
(a)
Find the Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall.
Find the location of the resultant.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall is
The location of the resultant is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The height (H) of the retaining wall is 3.05 m.
The depth
The unit weight
The saturated unit weight
The angle
The angle
The surcharge
Calculation:
Find the submerged unit weight
Here,
The unit weight
Substitute
The angle of internal friction above and below the water table is same. Therefore,
Find the coefficient of Rankine’s active earth pressure for frictionless wall
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the pore water pressure
Substitute
Sketch the active earth pressure diagram as shown in Figure 1.
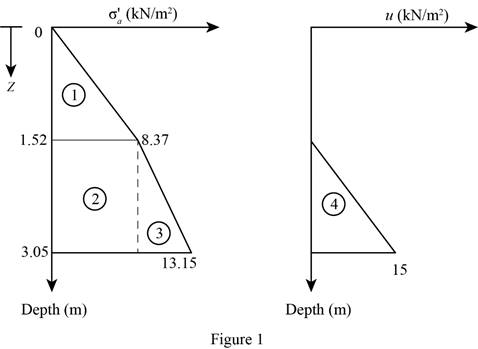
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 1
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 2
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 3
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 4
Substitute
Find the total active earth pressure per unit length
Substitute
Therefore, the Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall is
Refer Figure 1.
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location of resultant force
Take moment about the bottom of the wall.
Substitute
Therefore, the location of the resultant is
(b)
Find the Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall.
Find the location of the resultant.
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall is
The location of the resultant is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The height (H) of the retaining wall is 6 m.
The depth
The unit weight
The saturated unit weight
The angle
The angle
The surcharge
Calculation:
Find the submerged unit weight
The unit weight
Substitute
Find the coefficient of Rankine’s active earth pressure for frictionless wall
Substitute
Find the coefficient of Rankine’s active earth pressure for frictionless wall
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the pore water pressure
Substitute
Sketch the active earth pressure diagram as shown in Figure 2.
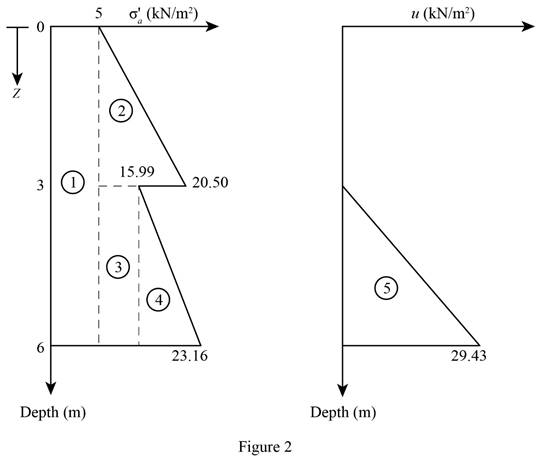
Find the active earth pressure of component 1 per unit length due to surcharge load
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 2
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 3
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 4
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 5
Substitute
Find the total active earth pressure per unit length
Substitute
Therefore, the Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall is
Refer Figure 1.
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location of resultant force
Take moment about the bottom of the wall.
Substitute
Therefore, the location of the resultant is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- S₂ S S,-40 S,-100 P S,=40 40 80 80 40arrow_forwardThe bolted connection shown is connected with M20 bolts in standard holes. The plate material is A36 steel. Find the allowable (ASD) tensile strength of each plate. 50 65 65 65 13 40 65 40 13arrow_forwardA 3.048 m long column (Fy = 483 MPa) carries an axial compression load of 5000 kN dead load. The column is braced at mid-height to strengthen the column in the weak direction. Use LRFD. Which of the following most nearly gives the nominal compressive strength? Show solution and drawingsarrow_forward
- When an open-ended square tube is placed vertically into a pool of water, the water rises 4 mm up inside of the tube. A) Determine the inner length of the square tube. A solid cylindrical rod is then placed vertically down the center of the open-ended square tube and the water rises an additional 4 mm up the tube. B) Determine the diameter of the solid rod that was inserted. 0.073 @ 20N m T C s = = o .arrow_forwardPlease use the following labels in the image such as Va, Vbr, Vbl and etc. Show step by step solution for each. Thanks!arrow_forwardThe single story building shown in Fig. 2 has an applied uniform load of 300 psf (0.3ksf) including the self weight of the beams and the girders. The roof has a 16 ft x 15 ft opening as shown. 1. Determine the axial loads on Columns C1 and C2 using reactions from the beams supported on the columns. 2. Determine the axial loads on Columns C1 and C2 using the concept of tributary areas.arrow_forward
- A built-up beam section is formed by welding 2xL8x6x1 angles to the bottom flange of W36x210 as shown in Fig. 1. Determine the following section properties of the built-up cross section: a. Cross sectional area, A (in2) b. The location of the centroids CG-X and CG-Y id of the built up section from the bottom of angle ( this value is given, so you need to check that you get this value) c. Moments of inertia ICG-X (in4) and ICG-Y (in4) d. Section modulus Sx (bot) (in3) and Sx (top) (in3) e. Radius of gyration rx (in) and ry (in) f. Weight of the built up section, w (lb/ft) (use density of steel = 490 pcf) g. Surface area of the built-up section, S(ft2/ft)arrow_forward11. Design the main beam of a building supporting concrete floor slab as shown in Fig. 10.61 and with the following data: (i) Beam centres: 6 m (ii) Span (simply supported): 7.4 m (iii) Concrete slab (spanning in two directions): 240-mm thick (iv) Finished screed: 40-mm thick (v) Imposed load: 4 kN/m² (vi) Take weight of concrete slab as 24 kN/m³ and total weight of 40-mm thick screed as 1.0 kN/m² Assume Fe 410 grade steel and take initial weight of beam as 1.0 kN/m. H H- Main beam 7.4 m 6.0 m H 40 mm screed I -H. Fig. 10.61 k 240 mm slab 6.0 m Typical bay of large floor areaarrow_forwardConsider the situation in Question 2. If all the cables are made of the same material and have a maximum tensile force of 500 lb, what is the heaviest load that can be supported by the system?arrow_forward
- A flexible circular area is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of 148 (see the figure below). The diameter of the load area is 2 . Estimate the average stress increase () below the center of the loaded area between depths of 3 and 6 . Use the equations: and (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) =arrow_forwardA square flexible foundation of width B applies a uniform pressure go to the underlying ground. (a) Determine the vertical stress increase at a depth of 0.625B below the center using Aσ beneath the corner of a uniform rectangular load given by Aσ = Variation of Influence Value I qoI. Use the table below. n 0.8 1.0 m 0.2 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.2 0.01790 0.03280 0.03866 0.04348 0.05042 0.05471 0.4 0.03280 0.06024 0.07111 0.08009 0.09314 0.10129 0.5 0.03866 0.07111 0.08403 0.09473 0.11035 0.12018 0.6 0.04348 0.08009 0.09473 0.10688 0.12474 0.13605 0.8 0.05042 0.09314 0.11035 0.12474 0.14607 0.15978 1.0 0.05471 0.10129 0.12018 0.13605 0.15978 0.17522 (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) Ασ/90 = (b) Determine the vertical stress increase at a depth of 0.625B below the center using the 2 : 1 method equation below. 90 x B x L Aσ = (B+ z) (L + z) (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) Ασ/90 = (c) Determine the vertical stress increase at a depth of 0.625B below the center using…arrow_forwardPoint loads of magnitude 100, 200, and 360 act at , , and , respectively (in the figure below). Determine the increase in vertical stress at a depth of 6 below point . Use Boussinesq's equation. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) =arrow_forward
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning



