
Concept explainers
16-6 Answer true or false.
- te/7-Butylamine is a 3°
amine .
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: tert-Butylamine is
Concept Introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more than one hydrogen atoms are substituted by an alkyl or aryl group.
The amines are categorized as primary, secondary or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms that are bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amine has only one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom. Similarly, secondary amines have two carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines nave three carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of a tert-butylamine is given below:
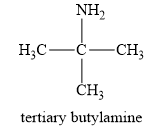
In a tert-butylamine, the carbon atom is bonded to three methyl groups, while nitrogen is attached to only one carbon group. Therefore, the tert-butyl amine is a primary amine. Therefore, this statement is false.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement about the aromatic amine is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more than one hydrogen atoms are substituted by an alkyl or aryl group.
The amines are categorized as primary, secondary or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms that are bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amine has only one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom. Similarly, secondary amines have two carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines nave three carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
If in an amine, the nitrogen is directly bonded to one or more aryl groups or aromatic rings, and then the amine is known as an aromatic amine.
For example, aniline is an aromatic amine, as it is attached to one aromatic ring benzene. The structure of aniline is given below:
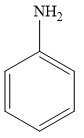
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: In a heterocyclic amine, the main nitrogen is the part of the ringis true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more than one hydrogen atoms are substituted by an alkyl or aryl group.
The amines are categorized as primary, secondary or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms that are bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amine has only one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom. Similarly, secondary amines have two carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines nave three carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
In a heterocyclic amine, the carbon group of the ring structure is replaced by the nitrogen atom. For example, in pyridine, the nitrogen atom replaces one —CH group of the benzene ring.
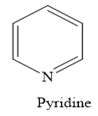
Thus, the heterocyclic amine is an amine in which nitrogen is one of the atoms of a ring. Therefore, this statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: The NH4+ and CH4have the same number of valence electrons and both have tetrahedral geometry as per the VSEPR model is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
The VSEPR (Valence-shell electron pair repulsion) model predicts the shape of the molecules or ions by identifying the position of atoms connected to the central atom.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory determines the shapes and the geometry of a molecule. In a CH4 molecule, one carbon atom is bonded to four hydrogen atoms with a single bond. In NH4+, one nitrogen atom is singly bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
According to the VSEPR model, each bond represents a pair of electrons. Since both compounds have four bonds around the central atom, they contain eight valence electrons. Also, according to the VSEPR model, these four bonding regions are arranged in a tetrahedral manner so that they are as far away from one another as possible, giving the molecule a tetrahedral geometry. Therefore, this statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: There are four constitutional isomers with the molecular formulaC3H9N, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Constitutional isomers are those compounds which have same molecular formula, but they differ in the arrangement of atoms in the molecules.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula is given as C3H9N. Therefore, the possible constitutional isomers for this molecular formula are given below:
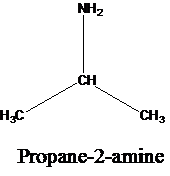
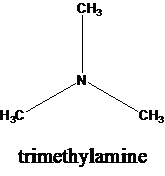
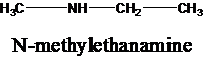
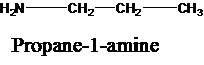
Thus, there are four constitutional isomers possible with the molecular formula C3H9N. Therefore, this statement is true.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Reagan is doing an atomic absorption experiment that requires a set of zinc standards in the 0.4-1.6 ppm range. A 1000 ppm Zn solution was prepared by dissolving the necessary amount of solid Zn(NO3)2 in water. The standards can be prepared by diluting the 1000 ppm Zn solution. Table 1 shows one possible set of serial dilutions (stepwise dilution of a solution) that Reagan could perform to make the necessary standards. Solution A was prepared by diluting 5.00 ml of the 1000 ppm Zn standard to 50.00 ml. Solutions C-E are called "calibration standards" because they will be used to calibrate the atomic absorption spectrometer. a. Compare the solution concentrations expressed as ppm Zn and ppm Zn(NO3)2. Compare the concentrations expressed as M Zn and M Zn(NO3)2 - Which units allow easy conversion between chemical species (e.g. Zn and Zn(NO3)2)? - Which units express concentrations in numbers with easily expressed magnitudes? - Suppose you have an analyte for which you don't know the molar…arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardHow will you prepare the following buffers? 2.5 L of 1.5M buffer, pH = 10.5 from NH4Cl and NH3arrow_forward
- How will you prepare the following buffers? 2.5 L of 1.5M buffer, pH = 10.5 from NH4Cl and NH3arrow_forwardCH₂O and 22 NMR Solvent: CDCl3 IR Solvent: neat 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 15 [ اند 6,5 9.8 3.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.8 3.0 2.0 1.0 9.8 200 100arrow_forwardprotons. Calculate the mass (in grams) of H3AsO4 (MW=141.9416) needed to produce 3.125 x 1026arrow_forward

 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning



