
A cylinder with a circular hole is rolling without slipping on a fixed curved surface as shown. The cylinder would have a weight of 16 lb without the hole, but with the hole it has a weight of 15 lb. Knowing that at the instant shown the disk has an angular velocity of 5 rad/s clockwise, determine (a) the angular acceleration of the disk, (b) the components of the reaction force between the cylinder and the ground at this instant.
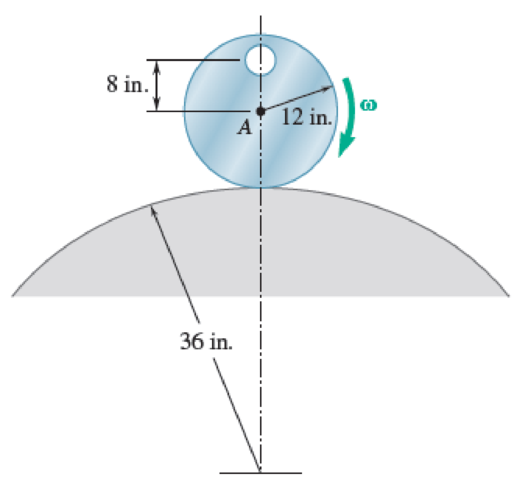
Fig. P16.161
(a)
The angular acceleration of the disk.
Answer to Problem 16.161RP
The angular acceleration of the disk is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the cylinder without hole is
The weight of the cylinder with hole is
The angular velocity of the disk is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Consider that the mass center of the cylinder is G and it lies at a distance b from center A, and C is the contact point between cylinder and the curved surface is the origin of the coordinate system.
Consider that the radius of cylinder is r and the radius of the curved surface is R.
Sketch the geometry of the cylinder as shown in Figure 1.
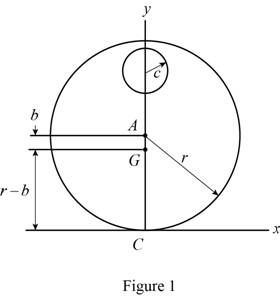
Refer to Figure 1.
Calculate the position vector
The position vector of P with respect to C.
The position vector of G with respect to C.
The position vector of A with respect to C.
The cylinder rolls without slipping on a fixed curved surface hence, the horizontal component of acceleration of point C is
Calculate the acceleration of point C
Substitute 0 for
The acceleration of the disk at A is
Calculate the acceleration of point A
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point P
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point G
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point A
Substitute
Subtract Equation (2) from Equation (1) as shown below.
Substitute
Calculate the velocity of point A
Calculate the vertical component of acceleration of point A
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point G
Substitute
Calculate the effective force at the mass center
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the cylinder as shown in Figure 2.
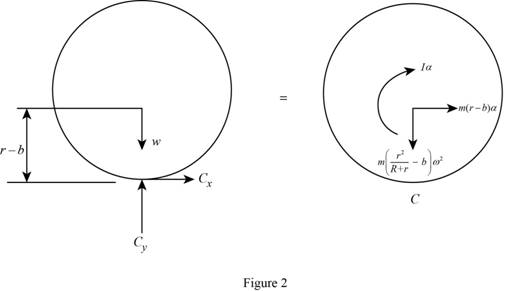
Refer to Figure 2.
Apply the Equilibrium of moment about C as shown below.
Hence, the angular acceleration of the disk is
(b)
The components of the reaction force between the cylinder and the ground.
Answer to Problem 16.161RP
The component of the reaction along x direction is
The component of the reaction along y direction is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the cylinder without hole is
The weight of the cylinder with hole is
The angular velocity of the disk is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
The angular acceleration of the disk is
Refer to Figure 2.
Apply the Equilibrium of force along x direction as shown below.
Substitute 0 for
Hence, the component of the reaction along x direction is
Apply the Equilibrium of force along y direction as shown below.
Sketch the cylinder with hole as shown in Figure 3.
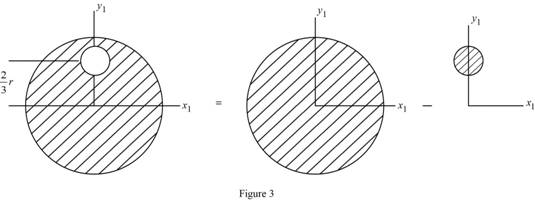
Refer to Figure 3.
Calculate the area of solid cylinder
Calculate the center of gravity of solid cylinder in vertical direction
Calculate the area of hole
Calculate the center of gravity of hole in vertical direction
Calculate the distance
Substitute
Calculate the component of the reaction along y direction as shown below.
Substitute
Therefore, the component of the reaction along y direction is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Two squirrels are sitting on the rope as shown. The squirrel at A has a weight of 1.2 lb. The squirrel at B found less food this season and has a weight of 0.8 lb. The angles 0 and > are equal to 50° and 60° respectively. Determine the tension force in each of the rope segments (T₁ in segment, T₂ in segment Я, and T3 in segment DD) as well as the angle a in degrees. Ө A α B Note the figure may not be to scale. T₁ = lb lb T2 T3 = = lb απ deg A BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbomarrow_forwardEach cord can sustain a maximum tension of 500 N. Determine the largest mass of pipe that can be supported. B 60° A E Harrow_forward2. Link BD consists of a single bar 1 in. wide and 0.5 in. thick. Knowing that each pin has a in. diameter, determine (a) the maximum value of the normal stress in link BD and the bearing stress in link BD if 0 = 0, (b) the maximum value of the normal stress in link BD if 0 = 90. -6 in.- 12 in. 30° D 4 kipsarrow_forward
- In the image is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q for e hat unit vectors.arrow_forwardauto controlsarrow_forwardI am having a hard time solving for the vector v in the equation in the image. Can you help me?arrow_forward
- A 4 ft 300 Ib 1000 Ib.ft 350 Ib C 2 ft 3. 45° 250 Ib B. 3ft B 25ft 200 Ib 150 Ib Replace the force system acting on the frame shown in the figure by a resultant force (magnitude and direction), and specify where its line of action intersects member (AB), measured from point (A).arrow_forwardCan you research the standard percentage of Steam Quality in:(1.) Boiler - leaving boilerBoiler -> Out(2.) Condenser - coming in condenser In -> CondenserProvide reference Also define: steam quality, its purpose and importancearrow_forwardNumbers 1 and 2 and 5 are are optional problems. However, I only need the values (with units) of 3, 4 and 6. Thank you :)arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





