
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977251
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.2, Problem 14.39P
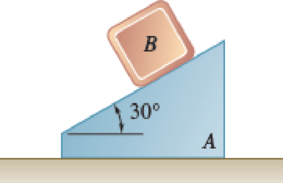
A 15-lb block B starts from rest and slides on the 25-lb wedge A, which is supported by a horizontal surface. Neglecting friction, determine (a) the velocity of B relative to A after it has slid 3 ft down the inclined surface of the wedge, (b) the corresponding velocity of A.
Fig. P14.39
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
8 in.
6 in.
B
PROBLEM 13.58
A 3-lb collar is attached to a spring and slides without friction along a
circular rod in a horizontal plane. The spring has an undeformed length of
7 in. and a constant k = 1.5 lb/in. Knowing that the collar is in
equilibrium at A and is given a slight push to get it moving, determine the
velocity of the collar (a) as it passes through B, (b) as it passes through C.
VB =
= 11.66 ft/s
15.01 ft/s
VC
=
The 15-kg block B is supported by the 25-kg block A and is attached to a cord to which a 225-N horizontal force is applied as shown. Neglecting friction, determine (a) the acceleration of block A, (b) the acceleration of block B relative to A.
applied mechanics 2
Chapter 14 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 14.1 - A 30-g bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical 1350-kg automobiles A and B are at...Ch. 14.1 - An airline employee tosses two suitcases in rapid...Ch. 14.1 - Car A weighing 4000 lb and car B weighing 3700 lb...Ch. 14.1 - Two swimmers A and B, of weight 190 lb and 125 lb,...Ch. 14.1 - A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand side by side...Ch. 14.1 - A 40-Mg boxcar A is moving in a railroad...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical cars A and B are at rest on a...Ch. 14.1 - A 20-kg base satellite deploys three...Ch. 14.1 - For the satellite system of Prob. 14.9, assuming...
Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three particles A, B, and C....Ch. 14.1 - For the system of particles of Prob. 14.13,...Ch. 14.1 - A 13-kg projectile is passing through the origin O...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.16PCh. 14.1 - A 2-kg model rocket is launched vertically and...Ch. 14.1 - An 18-kg cannonball and a 12-kg cannonball are...Ch. 14.1 - 14.19 and 14.20 Cruiser A was traveling east at 60...Ch. 14.1 - 14.19 and 14.20 Cruiser A was traveling east at 60...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.21PCh. 14.1 - Two spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a...Ch. 14.1 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with a...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.24PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.25PCh. 14.1 - In a scattering experiment, an alpha particle A is...Ch. 14.1 - Derive the relation HO=rmv+HG between the angular...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.28PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.29PCh. 14.1 - Show that the relation MA=HA, where HA is defined...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost due to friction and the...Ch. 14.2 - In Prob. 14.3, determine the energy lost (a) when...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.33PCh. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost as a result of the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.35PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.36PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.37PCh. 14.2 - Ball B is suspended from a cord of length l...Ch. 14.2 - A 15-lb block B starts from rest and slides on the...Ch. 14.2 - A 40-lb block B is suspended from a 6-ft cord...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.41PCh. 14.2 - 14.41 and 14.42 In a game of pool, ball A is...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.43PCh. 14.2 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.45PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.46PCh. 14.2 - Four small disks A, B, C, and D can slide freely...Ch. 14.2 - In the scattering experiment of Prob. 14.26, it is...Ch. 14.2 - Three identical small spheres, each weighing 2 lb,...Ch. 14.2 - Three small spheres A, B, and C, each of mass m,...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.51PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.52PCh. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 3 kg and 1.5 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 2 kg and 1 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Three small identical spheres A, B, and C, which...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.56PCh. 14.3 - A stream of water with a density of = 1000 kg/m3...Ch. 14.3 - A jet ski is placed in a channel and is tethered...Ch. 14.3 - Tree limbs and branches are being fed at A at the...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.60PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.61PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.62PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.63PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.64PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.65PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.66PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.67PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.68PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.69PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.70PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.71PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.72PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.73PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.74PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.75PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.76PCh. 14.3 - The propeller of a small airplane has a...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.78PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.79PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.80PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.81PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.82PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.83PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.84PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.85PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.86PCh. 14.3 - Solve Prob. 14.86, assuming that the chain is...