
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977251
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.1, Problem 14.18P
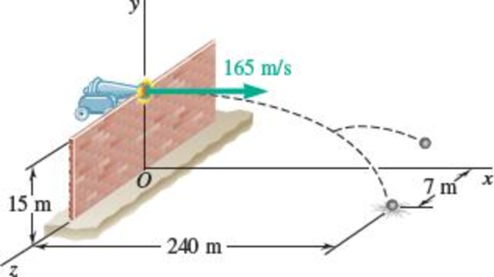
An 18-kg cannonball and a 12-kg cannonball are chained together and fired horizontally with a velocity of 165 m/s from the top of a 15-m wall. The chain breaks during the flight of the cannonballs and the 12-kg cannonball strikes the ground at t = 1.5 s, at a distance of 240 m from the foot of the wall, and 7 m to the right of the line of fire. Determine the position of the other cannonball at that instant. Neglect the resistance of the air.
Fig. P14.18
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
At an amusement park in the greater
area there are three 180-kg bumper cars occupied by
seniors. The riders in cars A, B, and C have individual masses of 50, 70, and 40 kg respectively. Car A
is observed to be moving to the right with a velocity v = 2 m/s and Car C is moving at vc = 1.5 m/s
to the left. Car B is initially at rest with a collision imminent. The bumper cars are designed with a
coefficient of restitution of 0.8 between each car,
VC
A
B
C
Determine the final velocity of each car, after all impacts for the following two collision scenarios:
(a) Cars A and Chit Car B at the same time,
(b) Car A hits Car B before car C does (note there will be more than two total collisions)
A projectile is fired from the edge of a 150-m cliff with an initial velocity of 180 m/s at an angle of 30° with the horizontal. Neglecting air resistance, find (a) the horizontal distance from the cannon to the point where the projectile strikes the ground, (b) the greatest elevation above the ground reached by the projectile.
Two spheres of equal mass, A and B, are projected off the edge of a 2.0 m
bench. Sphere A has a horizontal velocity of 5.0 m/s and sphere B has a
horizontal velocity of 2.0 m/s If both spheres leave the edge of the table at
the same instant, sphere A will land
at the same time as sphere B.
at some time after sphere B.
at some time before sphere B
There is not enough information to decide
If both spberesleave th e odge of the table at the same inctant cphere A
Chapter 14 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 14.1 - A 30-g bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical 1350-kg automobiles A and B are at...Ch. 14.1 - An airline employee tosses two suitcases in rapid...Ch. 14.1 - Car A weighing 4000 lb and car B weighing 3700 lb...Ch. 14.1 - Two swimmers A and B, of weight 190 lb and 125 lb,...Ch. 14.1 - A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand side by side...Ch. 14.1 - A 40-Mg boxcar A is moving in a railroad...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical cars A and B are at rest on a...Ch. 14.1 - A 20-kg base satellite deploys three...Ch. 14.1 - For the satellite system of Prob. 14.9, assuming...
Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three particles A, B, and C....Ch. 14.1 - For the system of particles of Prob. 14.13,...Ch. 14.1 - A 13-kg projectile is passing through the origin O...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.16PCh. 14.1 - A 2-kg model rocket is launched vertically and...Ch. 14.1 - An 18-kg cannonball and a 12-kg cannonball are...Ch. 14.1 - 14.19 and 14.20 Cruiser A was traveling east at 60...Ch. 14.1 - 14.19 and 14.20 Cruiser A was traveling east at 60...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.21PCh. 14.1 - Two spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a...Ch. 14.1 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with a...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.24PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.25PCh. 14.1 - In a scattering experiment, an alpha particle A is...Ch. 14.1 - Derive the relation HO=rmv+HG between the angular...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 14.28PCh. 14.1 - Prob. 14.29PCh. 14.1 - Show that the relation MA=HA, where HA is defined...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost due to friction and the...Ch. 14.2 - In Prob. 14.3, determine the energy lost (a) when...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.33PCh. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost as a result of the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.35PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.36PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.37PCh. 14.2 - Ball B is suspended from a cord of length l...Ch. 14.2 - A 15-lb block B starts from rest and slides on the...Ch. 14.2 - A 40-lb block B is suspended from a 6-ft cord...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.41PCh. 14.2 - 14.41 and 14.42 In a game of pool, ball A is...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.43PCh. 14.2 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.45PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.46PCh. 14.2 - Four small disks A, B, C, and D can slide freely...Ch. 14.2 - In the scattering experiment of Prob. 14.26, it is...Ch. 14.2 - Three identical small spheres, each weighing 2 lb,...Ch. 14.2 - Three small spheres A, B, and C, each of mass m,...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.51PCh. 14.2 - Prob. 14.52PCh. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 3 kg and 1.5 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 2 kg and 1 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Three small identical spheres A, B, and C, which...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.56PCh. 14.3 - A stream of water with a density of = 1000 kg/m3...Ch. 14.3 - A jet ski is placed in a channel and is tethered...Ch. 14.3 - Tree limbs and branches are being fed at A at the...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.60PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.61PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.62PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.63PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.64PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.65PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.66PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.67PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.68PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.69PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.70PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.71PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.72PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.73PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.74PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.75PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.76PCh. 14.3 - The propeller of a small airplane has a...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.78PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.79PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.80PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.81PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.82PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.83PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.84PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.85PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.86PCh. 14.3 - Solve Prob. 14.86, assuming that the chain is...