
Concept explainers
Catalytic antibodies catalyze a reaction by forcing the conformation of the substrate in the direction of the transition state. The synthesis of the antibody is carried out in the presence of a transition state analog—a stable molecule that structurally resembles the transition state. This causes an antibody to be generated that recognizes and binds to the transition state, thereby stabilizing it. For example, the following transition state analog has been used to generate a catalytic antibody that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the structurally similar ester:
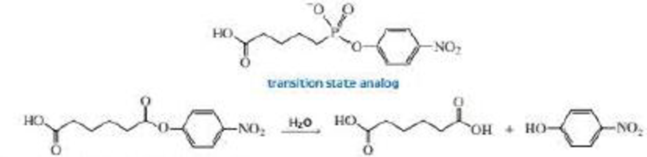
a. Draw a possible transition state for the hydrolysis reaction.
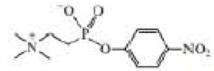
b. The following transition state analog is used to generate a catalytic antibody for the catalysis of ester hydrolysis. Draw the structure of an ester whose rate of hydrolysis would he increased by this catalytic antibody.
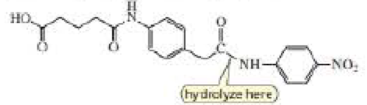
c. Design a transition state analog that catalyzes amide hydrolysis at the amide group indicated.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Organic Chemistry Study Guide A Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward2' P17E.6 The oxidation of NO to NO 2 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g), proceeds by the following mechanism: NO + NO → N₂O₂ k₁ N2O2 NO NO K = N2O2 + O2 → NO2 + NO₂ Ко Verify that application of the steady-state approximation to the intermediate N2O2 results in the rate law d[NO₂] _ 2kk₁[NO][O₂] = dt k+k₁₂[O₂]arrow_forwardPLEASE ANSWER BOTH i) and ii) !!!!arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