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.88PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.89PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.90PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.91PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.92PCh. 14.3 - A rocket sled burns fuel at the constant rate of...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.94PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.95PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.96PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.97PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.98PCh. 14.3 - Determine the distance traveled by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - A rocket weighs 2600 lb, including 2200 lb of...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the altitude reached by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.102PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.103PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.104PCh. 14 - Three identical cars are being unloaded from an...Ch. 14 - A 50-kg mother and her 26-kg son are sledding down...Ch. 14 - An 80-Mg railroad engine A coasting at 6.5 km/h...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.108RPCh. 14 - Mass C, which has a mass of 4 kg, is suspended...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.110RPCh. 14 - A 6000-kg dump truck has a 1500-kg stone block...Ch. 14 - For the ceiling-mounted fan shown, determine the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.113RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.114RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.115RPCh. 14 - A chain of length l and mass m falls through a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 2-lb collar C may slide without friction along a horizontal rod. It is attached to three springs, each of constant 30 lb/ft and 2-in. undeformed length. Knowing that the collar is released from rest in C the position shown, determine the maximum speed it will reach in the ensuing motion. www D 2 in. A В - 2 in.→-2 in.- wwarrow_forwardThe two blocks shown are originally at rest. Neglecting the masses of the pulleys and the effect of friction in the pulleys and knowing that the coefficients of friction between the blocks and the inclines are ls = 0.25 and = 0.2, determine (a) the acceleration of each block, (b) the tension in the cable. 200 lb 90° 20° 300 lb Вarrow_forwardThe block B start from rest and slides on the 30 wedge A , which is supported by a horizontal surface . Neglecting frictionarrow_forward
- A 8-kg block B starts from rest and slides on th 14-kg wedge A,which is supported by horizontal surface. neglecting friction,determine (a) the velocity of B relative to A after it has slid 1 mdown the inclined surface of the wedge, (b) the correspondingvelocity of A.arrow_forward12.124 Block A has a weight of 40 lb, and block B has a weight of 8 lb. The coefficient of kinetic friction between all surfaces of contact is k = 0.15. Knowing 0 = 20° and P = 50 lb, determine (a) the acceleration of block B, (b) the tension in the cord. Answer (a) 21.0 ft/s² & 37.9°, (b) 14.61 lb. B Fig. P12.124 01arrow_forwardPROBLEM 13.19 The system shown, consisting of a 20-kg collar A and a 10-kg counterweight B, is at rest when a constant 500-N force is applied to collar A. (a) Determine the velocity of A just before it hits the support at C. (b) Solve part a assuming that the counterweight B is replaced by a 98.1-N downward force. Ignore friction and the mass of the pulleys. V₁ = 3.16 m/s = 5.48 m/sarrow_forward
- Problem #2 A collar of mass m is attached to a spring and slides without friction along a circular rod in a vertical plane. The spring has an undeformed length of 5 in. and a constant k. Knowing that the collar has a speed v at Point C, draw the FBD and KD of the collar at this point. 5 in. 7 in. |Barrow_forward2- The two blocks shown are originally at rest. Neglecting the masses of the pulleys and the effect of friction in the pulleys and assuming that the coefficients of friction between block A and the horizontal surface are µz = 0.25 and u = 0.20, determine (a) the acceleration of each block, (b) the tension in the cable.arrow_forwardA small package of weight W is projected into a vertical return loop at A with a velocity v0 . The package travels without friction along a circle of radius r and is deposited on a horizontal surface at C. For each of the two loops shown, determine (a) the smallest velocity v0 for which the package will reach the horizontal surface at C, (b) the corresponding force exerted by the loop on the package as it passes point B.arrow_forward
- Three identical small spheres, each weighting 2 lb, can slide freely on a horizontal frictionless surface. Spheres B and C are connected by a light rod and are at rest in the position shown when sphere B is struck squarely by sphere A, which is moving to the right with a velocity v0 = (8 ft/s)i . Knowing that θ = 30° and that the velocities of spheres A and B immediately after the impact are vA = (0.5 ft/s)i and vB = (3.75 ft/s)i + (vB)yj, determine (vB)y and the velocity of C immediately after impact.arrow_forwardPravinbhaiarrow_forwardThree small spheres A, B and C, which weight 1, 2and 4 lb respectively, can slide freely on a horizontalfrictionless surface. Spheres B and C are connectedby a light rod and are at rest in the position shownwhen sphere B is struck squarely by sphere A whichis moving to the right with a velocity V0 = (8 ft/s)i.Knowing that θ = 45° and that the velocities of spheresA and B immediately after the impact are VA = 0 and VB = (2 ft/s)i + (VB)y j, determine(VB)y and the velocity of C immediately after impact. Please show every single step in the solution with the free body diagrams thanksarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY