
Concept explainers
Given this set of daily service operations, and assuming a processing order of A-B -C-D-E:
a. Give one reason that each arrangement might be preferred over the other.
b. Determine the number of repetitions for each service if four cycles are used.
c. Determine the number of repetitions for each service if two cycles are used.
a)
To determine: Reason each arrangement might be preferred over the other.
Introduction: A production cycle is a period through which the objects of labor like raw materials and goods stay in the creation procedure from the earliest starting point of assembling through the yield of completed item. Additionally the working time, the creation cycle incorporates interferences underway inferable from physical, synthetic, and organic forms or the character of the objects of work or the innovation and association of generation.
Explanation of Solution
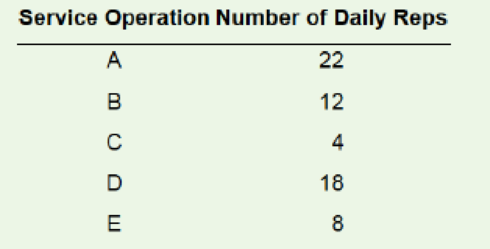
Given Information:
Process order: A-B-C-D-E
| Service Operation | Number of Daily Reps |
| A | 22 |
| B | 12 |
| C | 4 |
| D | 18 |
| E | 8 |
The following are the reasons each arrangement might be preferred over the other:
- Two cycles have low amounts of substitutions.
- Four cycles have low inventory and are considered as high on suppleness.
b)
To determine: The number of repetitions for each service if four cycles used.
Introduction: A production cycle is a period through which the objects of labor like raw materials and goods stay in the creation procedure from the earliest starting point of assembling through the yield of completed item. Additionally the working time, the creation cycle incorporates interferences underway inferable from physical, synthetic, and organic forms or the character of the objects of work or the innovation and association of generation.
Answer to Problem 5P
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the number of repetitions for each service if four cycles used.
It is calculated by dividing each product’s daily quantity by 4.
Hence the number of repetitions for service operation A is 5.5, B is 3, C is 1, D is 4.5 and E is 2.
Determine the processing order if four cycles used.
| Cycle | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| A | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| B | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| C | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| D | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| E | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
c)
To determine: The number of repetitions for each service if two cycles used.
Introduction: A production cycle is a period through which the objects of labor like raw materials and goods stay in the creation procedure from the earliest starting point of assembling through the yield of completed item. Additionally the working time, the creation cycle incorporates interferences underway inferable from physical, synthetic, and organic forms or the character of the objects of work or the innovation and association of generation.
Answer to Problem 5P
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the number of repetitions for each service if two cycles used.
It is calculated by dividing each product’s daily quantity by 2.
Hence the number of repetitions for service operation A is 11, B is 6, C is 2, D is 9 and E is 4.
Determine the processing order if two cycles used.
| Cycle | 1 | 2 |
| A | 11 | 11 |
| B | 6 | 6 |
| C | 2 | 2 |
| D | 9 | 9 |
| E | 4 | 4 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Accounting For Governmental & Nonprofit Entities
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Macroeconomics
- understand 4 Classwork LSC Drag the name of the figure of speech to its example. 12 February 2025 personification Onomatopoeia Simile Metaphor Hyperbole Onomatopoeia metaphor 1. He tried to help but his legs were wax. Metaphor 2. The man flights like a lion on the soccer field. Simile 3. The books fell on the table with a loud thump. Onomatopoeia 4. Rita heard the last piece of pie calling her name. Personification 5. The rustling leaves kept me away. Personification 6. Kisses are the flowers of affection. 7. He's running faster than the windarrow_forwardAnswer the question in the attached photo and draw the network that interprets the dataarrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- oimmnjjjharrow_forwardSummarize the ethical dilemma encountered in Walmart Inc. Which of Kohlberg's stages of moral development is represented? Is there other theories of moral development that better describes the example? Postulate the (hypothetical or real) best- and worst-case outcomes of this dilemma. Is it agreeable with the selection of Kohlberg's stages of moral development for their examples? Is there another theory of moral development that would better describe their examples?arrow_forwardFour-drive theory recommends that companies must keep fulfillment of the four drives in balance. What is this “balance” and why is it important? Can you Give an example (real or hypothetical) of how a company maintains balanced drive fulfillment. Also describe a company that does not provide this balance, including the consequences of this imbalance on employees’ attitudes and behavior. Thank youarrow_forward
- what criteria would you utilize to determine if someone's pay is “fair” or “egregious?” Additionally, what should be the mechanism or process to determine how much greater an organizational executive should be paid versus line-level employees?arrow_forwardDefine the concept of a compensation philosophy, including the components that should be addressed in a compensation philosophy. Assess why a compensation philosophy is so foreign to most organizations and how you can best encourage an organization to create its own compensation philosophy that is beneficial to attracting the best talent.arrow_forward1) View the videos Taco Bell test-drives Live Mas restaurant concept in South Bay (0.32 mins, Ctrl+Click on the link) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=04wRc5Wg8GU , and First-ever Taco Bell Live Mas Café serving exclusive drinks in Chula Vista (1.56 mins, Ctrl+Click on the link) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fq6jDxJk1LM , and answer the following questions: a) What is driving Taco Bell to try a beverage-focused format? b) What type of a process strategy does their beverage-focused format represent? c) What operational issues do you think Taco Bell would face from their beverage-focused format? d) What do you think are the main advantages and disadvantages of kiosk ordering? Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs for each of the questions. 2) Taipei Pharmaceuticals is planning to open a new manufacturing facility as part of its expansion plans. The firm has narrowed down the search to locate its new manufacturing facility…arrow_forward
- 1) View the videos Taco Bell test-drives Live Mas restaurant concept in South Bay (0.32 mins, Ctrl+Click on the link) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=04wRc5Wg8GU , and First-ever Taco Bell Live Mas Café serving exclusive drinks in Chula Vista (1.56 mins, Ctrl+Click on the link) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fq6jDxJk1LM , and answer the following questions: a) What is driving Taco Bell to try a beverage-focused format? b) What type of a process strategy does their beverage-focused format represent? c) What operational issues do you think Taco Bell would face from their beverage-focused format? d) What do you think are the main advantages and disadvantages of kiosk ordering? Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs for each of the questions. 2) Taipei Pharmaceuticals is planning to open a new manufacturing facility as part of its expansion plans. The firm has narrowed down the search to locate its new manufacturing facility…arrow_forwardThe Clothing Shack is an online retailer of men's, women's, and children's clothing. The company has been in business for four years and makes a modest profit from its online sales. However, in an effort to compete successfully against online retailing heavyweights, the Clothing Shack's marketing director, Makaya O'Neil, has determined that the Clothing Shack's marketing information systems need improvement. Ms. O'Neil feels that the Clothing Shack should begin sending out catalogs to its customers, keep better track of its customer's buying habits, perform target marketing, and provide a more personalized shopping experience for its customers. Several months ago, Ms. O'Neil submitted a systems service request (SSR) to the Clothing Shack's steering committee. The committee unanimously approved this project. You were assigned to the project at that time and have since helped your project team successfully complete the project initiation and planning phase. Your team is now ready to move…arrow_forwardb-1. Activity ES EF LS LF Slack 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 b-2. Identify the critical activities, and determine the duration of the project. The critical activities are .arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning



