
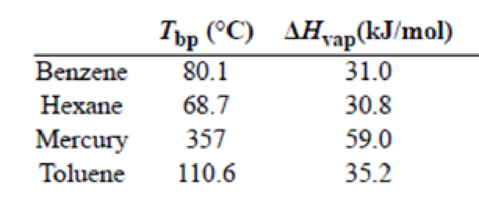
(a) Trouton’s rule states that the ratio of the molar heat of vaporization of a liquid (ΔHvap) to its boiling point in kelvins is approximately 90 J/K · mol. Use the following data to show that this is the case and explain why Trouton’s rule holds true.
(b) Use the values in Table 12.5 to calculate the same ratio for ethanol and water. Explain why Trouton’s rule does not apply to these two substances as well as it does to other liquids.
(a)
Interpretation:
To verify Trouton's rule for the given set of substances.
Concept Introduction:
According to Trouton's rule for, various liquids attheir boiling point the change in entropy value will be the same. The ratio of enthalpy of vaporization and boiling temperature of various liquids has the same value.
Where,
Answer to Problem 14.47QP
Trouton's rule is verified for benzene, hexane, mercury and toluene. All the four substances have
Explanation of Solution
To record the given data
To verify Trouton's rule for benzene
Trouton's rule can be verified by plugging in the values of
Since the value is approximately equal to
To verify Trouton's rule for hexane
Trouton's rule can be verified by plugging in the values of
Since the value is approximately equal to
To verify Trouton's rule for mercury
Trouton's rule can be verified by plugging in the values of
Since the value is approximately equal to
To verify Trouton's rule for Toluene
Trouton's rule can be verified by plugging in the values of
Since the value is approximately equal to
(b)
Interpretation:
To verify Trouton's rule for the given set of substances.
Concept Introduction:
According to Trouton's rule for, various liquids attheir boiling point the change in entropy value will be the same. The ratio of enthalpy of vaporization and boiling temperature of various liquids has the same value.
Where,
Answer to Problem 14.47QP
Trouton's rule is not obeyed by water and ethanol due to the high entropy of vaporization.
Explanation of Solution
To record the given data
To verify Trouton's rule for ethanol
Trouton's rule can be verified by plugging in the values of
Since, the value is greater than
To verify Trouton's rule for water
Trouton's rule can be verified by plugging in the values of
Since the value is greater than
To explain the reason for the deviation from hydrogen bond in case of water and ethanol.
For water and ethanol there exist strong hydrogen bonding attraction in the liquid state. Hydrogen bonding interaction decreases the entropy in the system. In gaseous state the hydrogen bonding interaction becomes weaker and the molecules will have more randomness in the system. The entropy of vaporization will be high. This is the reason why water and ethanol is showing larger deviation from Trouton's rule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST
- I need help working this problem out step by step, I was trying to use my example from the txt book but all I know how to do is set it up. I need to be shown step by step as I am a visual learner. Please help me.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solution and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- & Calculate the molar enthalpy of combustion (A combH) of 1.80 g of pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH; 88.1 g mol-1) at 37 °C when they are combusted in a calorimeter at constant volume with a calorimeter constant = 1.62 kJ °C-1 and the temperature rose by 1.55 °C. Given: R = 8.314 J mol −1 °C-1 and the combustion reaction: AN C3H4O3 + 2.502(g) → 3CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)arrow_forwardAn unknown salt, AB, has the following precipitation reaction:A+(aq) + B-(aq) ⇌ AB(s) the K value for this reaction is 4.50 x10-6. Draw a model that represents what will happen when 1.00 L each of 1.00 M solution of A+(aq) and 1.00M solution of B-(aq) are combined.arrow_forward5. a) Use the rules in Example 4.4 (p. 99) and calculate sizes of octahedral and tetrahedral cavities in titanium and in zirconium. Use values for atomic radii given in Fig. 9.1 (p.291). (3 points) b) Consider the formation of carbides (MC) of these metals. Which metal is able to accommodate carbon atoms better, and which cavities (octahedral or tetrahedral) would be better suited to accommodate C atoms into metal's lattice? (4 points)arrow_forward
- 2. Read paragraph 3.4 in your textbook ("Chiral Molecules"), and explain if Cobalt(ethylenediamine) 33+ shown in previous problem is a chiral species. If yes, draw projections of both enantiomers as mirror images, analogous to mirror projections of hands (below). Mirror (4 points)arrow_forward3. Borane (BH3) belongs to D3h point group. Consider the vibrational (stretching) modes possible for B-H bonds under D3h symmetry. Using the methods we used in class, construct the reducible representation I, and break it down into irreducible representations using the character table provided. Sketch those modes, indicate whether they are IR-active. (6 points) D3h E 2C3 3C2 σh 283 30% A₁' 1 1 1 1 1 1 x² + y², z² 1 -1 1 1 -1 R₂ E' 2 0 2 0 (x, y) (x² - y², xy) " A₁" 1 1 -1 A2" 1 -1 -1 1 Z E" 2 -1 0 -2 1 0 (Ry, Ry) (xz, yz)arrow_forward1. List all the symmetry elements, and assign the compounds to proper point groups: a) HCIBrC-BrCIH Cl Br H (2 points) H Br b) Pentacarbonylmanganese(I)bromide Br OEC-Mn-CEO 00- c) Phenazine (aromatic molecule, with delocalized bonding) 1 d) Cobalt(ethylenediamine)33+ (just the cation) 3+ H₂N H₂ .NH2 (CI)3 NH2 H2 H₂N. (2 points) (2 points) (2 points)arrow_forward
- Hello, I desperately need help figuring out 8-14; I also wanted to see if you would mind letting me know if I picked the right degree as my melting points on the two graphs. Please and thank you in advance! All the information is provided.arrow_forwardThe reaction: A + B ⇌ 2 C, can be represented by the equilibrium expression, KC =[C]2[A][B]=258 at 520K.When 1.00 M of C was allowed to reach equilibrium and 0.055 M of A was formed. If this reaction wasperformed at the same temperature using 0.500 M C, what would the equilibrium concentration of Abe?arrow_forward1. What is the functional group of an alcohol and a phenol? 2. Why are some alcohols soluble in water? 3. Classify each of the following alcohols as primary, secondary or tertiary. a. 3-pentanol b. 2-methyl-2-butanol c. 1-propanolarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





