
Concept explainers
(a)
The period of motion of pendulum for each lengths.
(a)
Answer to Problem 44P
The period of motion for length
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the time period of oscillation of a simple pendulum.
Here,
Conclusion:
Consider simple pendulum of length
Substitute
Consider simple pendulum of length
Substitute
Consider simple pendulum of length
Substitute
Tabulated form of the length of pendulum and the corresponding time periods is shown in Table 1 below.
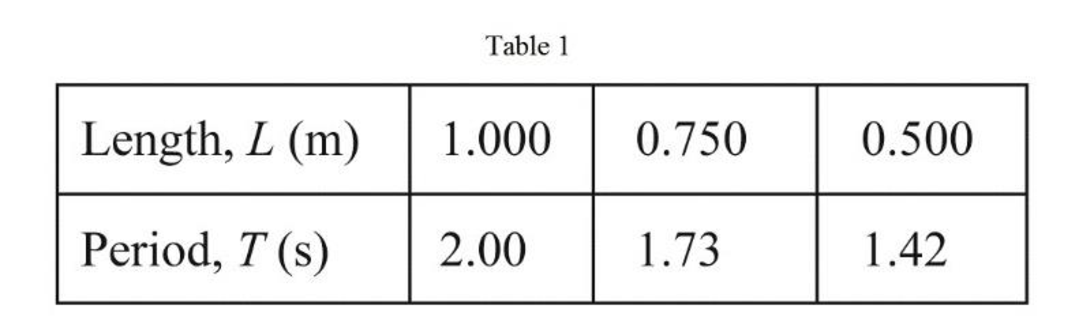
Therefore, the period of motion for length
(b)
The average value of
(b)
Answer to Problem 44P
The average value of
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the time period of the simple pendulum.
Here,
Square expression (II) and rearrange to find
Write the expression to find the average acceleration due to gravity.
Here,
Write the expression to find the degree of closeness of the average value to the accepted value of acceleration due to gravity.
Here,
Conclusion:
Consider simple pendulum of length
Substitute
Consider simple pendulum of length
Substitute
Consider simple pendulum of length
Substitute
The tabulate form of values of time period, length and acceleration due to gravity is given in Table 2 below.
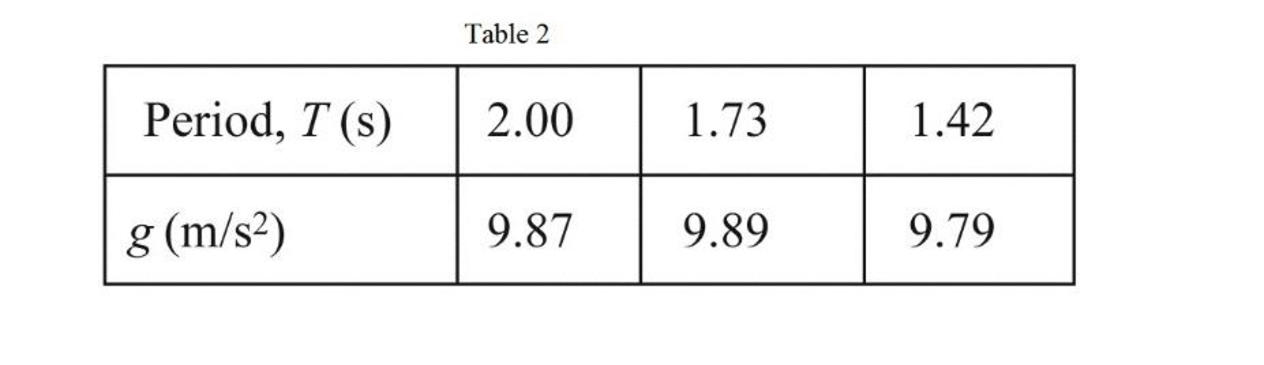
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the average value of
(c)
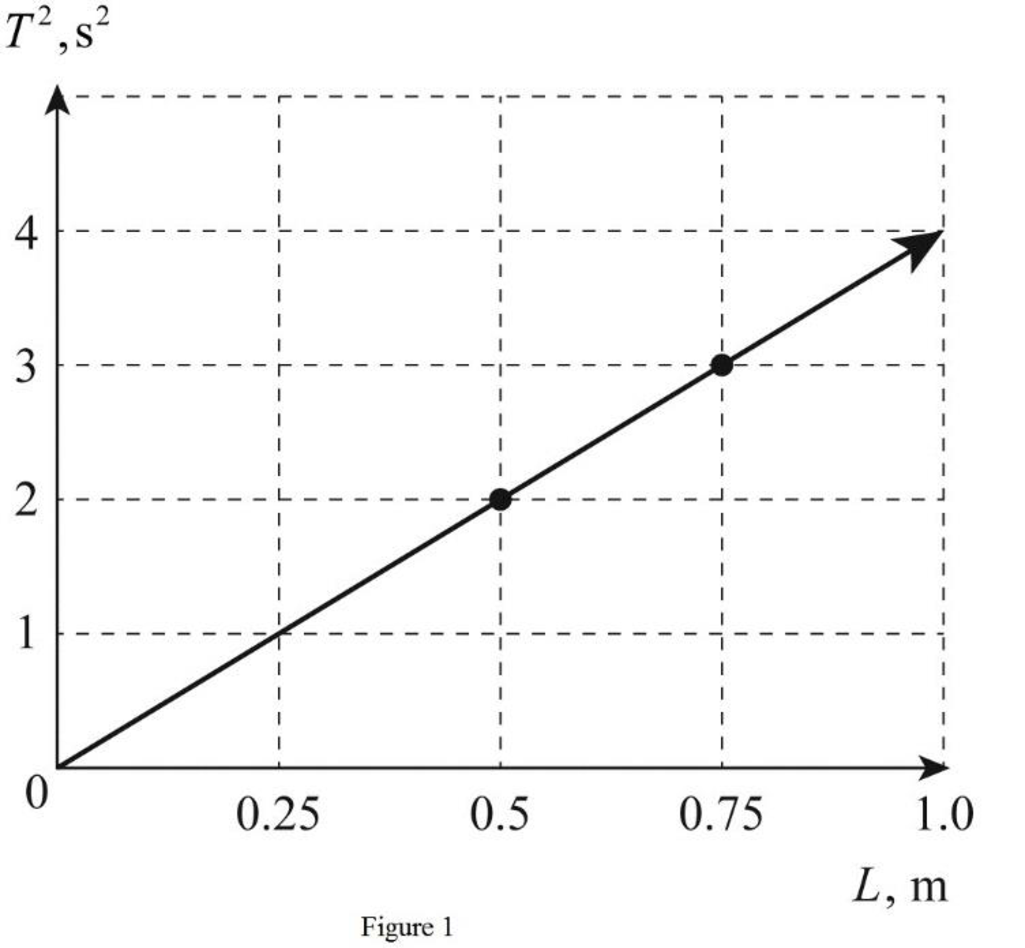
Plot
(c)
Answer to Problem 44P
Figure 1 gives the plot between
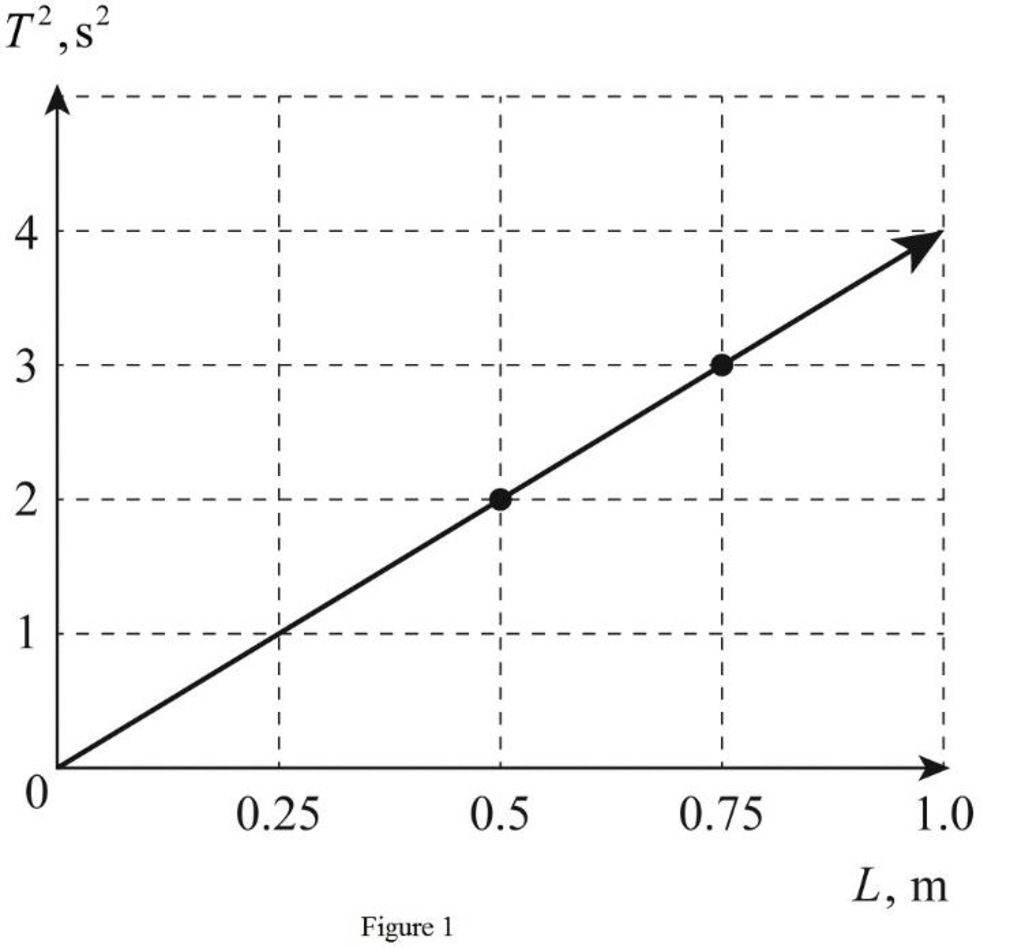
Explanation of Solution
From Table 2 obtain the values for length of pendulums and the corresponding time period of oscillations. Find the value of
Plot
Write the expression for
From equation (VI), slope of the graph is
Here,
Rearrange expression (VII) to find
Conclusion:
The slope of graph is got as
Therefore, Figure 1 gives the plot between
(d)
The level of closeness of
(d)
Answer to Problem 44P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to find the level of closeness of acceleration due to gravity from graph and accepted value of
