
Concept explainers
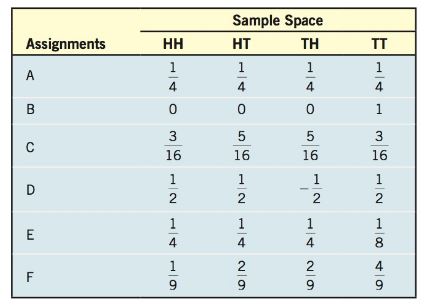
In Problems 23-26, consider the experiment of tossing a coin twice. The table lists six possible assignments of probabilities for this experiment. Using this table, answer the following questions.
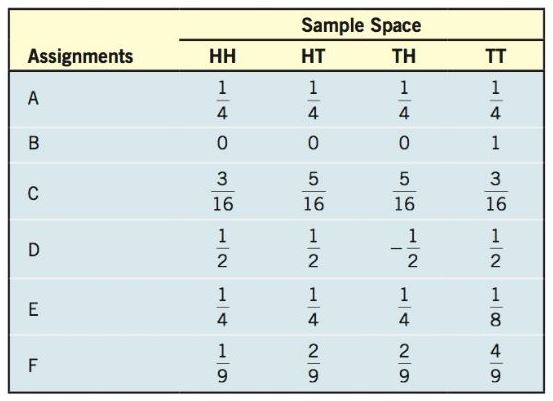
Which of the assignments of probabilities should be used if the coin is known to be fair?
Which of the assignments of probabilities should be used if the coin is known to be fair?
Answer to Problem 24AYU
A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Consider the experiment of tossing a coin twice. The table lists six possible assignments of probabilities for this experiment.
Formula used:
Probability of any event is .
Calculation:
Since the coin is fair, the four outcomes are equally likely, therefore, the probability of each of the four outcomes is . Hence assignment A represents assignment where a fair coin is used.
Chapter 13 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
College Algebra (7th Edition)
- 15. Please solve this and show each and every step please. PLEASE no chatgpt can I have a real person solve it please!! I am stuck. I am doing pratice problems and I do not even know where to start with this. The question is Please compute the indicated functional value.arrow_forwardUse a graph of f to estimate lim f(x) or to show that the limit does not exist. Evaluate f(x) near x = a to support your conjecture. Complete parts (a) and (b). x-a f(x)= 1 - cos (4x-4) 3(x-1)² ; a = 1 a. Use a graphing utility to graph f. Select the correct graph below.. A. W → ✓ Each graph is displayed in a [- 1,3] by [0,5] window. B. in ✓ ○ C. und ☑ Use the graphing utility to estimate lim f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. x-1 ○ A. The limit appears to be approximately ☐ . (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.) B. The limit does not exist. b. Evaluate f(x) for values of x near 1 to support your conjecture. X 0.9 0.99 0.999 1.001 1.01 1.1 f(x) ○ D. + ☑ (Round to six decimal places as needed.) Does the table from the previous step support your conjecture? A. No, it does not. The function f(x) approaches a different value in the table of values than in the graph, after the approached values are rounded to the…arrow_forwardx²-19x+90 Let f(x) = . Complete parts (a) through (c) below. x-a a. For what values of a, if any, does lim f(x) equal a finite number? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. x→a+ ○ A. a= (Type an integer or a simplified fraction. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) B. There are no values of a for which the limit equals a finite number. b. For what values of a, if any, does lim f(x) = ∞o? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. x→a+ A. (Type integers or simplified fractions) C. There are no values of a that satisfy lim f(x) = ∞. + x-a c. For what values of a, if any, does lim f(x) = -∞0? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. x→a+ A. Either a (Type integers or simplified fractions) B.arrow_forwardSketch a possible graph of a function f, together with vertical asymptotes, that satisfies all of the following conditions. f(2)=0 f(4) is undefined lim f(x)=1 X-6 lim f(x) = -∞ x-0+ lim f(x) = ∞ lim f(x) = ∞ x-4 _8arrow_forwardDetermine the following limit. lim 35w² +8w+4 w→∞ √49w+w³ 3 Select the correct choice below, and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. ○ A. lim W→∞ 35w² +8w+4 49w+w3 (Simplify your answer.) B. The limit does not exist and is neither ∞ nor - ∞.arrow_forwardCalculate the limit lim X-a x-a 5 using the following factorization formula where n is a positive integer and x-➡a a is a real number. x-a = (x-a) (x1+x-2a+x lim x-a X - a x-a 5 = n- + xa an-2 + an−1)arrow_forwardThe function s(t) represents the position of an object at time t moving along a line. Suppose s(1) = 116 and s(5)=228. Find the average velocity of the object over the interval of time [1,5]. The average velocity over the interval [1,5] is Vav = (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardFor the position function s(t) = - 16t² + 105t, complete the following table with the appropriate average velocities. Then make a conjecture about the value of the instantaneous velocity at t = 1. Time Interval Average Velocity [1,2] Complete the following table. Time Interval Average Velocity [1, 1.5] [1, 1.1] [1, 1.01] [1, 1.001] [1,2] [1, 1.5] [1, 1.1] [1, 1.01] [1, 1.001] ப (Type exact answers. Type integers or decimals.) The value of the instantaneous velocity at t = 1 is (Round to the nearest integer as needed.)arrow_forwardFind the following limit or state that it does not exist. Assume b is a fixed real number. (x-b) 40 - 3x + 3b lim x-b x-b ... Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (x-b) 40 -3x+3b A. lim x-b x-b B. The limit does not exist. (Type an exact answer.)arrow_forwardx4 -289 Consider the function f(x) = 2 X-17 Complete parts a and b below. a. Analyze lim f(x) and lim f(x), and then identify the horizontal asymptotes. x+x X--∞ lim 4 X-289 2 X∞ X-17 X - 289 lim = 2 ... X∞ X - 17 Identify the horizontal asymptotes. Select the correct choice and, if necessary, fill in the answer box(es) to complete your choice. A. The function has a horizontal asymptote at y = B. The function has two horizontal asymptotes. The top asymptote is y = and the bottom asymptote is y = ☐ . C. The function has no horizontal asymptotes. b. Find the vertical asymptotes. For each vertical asymptote x = a, evaluate lim f(x) and lim f(x). Select the correct choice and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. earrow_forwardExplain why lim x²-2x-35 X-7 X-7 lim (x+5), and then evaluate lim X-7 x² -2x-35 x-7 x-7 Choose the correct answer below. A. x²-2x-35 The limits lim X-7 X-7 and lim (x+5) equal the same number when evaluated using X-7 direct substitution. B. Since each limit approaches 7, it follows that the limits are equal. C. The numerator of the expression X-2x-35 X-7 simplifies to x + 5 for all x, so the limits are equal. D. Since x²-2x-35 X-7 = x + 5 whenever x 7, it follows that the two expressions evaluate to the same number as x approaches 7. Now evaluate the limit. x²-2x-35 lim X-7 X-7 = (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardA function f is even if f(x) = f(x) for all x in the domain of f. If f is even, with lim f(x) = 4 and x-6+ lim f(x)=-3, find the following limits. X-6 a. lim f(x) b. +9-←x lim f(x) X-6 a. lim f(x)= +9-←x (Simplify your answer.) b. lim f(x)= X→-6 (Simplify your answer.) ...arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage LearningMod-01 Lec-01 Discrete probability distributions (Part 1); Author: nptelhrd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6x1pL9Yov1k;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYDiscrete Probability Distributions; Author: Learn Something;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m9U4UelWLFs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYProbability Distribution Functions (PMF, PDF, CDF); Author: zedstatistics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YXLVjCKVP7U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYDiscrete Distributions: Binomial, Poisson and Hypergeometric | Statistics for Data Science; Author: Dr. Bharatendra Rai;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lHhyy4JMigg;License: Standard Youtube License
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage LearningMod-01 Lec-01 Discrete probability distributions (Part 1); Author: nptelhrd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6x1pL9Yov1k;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYDiscrete Probability Distributions; Author: Learn Something;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m9U4UelWLFs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYProbability Distribution Functions (PMF, PDF, CDF); Author: zedstatistics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YXLVjCKVP7U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYDiscrete Distributions: Binomial, Poisson and Hypergeometric | Statistics for Data Science; Author: Dr. Bharatendra Rai;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lHhyy4JMigg;License: Standard Youtube License