
Concept explainers
15-21 Answer true or false.
- For a molecule with two stereocenters, 22 = 4 stereoisomers are possible.
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images.
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- For a molecule with two stereocenters, 22 =4 stereoisomers are possible, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomerism deals with the study of the spatial arrangements of the atoms in space. It does not mean to alter the connectivity of the atoms by mean of forming or breaking the bonds.
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
Answer to Problem 15.21P
For a molecule with two stereocenters, 22 =4 stereoisomers are possible. Thus, given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
According to van't Hoff rule, if a molecule contains n number of chiral carbons, provided it does not contain any elements of symmetry, and then the number of stereoisomers is given by- 2n.
Therefore for a molecule with 2 stereocenters, the possible isomer is given as-
22 =4.
Therefore, 4 stereoisomers are possible.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- For a molecule with three stereocenters, 32 =9 stereoisomers are possible, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomerism deals with the study of the spatial arrangements of the atoms in space. It does not mean to alter the connectivity of the atoms by mean of forming or breaking the bonds.
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
Answer to Problem 15.21P
For a molecule with three stereocenters, 32 =9 stereoisomers are possible. Thus, given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
According to van't Hoff rule, if a molecule contains n number of chiral carbons, provided it does not contain any elements of symmetry, and then the number of stereoisomers is given by- 2n.
Therefore for a molecule with 3 stereocenters, the possible isomer is given as-
32 =9.
Therefore, 9 stereoisomers are possible.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- Enantiomers, like gloves, occur in pairs, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomerism deals with the study of the spatial arrangements of the atoms in space. It does not mean to alter the connectivity of the atoms by mean of forming or breaking the bonds.
Compounds with a chiral centre exist in enantiomeric forms. The phenomenon of enantiomerism is called as optical isomerism. If the configuration at each stereocenter is changed, the enantiomer is converted into another enantiomer.
Answer to Problem 15.21P
Enantiomers, like gloves, occur in pairs.
Explanation of Solution
Isomers which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other are called Enantiomers.
Compounds with a chiral centre exist in enantiomeric forms. The phenomenon of enantiomerism is called as optical isomerism. If the configuration at each stereocenter is changed, the enantiomer is converted into another enantiomer.
Hence, Enantiomers, like gloves, occur in pairs.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- 2-Pentanol and 3-Pentanol are both chiral and show enantiomerism, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomerism deals with the study of the spatial arrangements of the atoms in space. It does not mean to alter the connectivity of the atoms by mean of forming or breaking the bonds.
Compounds with a chiral centre exist in enantiomeric forms. The phenomenon of enantiomerism is called as optical isomerism. If the configuration at each stereocenter is changed, the enantiomer is converted into another enantiomer.
Answer to Problem 15.21P
Only 2-Pentanol is chiral and show enantiomerism.
Explanation of Solution
Isomers which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other are called Enantiomers.
In 2-Pentanol, the carbon-2 is attached to four different groups namely- a methyl group, a propyl group, hydroxyl group and hydrogen.
Therefore it has a stereocenter, it forms a mirror image that is non-superimposable, and therefore they show isomerism.
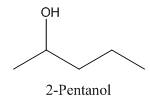 has a mirror image as
has a mirror image as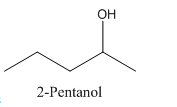
In 3-Pentanol, the carbon-2 is attached to four groups namely- two ethyl group, hydroxyl group and hydrogen.
Therefore it does not have a stereocenter, it forms a mirror image that is superimposable, and therefore they do not show isomerism.
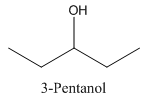 has a mirror image as
has a mirror image as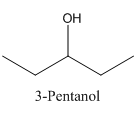
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- 1-Methylcyclohexanol is achiral and does not show enantiomerism, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomerism deals with the study of the spatial arrangements of the atoms in space. It does not mean to alter the connectivity of the atoms by mean of forming or breaking the bonds.
Compounds with a chiral centre exist in enantiomeric forms. The phenomenon of enantiomerism is called as optical isomerism. If the configuration at each stereocenter is changed, the enantiomer is converted into another enantiomer.
Answer to Problem 15.21P
1-Methylcyclohexanol is achiral and does not show enantiomerism.
Explanation of Solution
1- Methylcyclohexanol has a plane of symmetry due to which it is not optically active.
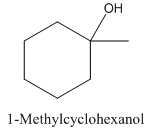
1- Methylcyclohexanol is achiral and doesn’t show enantiomerism.
(f)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images, is true or false.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomerism deals with the study of the spatial arrangements of the atoms in space. It does not mean to alter the connectivity of the atoms by mean of forming or breaking the bonds.
Compounds with a chiral centre exist in enantiomeric forms. The phenomenon of enantiomerism is called as optical isomerism. If the configuration at each stereocenter is changed, the enantiomer is converted into another enantiomer.
Answer to Problem 15.21P
Diastereomers are Stereoisomers that are not mirror images.
Explanation of Solution
Stereoisomers which don't have any mirror image relationship are called Diastereomers.
Diastereomers are non-enantiomeric stereoisomers which have two or more stereocenter and differ only in configuration of at least one of them.
Example-
In tartaric acid,
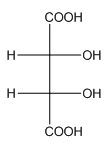 and
and 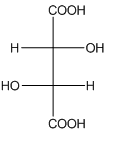 are diastereomers.
are diastereomers.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- A pdf file of your hand drawn, stepwise mechanisms for the reactions. For each reaction in the assignment, you must write each mechanism three times (there are 10 reactions, so 30 mechanisms). (A) do the work on a tablet and save as a pdf., it is expected to write each mechanism out and NOT copy and paste the mechanism after writing it just once. Everything should be drawn out stepwise and every bond that is formed and broken in the process of the reaction, and is expected to see all relevant lone pair electrons and curved arrows. Aldol: NaOH HO H Δ NaOH Δarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardDraw structures corresponding to the following names and give IUPAC names for the following compounds: (8 Point) a) b) c) CH3 CH2CH3 CH3CHCH2CH2CH CH3 C=C H3C H H2C=C=CHCH3 d) CI e) (3E,5Z)-2,6-Dimethyl-1,3,5,7-octatetraene f) (Z)-4-bromo-3-methyl-3-penten-1-yne g) cis-1-Bromo-2-ethylcyclopentane h) (5R)-4,4,5-trichloro-3,3-dimethyldecanearrow_forward
- Draw a Newman projection from carbon 3 to carbon 2 in the highest energy conformation for the following molecule. What is this conformation called? What kind of strain is present? Brarrow_forwardWhich of the following dienophiles is most reactive in a Diels-Alder reaction: Please explain why the correct answer to this question is option 5. Please provide a detailed explanation.arrow_forwardWhich of the following would you expect to be aromatic? Please provide a detailed explanation.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
