
(a)
Interpretation:
The compounds mesitylene, toluene, and
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds mesitylene, toluene, and
Explanation of Solution
The structure of mesitylene, toluene, and
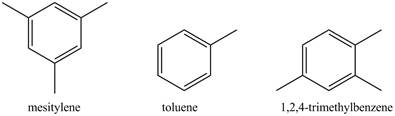
Figure 1
The reaction of any
The methyl group is electron-donating group. It activates the phenyl ring. The toluene has only one methyl group attached to it. Therefore, it will be least reactive towards
The order of reactivity toward nitration reaction is shown below.
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
(b)
Interpretation:
The compounds chlorobenzene, benzene, and nitrobenzene are to be arranged in increasing order of increasing reactivity toward
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds chlorobenzene, benzene, and nitrobenzene are arranged in increasing order of increasing reactivity toward
Explanation of Solution
The structure of chlorobenzene, benzene, and nitrobenzene are shown below.
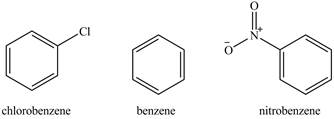
Figure 2
The reaction of any aromatic compound with
The nitro and chloro groups are electron-withdrawing groups. Therefore, the reactivity of the chlorobenzene and nitrobenzene will be less than that of benzene. The nitro group is stronger deactivating group than chloro group. Therefore, the order of reactivity toward nitration reaction is shown below.
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
(c)
Interpretation:
The compounds
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
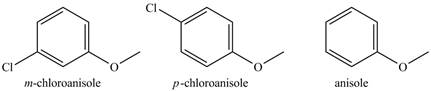
Figure 3
The reaction of any aromatic compound with
The methoxy group and chloro groups are ortho and para directing groups. The methoxy group is electron releasing group and chloro group is electron-withdrawing group.
Therefore, the reactivity of anisole will be highest among the rest of the compound toward
The order of reactivity toward nitration reaction is shown below.
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
(d)
Interpretation:
The compounds acetophenone,
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.44AP
The compounds acetophenone,
Explanation of Solution
The structure of acetophenone,
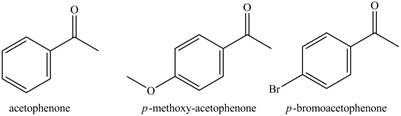
Figure 4
The reaction of any aromatic compound with
The acetyl group and bromo group is electron-withdrawing groups and methoxy group is electron releasing group. Acetophenone has a ring activating group attached on it. Therefore, it is most reactive toward nitration reaction among the rest of the compound. The compound
The increasing order of reactivity towards toward
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- Part 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism 1) Bakelite like polymer Using: Resorcinol + NaOH + Formalin 2) Polyester fiber Using a) pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + ethylene glycol B)pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + glycerol 3) Temporary cross-linked polymer Using: 4% polyvinyl alcohol+ methyl red + 4% sodium boratearrow_forwardUsing the table of Reactants and Products provided provide the correct letter that corresponds with the Carboxylic acid that is formed in the reaction below. 6 M NaOH Acid-workup WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES A) Pool of Reagents for Part B CI B) OH C) E) CI J) racemic F) K) OH N) OH P) G) OH D) HO H) L) M) HO Q) R) CI Aarrow_forwardIn the table below, the exact chemical structures for Methyl salicylate can be represented by the letter WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES CI B) A) E) Cl racemic F) J) CI K) N) OH P) Pool of Reagents for Part B OH OH G) L) OH D) HO H) M) HO Q) R) CIarrow_forward
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardPart I. a) Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl - 1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward3. The explosive decomposition of 2 mole of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) is shown below: Assume the C(s) is soot-basically atomic carbon (although it isn't actually atomic carbon in real life). 2 CH3 H NO2 NO2 3N2 (g)+7CO (g) + 5H₂O (g) + 7C (s) H a. Use bond dissociation energies to calculate how much AU is for this reaction in kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone and (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forwardShow the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





