
(a)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
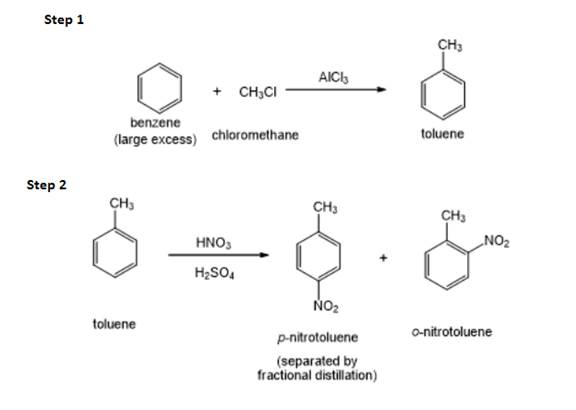
The structure of
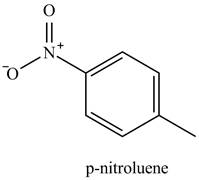
Figure 1
The methyl is an ortho and para directing group and nitro is a meta directing group. the compound is para compound. Therefore, the benzene will first undergo methylation reaction with chloromethane and
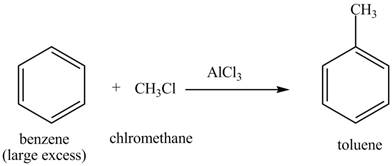
Figure 2
The toluene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to from ortho and para-substituted compounds. The para-substituted gets separated from ortho compound with the help of fractional distillation process. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
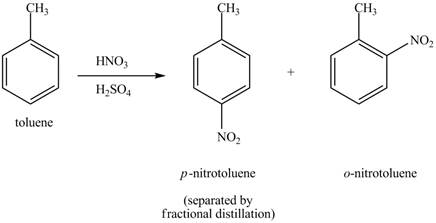
Figure 3
The laboratory synthesis of
(b)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
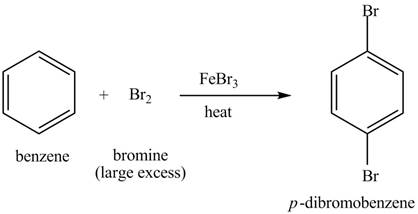
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
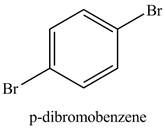
Figure 4
Benzene reacts with an excess of bromine gas in the presence of a
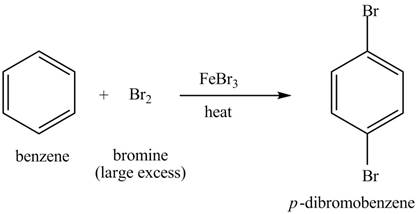
Figure 5
The laboratory synthesis of
(c)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
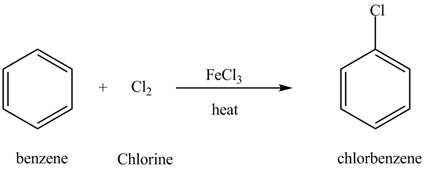
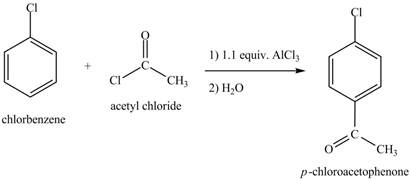
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
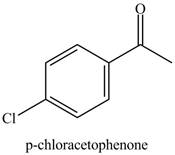
Figure 6
Benzene reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of a catalyst
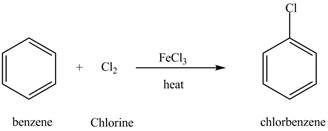
Figure 7
The chlorobenzene undergoes Friedel Craft acylation reaction with acetyl chloride in the presence of
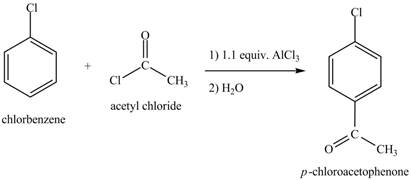
Figure 8
The laboratory synthesis of
(d)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
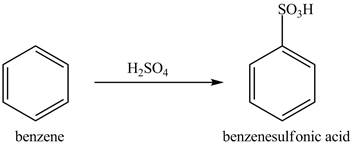
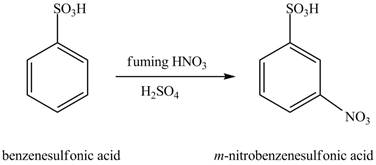
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
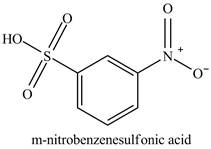
Figure 9
The benzene molecule will undergo sulfonation reaction with sulfuric acid. The electrophile
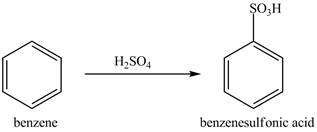
Figure 10
The benzenesulfonic acid will undergo nitration reaction with fuming nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form
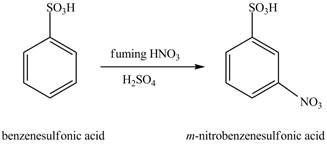
Figure 11
The laboratory synthesis of
(e)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
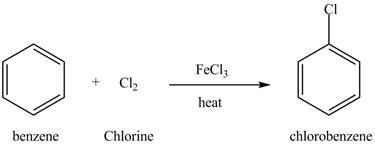
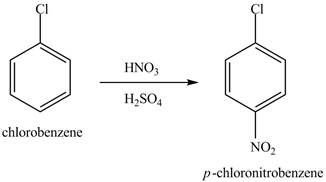
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
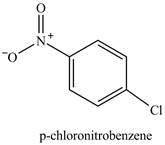
Figure 12
Benzene reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of a catalyst
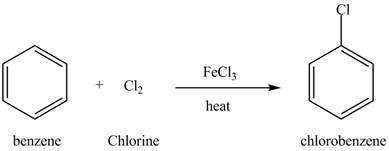
Figure 13
The chlorobenzene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form
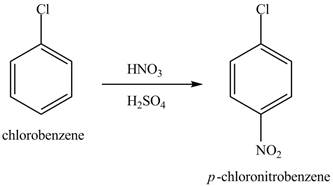
Figure 14
The laboratory synthesis of
(f)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
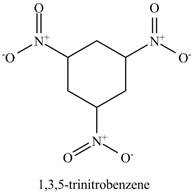
Figure 15
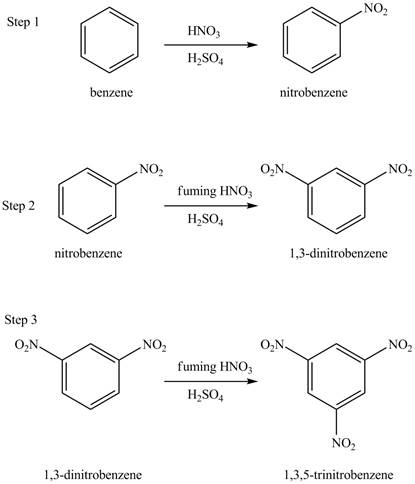
The benzene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form nitrobenzene. The nitro group is a ring deactivating group and meta directing group. Therefore, some strong condition is required to substitute another electrophile on it. The nitrobenzene reacts with fuming nitric acid and sulfuric acid to form
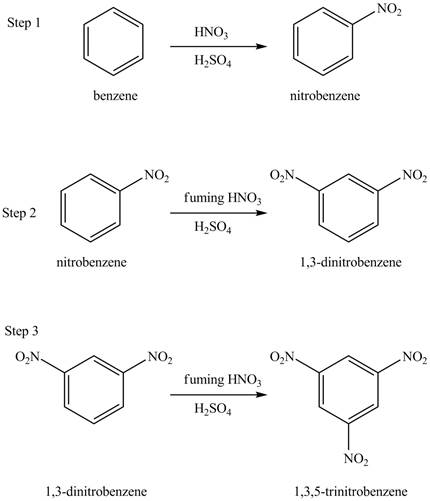
Figure 16
The laboratory synthesis of
(g)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
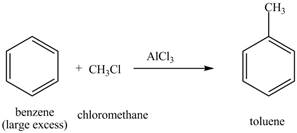
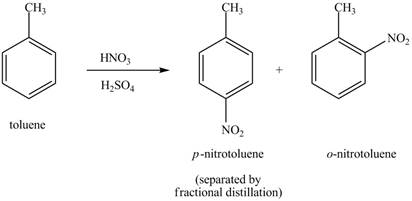
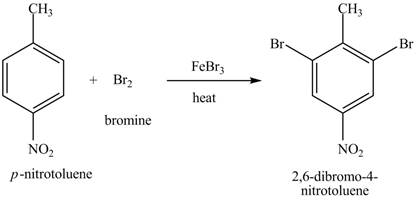
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
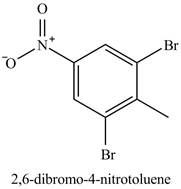
Figure 17
The benzene will first undergo methylation reaction with chloromethane and
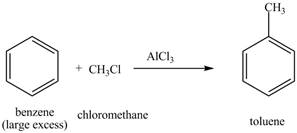
Figure 18
The toluene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form ortho and para-substituted compounds. The para-substituted gets separated from ortho compound with the help of fractional distillation process. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
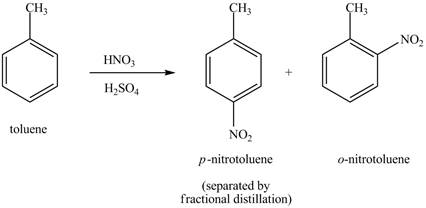
Figure 19
The compound
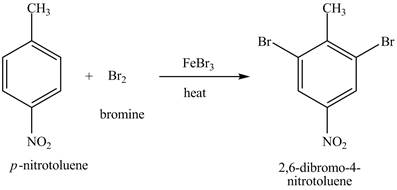
Figure 20
The laboratory synthesis of
(h)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
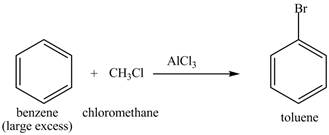
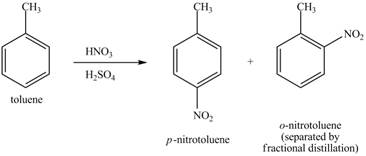
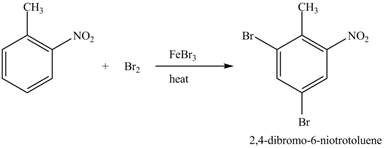
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
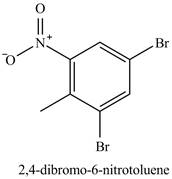
Figure 21
The benzene will first undergo methylation reaction with chloromethane and
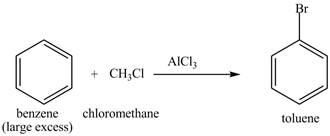
Figure 22
The toluene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form ortho and para-substituted compounds. The para-substituted gets separated from ortho compound with the help of fractional distillation process. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.

Figure 23
The compound
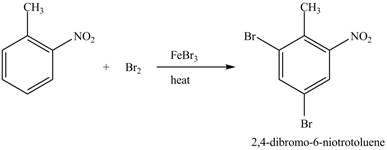
Figure 24
The laboratory synthesis of
(i)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
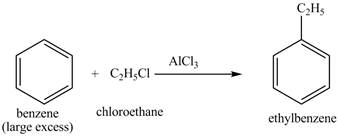
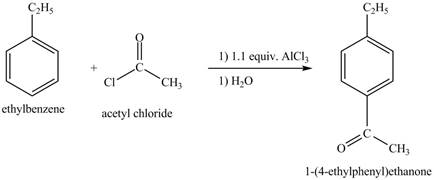
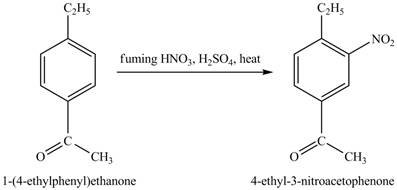
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
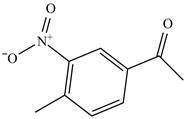
Figure 25
The benzene will first undergo ethylation reaction with chloromethane and
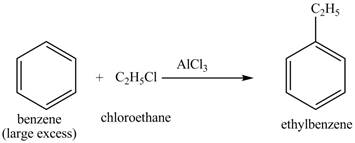
Figure 26
The ethylbenzene undergoes Friedel Craft acylation reaction with acetyl chloride in the presence of
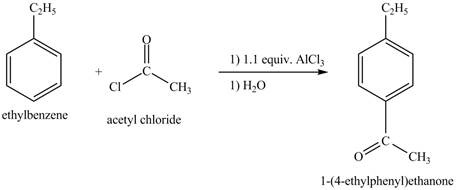
Figure 27
The compound
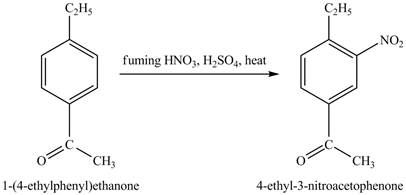
Figure 28
The laboratory synthesis of
(j)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of cyclopentylbenzene from benzene and any other reagents is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
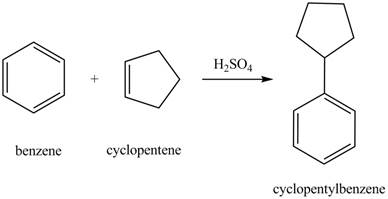
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of cyclopentylbenzene from benzene and any other reagents is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of cyclopentylbenzene is shown below.
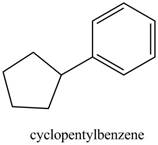
Figure 29
Benzene reacts with cyclopentene in the presence of sulfuric acid to form cyclopentyl benzene. The sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst to generate carbocation from cyclopentene. This carbonation acts as an electrophile and attacks the benzene ring. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.

Figure 30
The laboratory synthesis of cyclopentylbenzene from benzene and any other reagents is shown in Figure 30.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- Imagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule 0=0 H3N-CH-C-o HO CH2 OH The solution is... O acidic O basic O neutral O (unknown) H₂N acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) + H3N O OH O acidic O basic O neutral O (unknown) H2N-CH-C-O CH3 O acidic O basic neutral ○ (unknown) X ? olo HEarrow_forwardRecognizing ampli Draw an a amino acid with a methyl (-CH3) side chain. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Carrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure name × HO OH ☐ OH CI CI O CI OH OHarrow_forward
- く Check the box under each a amino acid. If there are no a amino acids at all, check the "none of them" box under the table. Note for advanced students: don't assume every amino acid shown must be found in nature. COO H3N-C-H CH2 HO CH3 NH3 O CH3-CH CH2 OH Onone of them Explanation Check + H3N O 0. O OH + NH3 CH2 CH3-CH H2N C-COOH H O HIC + C=O H3N-C-O CH3- - CH CH2 OH Х 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure HO-C-CH2-CH3 O -OH CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-C-OH CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-C-OH Explanation Check S namearrow_forwardtheres 2 productsarrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this solvolysis reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + CH3CH2OH Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OCH2CH3 || OEt Charges OH 00-> | Undo Reset | Br Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. CH3CO2Na CH3CO2H Drawing + Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OAC Charges OH ОАс Na ဂ Br Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardOrganic Functional Groups entifying positions labeled with Greek letters in acids and derivatives 1/5 ssible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a ce an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. ne of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substi er the drawing area. O H OH Oneither substituent can be added. Check D 1 Accessibility ado na witharrow_forward
- Differentiate between electrophilic and nucleophilic groups. Give examples.arrow_forwardAn aldehyde/ketone plus an alcohol gives a hemiacetal, and an excess of alcohol gives an acetal. The reaction is an equilibrium; in aldehydes, it's shifted to the right and in ketones, to the left. Explain.arrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection or a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H- -OH H- OH H- -OH CH₂OHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





