
Concept explainers
(a)
The length of the spring.
(a)
Answer to Problem 45PQ
The length of the spring is
Explanation of Solution
Following figure gives rod and spring system.
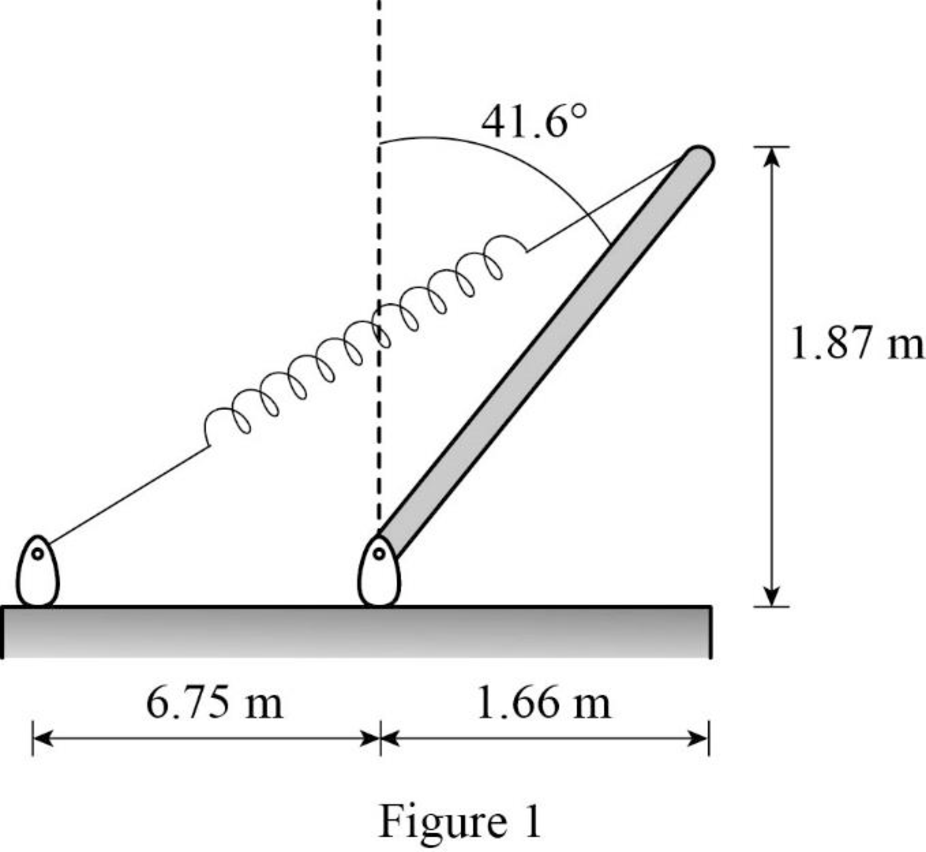
Following figure is the free body diagram of rod and spring system.
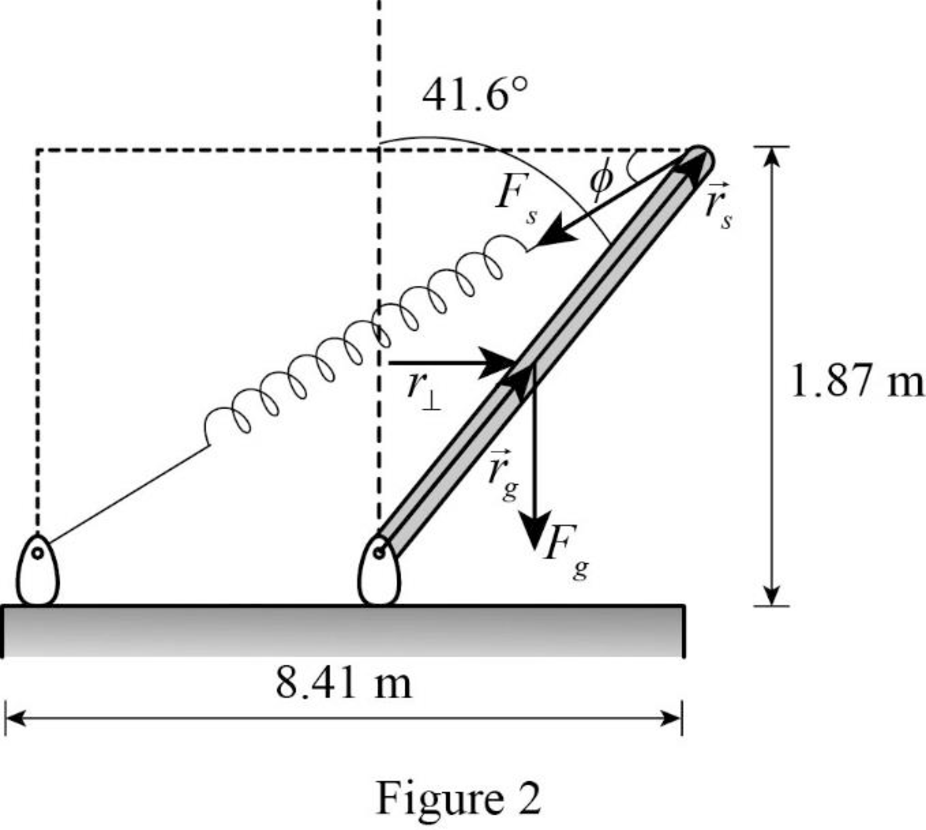
Write the expression for the horizontal distance between one end to other end of the spring.
