
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
![]()
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given aldehyde is ethanal.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
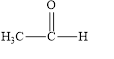
Figure 1
The given compound is aldehyde. The first step in the naming of aldehyde is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of two
The given aldehyde is ethanal.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl ![]() functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given aldehyde is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
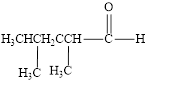
Figure 2
The given compound is aldehyde. The first step in the naming of aldehyde is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of five
The given aldehyde is
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl ![]() functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given ketone is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
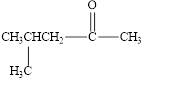
Figure 3
The given compound is ketone. The first step in the naming of ketone is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of five
The given ketone is
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl ![]() functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given aldehyde is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
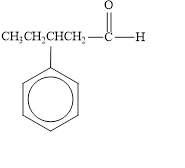
Figure 4
The given compound is aldehyde. The first step in the naming of aldehyde is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of five
The given aldehyde is
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given compound is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done in such a way that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing the structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ane, ene, yne, ol, al and so on.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl ![]() functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
functional group in their parent chain and are named by adding suffix –al and –one to the name of the parent alkane.
Answer to Problem 14.5E
The IUPAC name of the given cyclic ketone is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is shown below.
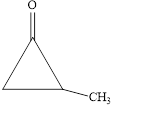
Figure 5
The given compound is cyclic ketone. The first step in the naming of ketone is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of three
The given cyclic ketone is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry, Loose-Leaf Version, 9th + LMS Integrated OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





