
Interpretation:
The structure of a given molecular formula C11H16 to be predicted using 13CNMR spectra.
Concept introduction:
The 13CNMR spectrum gives information on the different electronic environments of carbon. As like 1HNMR, the number of signals generated in 13CNMR are predicted by performing symmetry operations (rotation or reflection symmetry). Only chemical shift values are reported in the spectrum but not the multiplicity and integration values because the coupling between two neighboring 13C-13C nuclei are weakly involved due to the low abundance of 13C isotopes of carbon atom.
To Identify:
The structure of an alcohol of given molecular formula C11H6.
Broadband-decoupled spectrum:
The spectrum shows seven signals whereas the given molecular formula also has seven carbon atoms. Thus all the seven carbons have chemically different electronic environments showing signals.
- The signal in the region of 150-220 ppm indicates the carbon atom of carbonyl group (C=O).
- The three signals in the region of 10-25 ppm indicate the sp3 hybridized carbon atoms which can be methyl / methylene or methine groups.
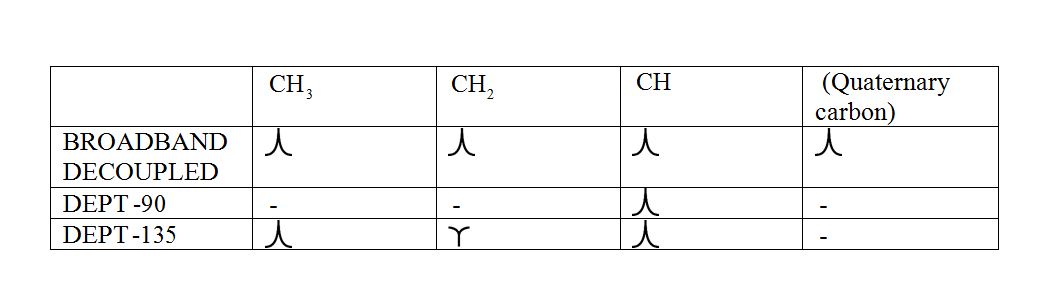
DEPT (Distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer):
a) DEPT-90: The spectrum exhibits signal only from CH group and no signals from CH3, CH2, CH and quaternary carbon (carbon with no protons).
b) DEPT-135: The spectrum exhibits CH3 groups and CH groups as positive signals (pointing up); CH2 groups appear as negative signals (pointing down) and quaternary carbon does not appear.
The signals appear in each type of spectrum:
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- help draw the moleculearrow_forwardHow to draw this claisen condensation reaction mechanisms/arrow_forwardWrite all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forward
- How can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