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the expression for the vertical distance of the end of the spring from ground.
Here,
Write the expression for the length of the spring using Pythagoras theorem.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
This distance is also equal to vertical distance of the end of the spring from ground.
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the length of the spring is
(b)
The weight of the bar.
(b)
Answer to Problem 45PQ
The weight of the bar is
Explanation of Solution
At equilibrium, the net torque acting on the bar around the bottom pivot must be zero.
Write the expression for the torque about pivot in the rod due to gravity.
Here,
The direction of torque is into the page.
Using figure2, write the expression for the perpendicular distance between pivot of the rod and point where weight acts.
Write the expression for the radial vector from the pivot point to the end of the bar where the spring acts.
Here,
Write the expression for the relaxed length.
Here,
The magnitude of spring force depends on the extension relative to the relaxed spring length.
Write the expression for the magnitude of spring force.
Here,
Write the expression for the extension of spring relative to the relaxed spring length.
From figure2, write the expression for the angle spring force makes below the horizontal.
Here,
Write the expression for the spring force as a vector.
Here,
Write the expression for the torque on the rod due to spring force.
Here,
The direction of above torque is out of the page.
At equilibrium torque due to spring force and weight will cancel each other. Since, the directions of torques are opposite, their magnitude should be equal.
Write the equilibrium condition of the torques.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Use equations (XV) and (XVI) in (XIII) to get
Substitute
Therefore, The weight of the bar is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- 7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forwardганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forward
- A small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius cc and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What is the direction of the electric field for b<r<c? Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for c<r<d. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for r>d.arrow_forwardTICE D Conservation of Momentum 1. A 63.0 kg astronaut is on a spacewalk when the tether line to the shuttle breaks. The astronaut is able to throw a spare 10.0 kg oxygen tank in a direction away from the shuttle with a speed of 12.0 m/s, propelling the astronaut back to the shuttle. Assuming that the astronaut starts from rest with respect to the shuttle, find the astronaut's final speed with respect to the shuttle after the tank is thrown. 2. An 85.0 kg fisherman jumps from a dock into a 135.0 kg rowboat at rest on the west side of the dock. If the velocity of the fisherman is 4.30 m/s to the west as he leaves the dock, what is the final velocity of the fisher- man and the boat? 3. Each croquet ball in a set has a mass of 0.50 kg. The green ball, traveling at 12.0 m/s, strikes the blue ball, which is at rest. Assuming that the balls slide on a frictionless surface and all collisions are head-on, find the final speed of the blue ball in each of the following situations: a. The green…arrow_forward
- The 5.15 A current through a 1.50 H inductor is dissipated by a 2.15 Q resistor in a circuit like that in the figure below with the switch in position 2. 0.632/ C A L (a) 0.368/ 0+ 0 = L/R 2T 3r 4 (b) (a) What is the initial energy (in J) in the inductor? 0 t = L/R 2t (c) Эт 4t 19.89 ] (b) How long will it take (in s) the current to decline to 5.00% of its initial value? 2.09 S (c) Calculate the average power (in W) dissipated, and compare it with the initial power dissipated by the resistor. 28.5 1.96 x W X (ratio of initial power to average power)arrow_forwardImagine a planet where gravity mysteriously acts tangent to the equator and in the eastward directioninstead of radially inward. Would this force do work on an object moving on the earth? What is the sign ofthe work, and does it depend on the path taken? Explain by using the work integral and provide a sketch ofthe force and displacement vectors. Provide quantitative examples.arrow_forwardIf a force does zero net work on an object over a closed loop, does that guarantee the force is conservative? Explain with an example or counterexamplearrow_forward
- A futuristic amusement ride spins riders in a horizontal circle of radius 5 m at a constant speed. Thefloor drops away, leaving riders pinned to the wall by friction (coefficient µ = 0.4). What minimum speedensures they don’t slip, given g = 10 m/s²? Draw diagram (or a few) showing all forces, thevelocity of the rider, and their accelerationarrow_forwardYour RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? 0.00897 × H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? 8.97 * ΜΩarrow_forwardYour RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? ΜΩarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





