
Identify each of the following compounds as an
a.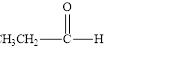 d.
d.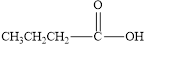
b.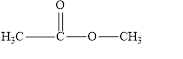 e.
e.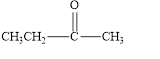
c.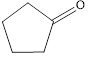 f.
f.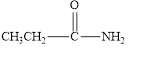
(a)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is an aldehyde.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
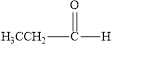
Figure 1
The given compound contains carbonyl group that is connected to one carbon atom and one hydrogen atom. Hence, it is an aldehyde.
The given compound is an aldehyde.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
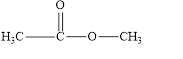
Figure 2
In the given compound, the carbonyl group is not attached with two carbon atoms. Therefore, it is not a ketone. Also, the carbonyl group is not attached with at least one hydrogen atom. Thus, it is not an aldehyde. Hence, it is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is a ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
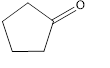
Figure 3
The given compound contains carbonyl group that is connected to two carbon atoms in the ring. Hence, it is a ketone.
The given compound is a ketone.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
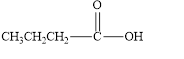
Figure 4
In the given compound, the carbonyl group is not attached with two carbon atoms. Therefore, it is not a ketone. Also, the carbonyl group is not attached with at least one hydrogen atom. Thus, it is not an aldehyde. Hence, it is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to at least one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is a ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
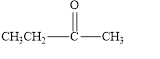
Figure 5
The given compound contains carbonyl group that is connected to two carbon atoms. Hence, it is a ketone.
The given compound is a ketone.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given compound is to be identified as an aldehyde, a ketone, or neither.
Concept introduction:
An aldehyde consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to minimum one hydrogen atom, whereas a ketone consists of a carbonyl group that is single bonded to two carbon atoms. The structural formula of an aldehyde is
Answer to Problem 14.4E
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
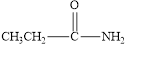
Figure 6
In the given compound, the carbonyl group is not attached with two carbon atoms. Therefore, it is not a ketone. Also, the carbonyl group is not attached with at least one hydrogen atom. Thus, it is not an aldehyde. The carbonyl group is attached to one nitrogen atom and one carbon atom. Hence, it is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
The given compound is neither aldehyde nor ketone.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry, Loose-Leaf Version, 9th + LMS Integrated OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Follow the curved arrows to draw a second resonance structure for each species. Explain and steps for individual understanding.arrow_forwardDraw all reasonable resonance structures for the following cation. Then draw the resonance hybrid. Provide steps and explanationarrow_forwardHow are the molecules or ions in each pair related? Classify them as resonance structures, isomers, or neither.arrow_forward
- How do I solve this Alkyne synthesis homework problem for my Organic Chemistry II class? I have to provide both the intermediate products and the reagents used.arrow_forwardSubstance X is known to exist at 1 atm in the solid, liquid, or vapor phase, depending on the temperature. Additionally, the values of these other properties of X have been determined: melting point enthalpy of fusion 90. °C 8.00 kJ/mol boiling point 130. °C enthalpy of vaporization 44.00 kJ/mol density 2.80 g/cm³ (solid) 36. J.K mol (solid) 2.50 g/mL (liquid) heat capacity 32. J.Kmol (liquid) 48. J.Kmol (vapor) You may also assume X behaves as an ideal gas in the vapor phase. Ex Suppose a small sample of X at 50 °C is put into an evacuated flask and heated at a constant rate until 15.0 kJ/mol of heat has been added to the sample. Graph the temperature of the sample that would be observed during this experiment. o0o 150- 140 130- 120- 110- 100- G Ar ?arrow_forwardMechanism. Provide the mechanism for the reaction below. You must include all arrows, intermediates, and formal charges. If drawing a Sigma complex, draw all major resonance forms. The ChemDraw template of this document is available on Carmen. Br FeBr3 Brarrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning




