
Concept explainers
(a)
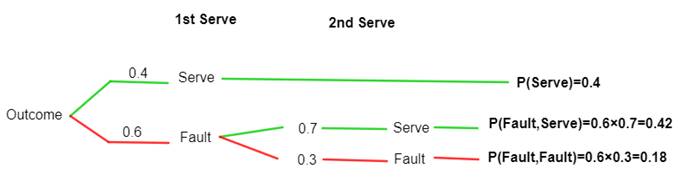
Draw a probability tree that shows each outcome.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A double fault in tennis is when the serving player fails to land their serve “in” without stepping on or over the serving line in two chances.K’s first serve percentange is 40% , while her second serve percentage is 70%.
Calculation:
The probability tree is :
(b)
Find the probability that K will double fault.
(b)
Answer to Problem 21PPS
0.18 or 18%
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A double fault in tennis is when the serving player fails to land their serve “in” without stepping on or over the serving line in two chances.K’s first serve percentange is 40% , while her second serve percentage is 70%.
Calculation:
The double fault is back to back faults , and given probabilities of serves in 1st and 2nd serving are 0.4 and 0.7 respectively.
So, the probabilities of faults in 1st and 2nd serving are (1-0.4 =) 0.6 and (1-0.7 = ) 0.3 .
Hence the probability that K will double fault = P(F,F) =
(c)
Design a simulation using a random number generator that can be used to estimate the probability that K double faults on her next serve.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A double fault in tennis is when the serving player fails to land their serve “in” without stepping on or over the serving line in two chances.K’s first serve percentange is 40% , while her second serve percentage is 70%.
Calculation:
Step 1 :
From part (a),
| Possible Outcomes (2 serving) | Theoritical Probability |
| Serve | 0.4 |
| Fault,Serve | 0.42 |
| Fault, Fault | 0.18 |
Step 2:
Assume that the servings will fall into these three categories.
Step 3:
Use a random number generator on your calculator.Use the ten integers 0-9 to accurately represent the probability data.The actual numbers used to represent the outcome does not matter.
| Possible Outcomes (2 serving) | Represented By |
| Serve | 0,1,2,3 |
| Fault,Serve | 4,5,6,7,8 |
| Fault, Fault (double fault) | 9 |
Step 4:
A trial means two servings and recording the serve or fault. The simulation will consist of 20 trials.
Chapter 13 Solutions
Glencoe Geometry Student Edition C2014
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- Can someone help me with this please?arrow_forwardMariela is in her classroom and looking out of a window at a tree, which is 20 feet away. Mariela’s line of sight to the top of the tree creates a 42° angle of elevation, and her line of sight to the base of the tree creates a 31° angle of depression. What is the height of the tree, rounded to the nearest foot? Be sure to show your work to explain how you got your answer.arrow_forward1arrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

