
Concept explainers
Refer to Cornerstone Exercise 15.3. Choctaw Company provides the following additional information so that total productivity can be valued:
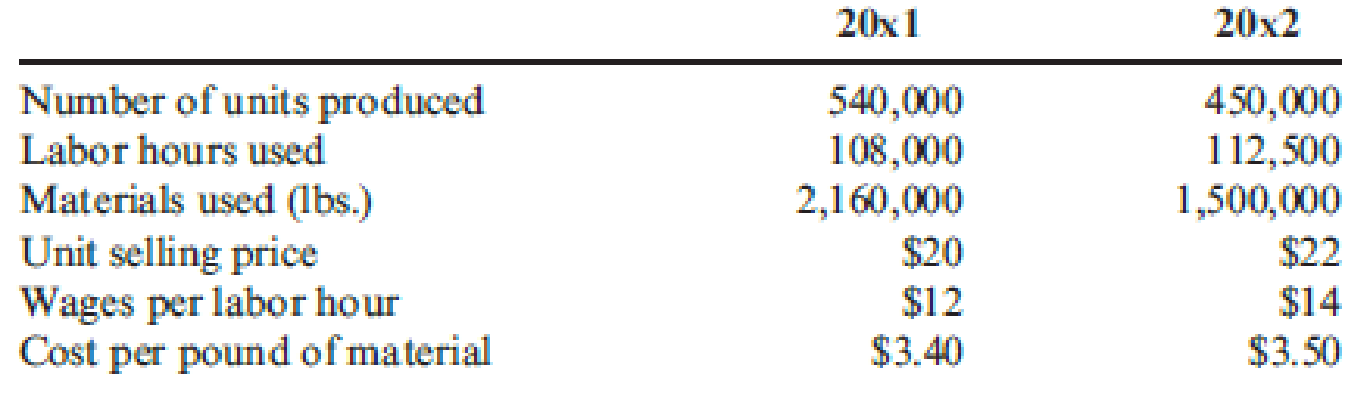
Required:
- 1. Calculate the cost of inputs in 20x2, assuming no productivity change from 20x1 to 20x2.
- 2. Calculate the actual cost of inputs for 20x2. What is the net value of the productivity changes? How much profit change is attributable to each input’s productivity change?
- 3. What if a manager wants to know how much of the total profit change from 20x1 to 20x2 is attributable to price recovery? Calculate the price-recovery component, and comment on its meaning.
1.
Compute the cost of inputs for the profile 20x2, if there is no change from productivity profile 20x1 to 20x2.
Explanation of Solution
Productivity measurement: The productivity measurement refers to the quantitative assessment of the changes in the productivity.
Profile measurement and analysis: The profile measurement and analysis refers to the computation of a set of operational partial productivity measures and their comparison to the corresponding set of base period, for the assessment of the nature of changes in productivity.
Calculate the cost of inputs for the profile 20x2:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cost of labor (3) | $1,260,000 |
| Cost of materials (4) | $6,300,000 |
| Total PQ Cost | $7,560,000 |
Table (1)
Working Notes (1):
Compute the base period productivity ratios for profile 20x1:
Compute the Labor Productivity Profile for 20x1:
Working Notes (2):
Compute the Material Productivity Profile for 20x1:
The Labor Productivity Profile is 5.00 and Material Productivity Profile is 0.25 for 20x1.
Working Notes (3):
Calculate the cost of labor:
Working Notes 4):
Calculate the cost of materials:
2.
Compute the actual cost of inputs for the profile 20x2. Indicate the net value of productivity changes and identify the profit change attributable to productivity change of each unit.
Explanation of Solution
Profit-linked productivity measurement and analysis: The profit-linked productivity measurement and analysis is the ascertainment of the amount of change in profit, from the base period to the current period, due to the various changes in the productivity.
Calculate the current cost of inputs for the profile 20x2:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cost of labor (5) | $1,575,000 |
| Cost of materials (6) | $5,250,000 |
| Total Current Cost | $6,825,000 |
Table (2)
Working Notes (5):
Calculate the cost of labor:
Working Notes (6):
Calculate the cost of materials:
Compute the profit linked productivity measure:
| Input | A | C | E | ||||
| Labor | 5 | 90,000 | $14 | $1,260,000 | 112,500 | $1,575,000 | ($315,000) |
| Materials | 0.25 | 1,800,000 | $3.50 | $6,300,000 | 1,500,000 | $5,250,000 | $1,050,000 |
| Total | $7,560,000 | $6,825,000 | $735,000 |
Table (3)
The Net productivity change is $735,000.
The Labor productivity change is ($315,000).
The materials productivity change is $1,050,000.
3.
Compute and describe the price recovery component.
Explanation of Solution
Price-recovery component: The price-recovery component refers to the differences amongst the changes in the total profit with the changed in the productivity effects.
Compute the profit linked productivity measure:
| Particulars | Profile 20x1 | Profile 20x2 | Amount ($) |
| Revenues | (7) $10,800,000 | (8) $9,900,000 | (9) ($900,000) |
| Costs | (10) $8,640,000 | $6,825,000 | (11) $1,815,000 |
| Total Profit | $2,160,000 | $3,075,000 | $915,000 |
Table (4)
Working Notes (7):
Calculate the Revenues for Profile for 20x1:
Working Notes (8):
Calculate the Revenues for Profile for 20x2:
Working Notes (9):
Calculate the changes in revenues:
Working Notes (10):
Calculate the cost of inputs for Profile 20x1:
Working Notes (11):
Calculate the changes in cost of inputs:
Compute the Price-recovery component:
The Price-recovery component is $180,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Please give me correct answer this financial accounting question not use aiarrow_forwardProblem related to Accounting 23arrow_forwardPinhead Manufacturers Inc. has estimated total factory overhead costs of $147,000 and 12,800 direct labor hours for the current fiscal year. If job number 218 incurred 3,400 direct labor hours, the work-in-process account will be debited and factory overhead will be credited for $____?arrow_forward
- Ans ? Financial accounting questionarrow_forwardBella's Florist purchased a delivery truck for $25,000. The company was given a $3,000 cash discount by the dealer and paid $1,200 sales tax. Annual insurance on the truck is $600. As a result of the purchase, by how much will Bella's Florist increase its truck account?arrow_forwardYou are given the following information about XX Company in 2020arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning


