
Concept explainers
(a)
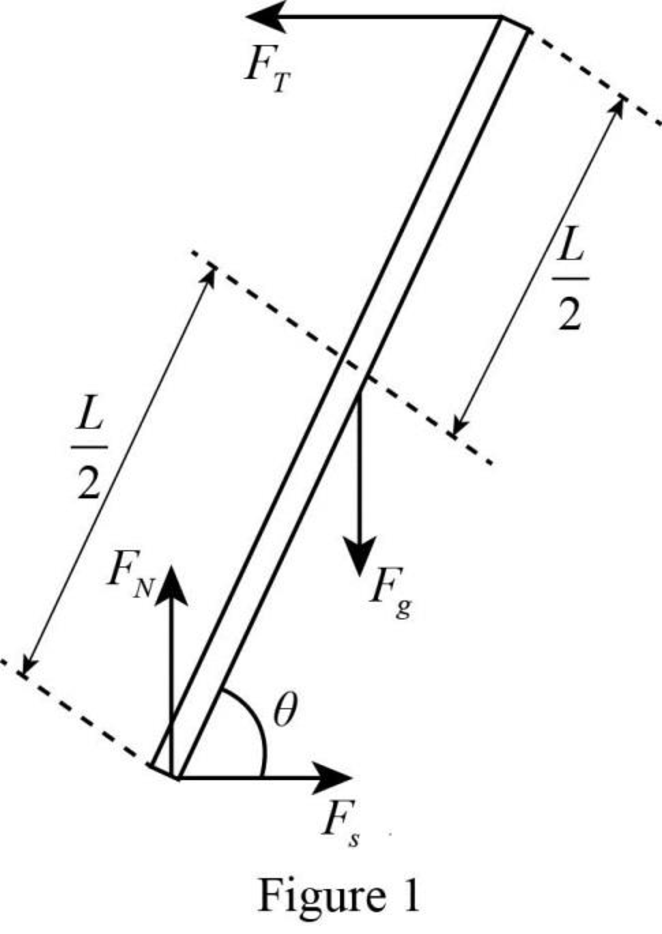
The free-body diagram of the forces acting on the ladder.
(a)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The free-body diagram of the forces acting on the ladder is
Explanation of Solution
A free-body diagram is a graphical tool used to illustrate the different forces acting on a particular object. It helps to solve complex physical problems. The free-body diagram of the ladder in the given situation is drawn in figure 1.
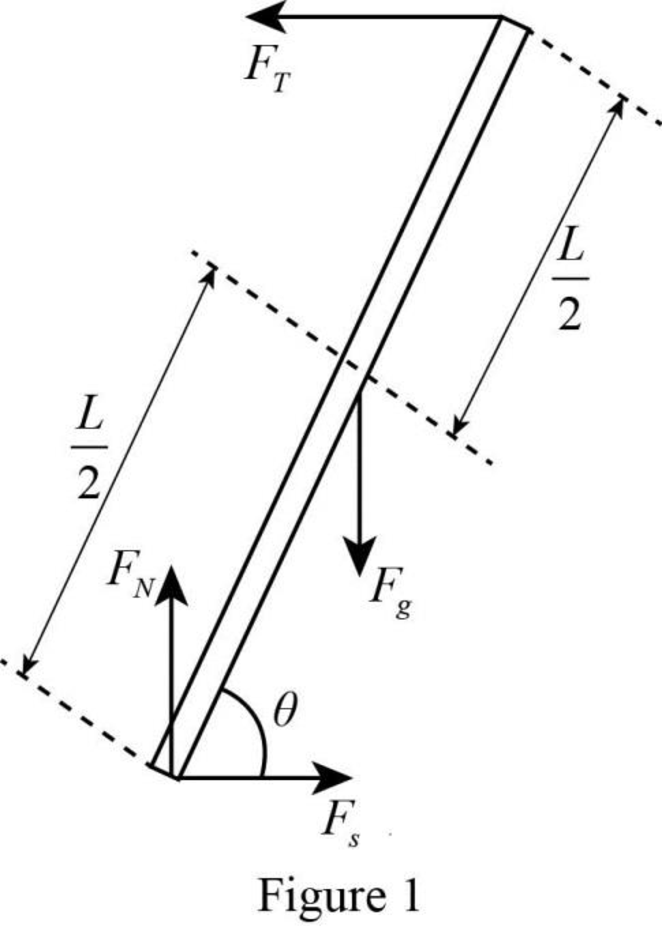
The forces acting on the ladder are the weight, the normal force, the tension and the force of static friction. In the figure weight is represented as
Conclusion:
Thus, the free-body diagram of the forces acting on the ladder is drawn in figure 1.
(b)
The tension in the rope in terms of
(b)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The tension in the rope in terms of
Explanation of Solution
Take the lower end of the ladder as the pivot point. This will eliminate the torque due to normal force and the torque due to force of static friction.
Since the ladder is in rotational equilibrium, the net torque about the lower end of the ladder must be zero.
Write the condition for the rotational equilibrium.
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (I).
Write the expression for
Write the expression for
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above four equations in equation (II) and rewrite it for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the tension in the rope in terms of
(c)
The expression for the tension in the rope in terms of
(c)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The expression for the tension in the rope in terms of
Explanation of Solution
Since the ladder is in translational equilibrium, the net force in
Write the conditions for the translational equilibrium.
Here,
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (VI).
Put the above equation in equation (IV) and rewrite it for
Write the equation for
Here,
Write the equation for
Put the above equation in equation (VIII).
Put the above equation in equation (V) and rewrite it for
Put the above equation in equation (VII).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the expression for the tension in the rope in terms of
(d)
The coefficient of static friction in terms of the angle
(d)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The coefficient of static friction in terms of the angle
Explanation of Solution
Equate equations (III) and (IX).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the coefficient of static friction in terms of the angle
(e)
The after effect of moving the ladder slightly so as to reduce the angle
(e)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The ladder will slip if it is moved slightly to reduce the angle
Explanation of Solution
The expression for the angle
The expression for the tension force obtained in part (b),
Conclusion:
Thus, the ladder will slip if it is moved slightly to reduce the angle
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- What is the force (in N) on the 2.0 μC charge placed at the center of the square shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) 5.0 με 4.0 με 2.0 με + 1.0 m 1.0 m -40 με 2.0 μCarrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 5.4 µC charge shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) −3.1 µC5.4 µC9.2 µC6.4 µCarrow_forwardAn ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forward
- The outside temperature is 25 °C. A heat engine operates in the environment (Tc = 25 °C) at 50% efficiency. How hot does it need to get the high temperature up to in Celsius?arrow_forwardGas is compressed in a cylinder creating 31 Joules of work on the gas during the isothermal process. How much heat flows from the gas into the cylinder in Joules?arrow_forwardThe heat engine gives 1100 Joules of energy of high temperature from the burning gasoline by exhausting 750 Joules to low-temperature . What is the efficiency of this heat engine in a percentage?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