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- Imagine a planet where gravity mysteriously acts tangent to the equator and in the eastward directioninstead of radially inward. Would this force do work on an object moving on the earth? What is the sign ofthe work, and does it depend on the path taken? Explain by using the work integral and provide a sketch ofthe force and displacement vectors. Provide quantitative examples.arrow_forwardIf a force does zero net work on an object over a closed loop, does that guarantee the force is conservative? Explain with an example or counterexamplearrow_forwardA futuristic amusement ride spins riders in a horizontal circle of radius 5 m at a constant speed. Thefloor drops away, leaving riders pinned to the wall by friction (coefficient µ = 0.4). What minimum speedensures they don’t slip, given g = 10 m/s²? Draw diagram (or a few) showing all forces, thevelocity of the rider, and their accelerationarrow_forward
- Your RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? 0.00897 × H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? 8.97 * ΜΩarrow_forwardYour RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? ΜΩarrow_forwardAt a distance of 0.212 cm from the center of a charged conducting sphere with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.598 cm from the center of the sphere? At a distance of 0.196 cmcm from the axis of a very long charged conducting cylinder with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.620 cm from the axis of the cylinder? At a distance of 0.202 cm from a large uniform sheet of charge, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 1.21 cm from the sheet?arrow_forward
- A hollow, conducting sphere with an outer radius of 0.260 m and an inner radius of 0.200 m has a uniform surface charge density of +6.67 × 10−6 C/m2. A charge of -0.800 μC is now introduced into the cavity inside the sphere. What is the new charge density on the outside of the sphere? Calculate the strength of the electric field just outside the sphere. What is the electric flux through a spherical surface just inside the inner surface of the sphere?arrow_forwardA point charge of -3.00 μC is located in the center of a spherical cavity of radius 6.60 cm inside an insulating spherical charged solid. The charge density in the solid is 7.35 × 10−4 C/m3. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field inside the solid at a distance of 9.10 cm from the center of the cavity. Find the direction of this electric field.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is E(r), the radial component of the electric field between the rod and cylindrical shell as a function of the distance r from the axis of the cylindrical rod? Express your answer in terms of λ, r, and ϵ0, the permittivity of free space. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouterσouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.) What is the radial component of the electric field, E(r), outside the shell?arrow_forward
