
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To predict the compound formed by the reaction of phosgene with given compound.
Concept introduction:
Carbonyl carbon of phosgene is highly polar in nature because of the presence of electronegative groups attached to it. So phosgene will undergo nucleophilic addition-eliminationreaction. Tetrahedral intermediate is formed when nucleophile is added to the carbonyl carbon of phosgene. The tetrahedral intermediate is unstable therefore chloride ion gets eliminated. The acyl chloride reacts with neutral nucleophile by the following mechanism:
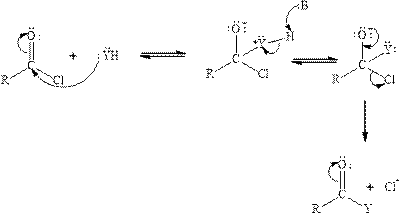
(b)
Interpretation:
To predict the compound formed by the reaction of phosgene with given compound.
Concept introduction:
Carbonyl carbon of phosgene is highly polar in nature because of the presence of electronegative groups attached to it. So phosgene will undergo nucleophilic addition-eliminationreaction. Tetrahedral intermediate is formed when nucleophile is added to the carbonyl carbon of phosgene. The tetrahedral intermediate is unstable therefore chloride ion gets eliminated. The acyl chloride reacts with neutral nucleophile by the following mechanism:

(c)
Interpretation:
To predict the compound formed by the reaction of phosgene with given compound.
Concept introduction:
Carbonyl carbon of phosgene is highly polar in nature because of the presence of electronegative groups attached to it. So phosgene will undergo nucleophilic addition-eliminationreaction. Tetrahedral intermediate is formed when nucleophile is added to the carbonyl carbon of phosgene. The tetrahedral intermediate is unstable therefore chloride ion gets eliminated. The acyl chloride reacts with neutral nucleophile by the following mechanism:

(d)
Interpretation:
To predict the compound formed by the reaction of phosgene with given compound.
Concept introduction:
Carbonyl carbon of phosgene is highly polar in nature because of the presence of electronegative groups attached to it. So phosgene will undergo nucleophilic addition-eliminationreaction. Tetrahedral intermediate is formed when nucleophile is added to the carbonyl carbon of phosgene. The tetrahedral intermediate is unstable therefore chloride ion gets eliminated. The acyl chloride reacts with neutral nucleophile by the following mechanism:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Organic Chemistry Study Guide A Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
- A covalent bond is the result of the a) b) c) d) e) overlap of two half-filled s orbitals overlap of a half-filled s orbital and a half-filled p orbital overlap of two half-filled p orbitals along their axes parallel overlap of two half-filled parallel p orbitals all of the abovearrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forwardWhich one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forward
- All of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forwardA student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction:arrow_forward
- Name the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH₂ || CH3-C-NH2 0 ။ CH3-C-CH₂ CH=O–CH=CH, CH₂ HO CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 family amine Darrow_forward1b. Br LOHarrow_forwardI would like my graphs checked please. Do they look right? Do I have iodine and persulfate on the right axis ?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





