
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of
- 1) The simplest aromatic
carboxylic acid is benzoic acid. - 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
The structure of the given compound is,
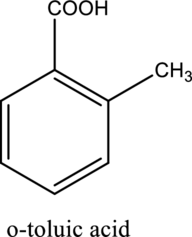
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The structure of the given compound is,
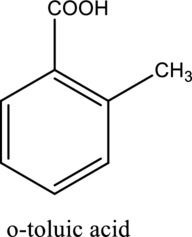
This compound is
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
The structure of the given compound is,
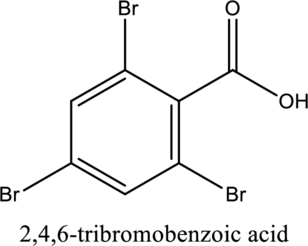
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The substituent
The structure of the given compound is,
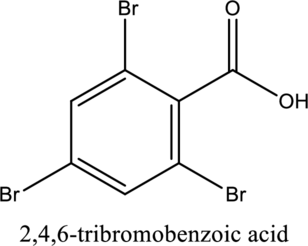
This compound is
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
The structure of the given compound is,
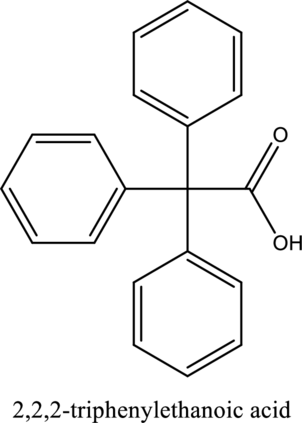
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The substituent phenyl is bonded to carbon
The structure of the given compound is,
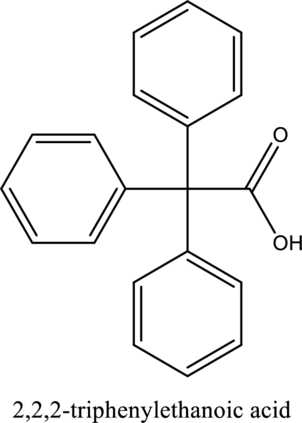
This compound is
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(d)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
The structure of the given compound is,
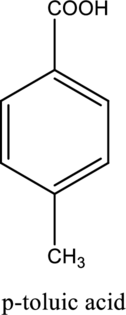
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The structure of the given compound is,
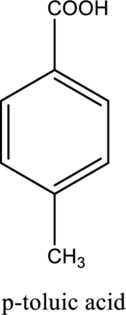
This compound is
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(e)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
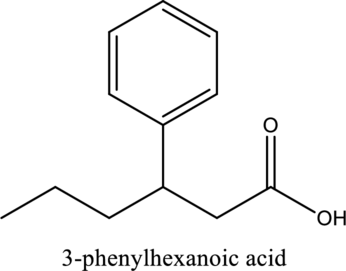
The structure of the given compound is,
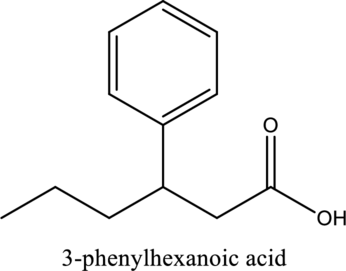
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The substituent phenyl is bonded to carbon
The structure of the given compound is,
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(f)
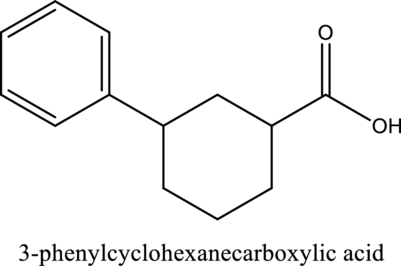
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
The structure of the given compound is,
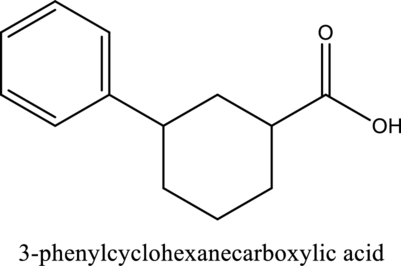
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The substituent phenyl is bonded to carbon
The structure of the given compound is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- Can I get helpp drawing my arrowsarrow_forwardWhich of the m/z values corresponds to the base peak in the mass spectrum shown? 100 80 A. 45 B. 44 C. 29 D. 15 Intensity 20 0 10 20 30 40 B- m/z -8 50 E. 30 Which of the m/z values correspond to the molecular ion for the compound shown? A. 18 B. 82 OH C. 100 D. 102 E. 103arrow_forwardCan someone help me with drawing my arrows.arrow_forward
- I'm having trouble with converting lewis diagrams into VSEPR diagrams. I currently have this example of C2BrCl3 which I want to turn into a lewis structure, but I'm not sure what steps I need to do in order to do so. I have the table written down, however, there's two central atoms so what would I do? There seems to be 4 electron domains on the carbon atom and no lone pairs so it would seem like this shape would be tetrahedral. Here's what I have now. Thanks!arrow_forwardWe discussed the solid phase resin using in peptide synthesis. Provide a mechanism, for its formation. DRAW THE MECHANISM.arrow_forwardPlease help. Every time I've asked an expert in the past, it's been wrong :(arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