- A very long conducting tube (hollow cylinder) has inner radius aa and outer radius b. It carries charge per unit length +α, where αα is a positive constant with units of C/m. A line of charge lies along the axis of the tube. The line of charge has charge per unit length +α. Calculate the electric field in terms of α and the distance r from the axis of the tube for r<a. Calculate the electric field in terms of α and the distance rr from the axis of the tube for a<r<b. Calculate the electric field in terms of αα and the distance r from the axis of the tube for r>b. What is the charge per unit length on the inner surface of the tube? What is the charge per unit length on the outer surface of the tube?arrow_forwardTwo small insulating spheres with radius 9.00×10−2 m are separated by a large center-to-center distance of 0.545 m . One sphere is negatively charged, with net charge -1.75 μC , and the other sphere is positively charged, with net charge 3.70 μC . The charge is uniformly distributed within the volume of each sphere. What is the magnitude E of the electric field midway between the spheres? Take the permittivity of free space to be ϵ0 = 8.85×10−12 C2/(N⋅m2) . What is the direction of the electric field midway between the spheres?arrow_forwardA conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius bb has a positive point charge Q located at its center. The total charge on the shell is -3Q, and it is insulated from its surroundings. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance r from the center for the region r<a. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables Q, a, b, and appropriate constants. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance rr from the center for the region a<r<b. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance rr from the center for the region r>b. What is the surface charge density on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is the surface charge density on the outer surface of the conducting shell?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





