
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the reaction between ethanal and the Grignard reagent of bromobenzene after a final reaction with water has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Grignard reagent:
The reagent formed by the interaction of magnesium with organic halide in presence of ether is known as Grignard reagent. They are used to change the carbon skeleton of a starting carbonyl compound.
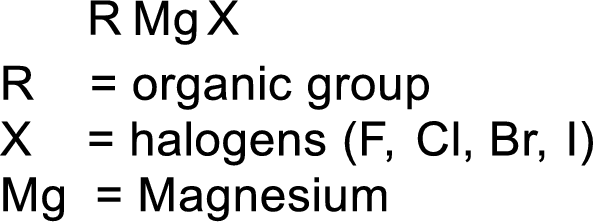
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the reaction between 2-butanone and the Grignard reagent of 2-bromopropane after a final reaction with water has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Grignard reagent:
The reagent formed by the interaction of magnesium with organic halide in presence of ether is known as Grignard reagent. They are used to change the carbon skeleton of a starting carbonyl compound.
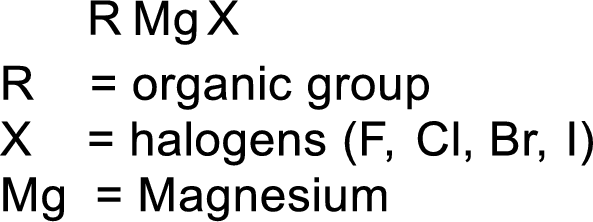
(c)
Interpretation:
There are often two combinations of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound that will give the same product. Another pair of reactants has to be chosen to give the product formed in part (a).
Concept Introduction:
Grignard reagent:
The reagent formed by the interaction of magnesium with organic halide in presence of ether is known as Grignard reagent. They are used to change the carbon skeleton of a starting carbonyl compound.
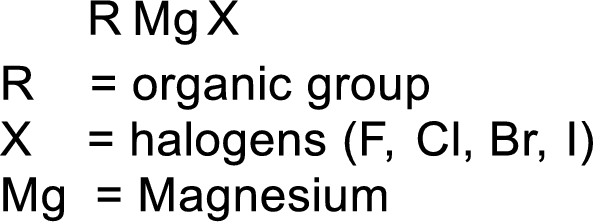
(d)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl compound that reacts with the Grignard reagent to yield a product with the
Concept Introduction:
Grignard reagent:
The reagent formed by the interaction of magnesium with organic halide in presence of ether is known as Grignard reagent. They are used to change the carbon skeleton of a starting carbonyl compound.
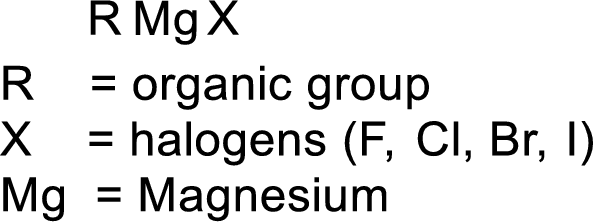
(e)
Interpretation:
The Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound used to prepare 2-methyl-2-butanol has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Grignard reagent:
The reagent formed by the interaction of magnesium with organic halide in presence of ether is known as Grignard reagent. They are used to change the carbon skeleton of a starting carbonyl compound.
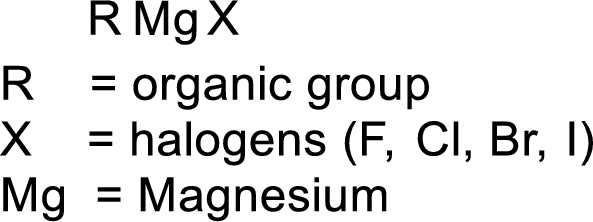
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
CHEMISTRY MOLECULAR NATURE OF MATTER
- Challenging samples: 1. Metal complexes with low volatility are often difficult to analyze when performing atomic absorption measurements because the atomization efficiency is reduced to unacceptably low levels. Devise a strategy or strategies for eliminating the problem of a non-volatile metal complex? Explain how you would do that. 2. Devise a strategy to overcome unwanted ionization of the analyte? Explain what it would be. 3. Devise a general method that can be used to account for the presence of unknown matrix effects.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Homework: Atomic Structure This homework is due at the beginning of class next lecture period and is worth 6 points. Please place the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and then put the number of electrons in the correct shell. Also give the correct atomic mass. Also, state if the atom is an ion (cation or anion). H* 1. Number of protons Number of electrons Number of neutrons Atomic mass 2. 26 13AI +++ Number of protons Number of neutrons Number of electrons Atomic massarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardI need help working this problem out step by step, I was trying to use my example from the txt book but all I know how to do is set it up. I need to be shown step by step as I am a visual learner. Please help me.arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solution and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward& Calculate the molar enthalpy of combustion (A combH) of 1.80 g of pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH; 88.1 g mol-1) at 37 °C when they are combusted in a calorimeter at constant volume with a calorimeter constant = 1.62 kJ °C-1 and the temperature rose by 1.55 °C. Given: R = 8.314 J mol −1 °C-1 and the combustion reaction: AN C3H4O3 + 2.502(g) → 3CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)arrow_forward
- An unknown salt, AB, has the following precipitation reaction:A+(aq) + B-(aq) ⇌ AB(s) the K value for this reaction is 4.50 x10-6. Draw a model that represents what will happen when 1.00 L each of 1.00 M solution of A+(aq) and 1.00M solution of B-(aq) are combined.arrow_forward5. a) Use the rules in Example 4.4 (p. 99) and calculate sizes of octahedral and tetrahedral cavities in titanium and in zirconium. Use values for atomic radii given in Fig. 9.1 (p.291). (3 points) b) Consider the formation of carbides (MC) of these metals. Which metal is able to accommodate carbon atoms better, and which cavities (octahedral or tetrahedral) would be better suited to accommodate C atoms into metal's lattice? (4 points)arrow_forward2. Read paragraph 3.4 in your textbook ("Chiral Molecules"), and explain if Cobalt(ethylenediamine) 33+ shown in previous problem is a chiral species. If yes, draw projections of both enantiomers as mirror images, analogous to mirror projections of hands (below). Mirror (4 points)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





