortho and para substituted product. The product 4-methoxy-3-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid is formed after nitration. The nitro group is strong deactivating group so it will direct the bromine at meta position with respect to nitro group. 4-methoxy-3-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid reacts with bromine to form 3-bromo-4-methoxy-5-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid. The complete reaction is shown below.
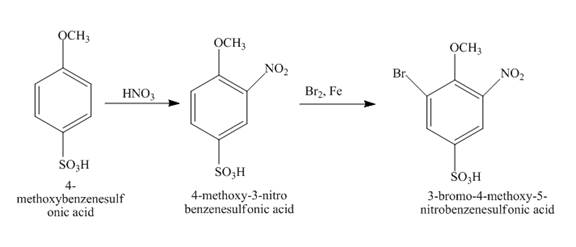
Figure 15
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 15.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- Provide the semi-developed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (R1-CO-CH2-CO-R2), indicate the formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardAn orange laser has a wavelength of 610 nm. What is the energy of this light?arrow_forward
- The molar absorptivity of a protein in water at 280 nm can be estimated within ~5-10% from its content of the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan and from the number of disulfide linkages (R-S-S-R) between cysteine residues: Ε280 nm (M-1 cm-1) ≈ 5500 nTrp + 1490 nTyr + 125 nS-S where nTrp is the number of tryptophans, nTyr is the number of tyrosines, and nS-S is the number of disulfide linkages. The protein human serum transferrin has 678 amino acids including 8 tryptophans, 26 tyrosines, and 19 disulfide linkages. The molecular mass of the most dominant for is 79550. Predict the molar absorptivity of transferrin. Predict the absorbance of a solution that’s 1.000 g/L transferrin in a 1.000-cm-pathlength cuvet. Estimate the g/L of a transferrin solution with an absorbance of 1.50 at 280 nm.arrow_forwardIn GC, what order will the following molecules elute from the column? CH3OCH3, CH3CH2OH, C3H8, C4H10arrow_forwardBeer’s Law is A = εbc, where A is absorbance, ε is the molar absorptivity (which is specific to the compound and wavelength in the measurement), and c is concentration. The absorbance of a 2.31 × 10-5 M solution of a compound is 0.822 at a wavelength of 266 nm in a 1.00-cm cell. Calculate the molar absorptivity at 266 nm.arrow_forward
- How to calculate % of unknown solution using line of best fit y=0.1227x + 0.0292 (y=2.244)arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, state the (condensed) formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardComplete the following acid-base reactions and predict the direction of equilibrium for each. Justify your prediction by citing pK values for the acid and conjugate acid in each equilibrium. (a) (b) NHs (c) O₂N NH NH OH H₁PO₁arrow_forward
- 23.34 Show how to convert each starting material into isobutylamine in good yield. ཅ ནད ཀྱི (b) Br OEt (c) (d) (e) (f) Harrow_forwardPlease help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