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.88PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.89PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.90PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.91PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.92PCh. 14.3 - A rocket sled burns fuel at the constant rate of...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.94PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.95PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.96PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.97PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.98PCh. 14.3 - Determine the distance traveled by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - A rocket weighs 2600 lb, including 2200 lb of...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the altitude reached by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 14.102PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.103PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 14.104PCh. 14 - Three identical cars are being unloaded from an...Ch. 14 - A 50-kg mother and her 26-kg son are sledding down...Ch. 14 - An 80-Mg railroad engine A coasting at 6.5 km/h...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.108RPCh. 14 - Mass C, which has a mass of 4 kg, is suspended...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.110RPCh. 14 - A 6000-kg dump truck has a 1500-kg stone block...Ch. 14 - For the ceiling-mounted fan shown, determine the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.113RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.114RPCh. 14 - Prob. 14.115RPCh. 14 - A chain of length l and mass m falls through a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 0.01 kg bullet is shot at a 1.00 kg block of wood. The block of wood is on a horizontal frictionlesssurface.As viewed from above, the bullet has an initial velocity v1 in the positive x-direction. The block ofwood has an initial velocity v2 in the positive y-direction.The bullet gets stuck in the block of wood when it hits.After the collision, the block and bullet together are observedto move as shown in the diagram:a) What were the initial velocities of the bullet and block of wood?This problem should be solved using... What is the system? Are there external forces? Diagram before/after Calculations before/after What stays the same? Solve! Since this problem is in 2D, write step 4 using vector notation.Please write your final answers to two decimal places.b) Suppose the bullet bounced backwards when it hit the wood, instead of getting stuck. Would thespeed of the wood after the collision be faster or slower than 2 m/s? Or would it be the same?No calculation required, but very…arrow_forwardAt an amusement park there are 200-kg bumper cars A, B, and C that have riders with masses of 45 kg, 70 kg, and 37.5 kg respectively. Car A is moving to the right with a velocity VA = 2 m/s and car Chas a velocity vc=1.5 m/s to the left, but car B is initially at rest. The coefficient of restitution between each car is 0.8. A The velocity of car A, v"" A is The velocity of car B, v"" Bis The velocity of car A, v" cis B Determine the final velocity of each car, after all impacts, assuming car A hits car B before car C does. Assume positive sign denoting forward motion and negative sign denoting backward motion. C m/s ((Click to select) ✔). m/s ((Click to select)). m/s ( (Click to select)).arrow_forwardA 2-oz pellet shot vertically from a spring-loaded pistol on the surface of the earth rises to a height of 300 ft. The same pellet shot from the same pistol on the surface of the moon rises to a height of 1900 ft. Determine the energy dissipated by aerodynamic drag when the pellet is shot on the surface of the earth. (The acceleration of gravity on the surface of the moon is 0.165 times that on the surface of the earth.)arrow_forward
- pls help me, enlightened onesarrow_forwardA pingpong ball is thrown 45 degree from the vertical. The distance of the pingpong player is 15ft from the ring. Upon the release of the ball, it has a distance of 8 ft measured from the ground and 2 ft away from the player. Determine the velocity at release if the height of the ring is to be 11 ft.arrow_forwardA 2-kg model rocket is launched vertically and reaches an altitude of 70 m with a speed of 30 m/s at the end of powered flight, time t= 0. As the rocket approaches its maximum altitude it explodes into two parts of masses mA = 0.7 kg and mB = 1.3 kg. Part A is observed to strike the ground 80 m west of the launch point at t = 6 s. Determine the position of part B at that time.arrow_forward
- Two identical 1350-kg automobiles A and B are at rest with their brakes released when B is struck by a 5400-kg truck C that is moving to the left at 8 km/h. A second collision then occurs when B strikes A. Assuming the first collision is perfectly plastic and the second collision is perfectly elastic, determine the velocities of the three vehicles just after the second collision.arrow_forwardA 4-lb collar can slide without friction along a horizontal rod and is released from rest at A . The undeformed lengths of springs BA and CA are 10 in. and 9 in., respectively, and the constant of each spring is 2800 lb/in. Determine the velocity of the collar when it has moved 1 in. to the right.arrow_forwardA 40-Mg boxcar A is moving in a railroad switchyard with a velocity of 9 km/h toward cars B and C , which are both at rest with their brakes off at a short distance from each other. Car B is a 25-Mg flatcar supporting a 30-Mg container, and car C is a 35-Mg boxcar. As the cars hit each other they get automatically and tightly coupled. Determine the velocity of car A immediately after each of the two couplings, assuming that the container (a) does not slide on the flatcar, (b) slides after the first coupling but hits a stop before the second coupling occurs, (c) slides and hits the stop only after the second coupling has occurred.arrow_forward
- vehicles are approaching a road junction, both moving with speed (12.5 m/s). One vehicle has mass 1000 kg and the other mass kg, and the roads meet at an angle of 60° as shown. The vehicles collide and initially move as a single body. ss of Car A= 100 kg ss of Car B = 70 kg A 12.5 m/s B 60° 12.5 m/s culate the magnitude of the velocity of the two vehicles immediately after the collision (treating them as a gle body) (m/s) culate the linear momentum in the vector form of car B. (m/s) culate the linear momentum in the vector form of car A. (m/s) Choose... Choose... Choose... 4arrow_forwardIMPULSE AND MOMENTUM A 4kg ball and 3kg ball move on a smooth plane along a straight path withspeeds equivalent to 6m/s going to the right and 8 m/s going to the left, respectively.1. Determine the speed of the 3kg ball after impact if the impact is elastic.2. Determine the speed of the 3kg ball after impact if the coefficient of restitutionis 0.50.arrow_forwardA ball is thrown vertically upward the ground with an initial velocity of 128 ft/s . (a) Determine when the ball hits the ground. (b) What is the velocity of the ball when it strikes the ground? (c) Determine how high will the ball reach the maximum height.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY