
Concept explainers
Propose structures for compounds that fit the following 1H NMR data:
(a) C4H6Cl2
2.18 δ (3 H, singlet)
4.16 δ (2 H, doublet, J=7 Hz)
5.71 δ (1 H, triplet, J=7 Hz)
(b) C10H14
1.30 δ (9 H, singlet)
7.30 δ (5 H, singlet)
(c) C4H7BrO
2.11 δ (3 H, singlet)
3.52 δ (2 H, triplet, J=6 Hz)
4.40 δ (2 H, triplet, J=6 Hz)
(d) C9H11Br
2.15 δ (2 H, quintet, J=7 Hz)
2.75 δ (2 H, triplet, J=7 Hz)
3.38 δ (2 H, triplet, J=7 Hz)
7.22 δ (5 H, singlet)
a)

Interpretation:
The proposed structure of the compound to be identified for the given 1HNMR spectrum.
Concept introduction:
HDI calculation:
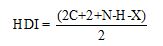
Where
C represent number of carbons.
N represent number of nitrogens.
H represent number of hydrogens.
X represent number of halogens.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Multiplicity: The number of peaks on the each signal in NMR spectrum is defined as multiplicity; the multiplicity of each signal indicates the neighboring protons. It is generated by coupling of the subjected protons with the neighboring protons (both subjected and neighbor protons are to be chemically not equivalent) separated by either two or three sigma bonds.
Rule: Multiplicity of each signal is calculated using (n+1) rule only when the neighboring protons are chemically equivalent to each other.
(n+1)
where
n indicates number of neighboring protons
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the 1HNMR spectrum represents the number of protons giving rise to the signal.
To find:
The structure of the compound to be identified for the given molecular formula and 1HNMR spectrum.
Answer to Problem 55GP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI value:
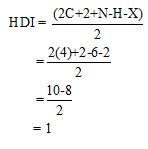
The HDI calculation confirms the presence of an aliphatic ring and double bond
Adjust the relative integration with the number of protons from the molecular formula.
The total number of protons in the molecular formula C10H14 is 6.
Interpret the given information.
Given information:
Three signals with multiplicity and integration values.
2.18ppm(3H, singlet)
4.16ppm(2H, doublet, J=7HZ)
5.71ppm(1H , triplet, J=7HZ)
The HDI value confirms the compound has either a ring or a double bond (one level of unsaturation). The total integration value (3+2+1=6 protons) is also an exact value with the protons of the molecular formula.
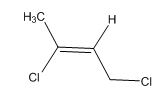
A signal at 2.18ppm with integration of 3H’s represents methyl groups which are chemically equivalent having one neighboring proton indicates the characteristic pattern of isopropyl group.
A signal with integration of 2H’s represent a methylene group appears at 4.16ppm rather 5.17ppm, consistent with the value of protons which present at alpha position to vinyl group (C=O) and accounts for the one degree of unsaturation.
The overall predicted structure is:

The methyl groups can be interchanged via no reflectional symmetry and the compound gives rise to totally three signals in spectrum.
The structure of the compound is identified using the details of spectrum and DHI calculation.
b)
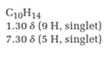
Interpretation:
The proposed structure of the compound to be identified for the given 1HNMR spectrum.
Concept introduction:
HDI calculation:
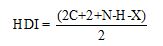
Where
C represent number of carbons.
N represent number of nitrogens.
H represent number of hydrogens.
X represent number of halogens.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Multiplicity: The number of peaks on the each signal in NMR spectrum is defined as multiplicity; the multiplicity of each signal indicates the neighboring protons. It is generated by coupling of the subjected protons with the neighboring protons (both subjected and neighbor protons are to be chemically not equivalent) separated by either two or three sigma bonds.
Rule: Multiplicity of each signal is calculated using (n+1) rule only when the neighboring protons are chemically equivalent to each other.
(n+1)
where
n indicates number of neighboring protons
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the 1HNMR spectrum represents the number of protons giving rise to the signal.
To find:
The structure of the compound to be identified for the given molecular formula and 1HNMR spectrum.
Answer to Problem 55GP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI value:
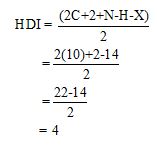
The HDI calculation confirms the presence of an aliphatic ring and double bond
Adjust the relative integration with the number of protons from the molecular formula.
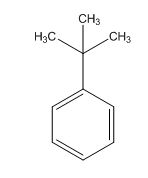
The total number of protons in the molecular formula C10H14 is 14.
Interpret the given information.
Given information:
Three signals with multiplicity and integration values.
1.30ppm(9H, singlet)
7.30ppm(5H, singlet)
The HDI value confirms the compound has either a ring or a double bond (four level of unsaturation). The total integration value (9+5=14 protons) is also an exact value with the protons of the molecular formula.
A signal at 1.30ppm with integration of 9H’s represents methyl groups which are chemically equivalent having one neighboring proton indicates the characteristic pattern of isopropyl group.
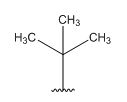
A signal with integration of 5H’s represent a benzene appears at 7.30ppm which present at aromatic group and accounts for the four degree of unsaturation.
The overall predicted structure is:

The methyl groups can be interchanged via reflectional symmetry and the compound gives rise to totally two signals in 1HNMR spectrum.
The structure of the compound is identified using the details of 1HNMR spectrum and DHI calculation.
c)

Interpretation:
The proposed structure of the compound to be identified for the given 1HNMR spectrum.
Concept introduction:
HDI calculation:
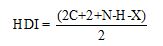
Where
C represent number of carbons.
N represent number of nitrogens.
H represent number of hydrogens.
X represent number of halogens.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Multiplicity: The number of peaks on the each signal in NMR spectrum is defined as multiplicity; the multiplicity of each signal indicates the neighboring protons. It is generated by coupling of the subjected protons with the neighboring protons (both subjected and neighbor protons are to be chemically not equivalent) separated by either two or three sigma bonds.
Rule: Multiplicity of each signal is calculated using (n+1) rule only when the neighboring protons are chemically equivalent to each other.
(n+1)
where
n indicates number of neighboring protons
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the spectrum represents the number of protons giving rise to the signal.
To find:
The structure of the compound to be identified for the given molecular formula and 1HNMR spectrum.
Answer to Problem 55GP
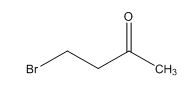
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI value:
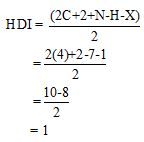
The HDI calculation confirms the presence of an aliphatic ring and double bond
Adjust the relative integration with the number of protons from the molecular formula.
The total number of protons in the molecular formula C4H7Bro is 7.
Interpret the given information.
Given information:
Three signals with multiplicity and integration values.
2.11ppm(3H, singlet)
3.52ppm(2H, triplet, J=6HZ)
4.40ppm(2H, triplet, J=6HZ)
The HDI value confirms the compound has either a ring or a double bond (one level of unsaturation). The total integration value (3+2+2=7 protons) is also an exact value with the protons of the molecular formula.
A signal at 2.11ppm with integration of 3H’s represents methyl groups which are chemically equivalent having one neighboring proton indicates the characteristic pattern of isopropyl group.

A two signal with integration of 2H’s represent a methylene group appears at 3.52ppm rather 4.40ppm, consistent with the value of protons which present at alpha position to carbonyl group(C=O) and accounts for the one degree of unsaturation.
The overall predicted structure is:

The methyl groups can be interchanged via no reflectional symmetry and the compound gives rise to totally three signals in spectrum.
The structure of the compound is identified using the details of 1HNMR spectrum and DHI calculation.
d)
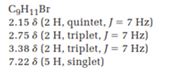
Interpretation:
The proposed structure of the compound to be identified for the given 1HNMR spectrum.
Concept introduction:
HDI calculation:
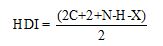
Where
C represent number of carbons.
N represent number of nitrogens.
H represent number of hydrogens.
X represent number of halogens.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Multiplicity: The number of peaks on the each signal in NMR spectrum is defined as multiplicity; the multiplicity of each signal indicates the neighboring protons. It is generated by coupling of the subjected protons with the neighboring protons (both subjected and neighbor protons are to be chemically not equivalent) separated by either two or three sigma bonds.
Rule: Multiplicity of each signal is calculated using (n+1) rule only when the neighboring protons are chemically equivalent to each other.
(n+1)
where
n indicates number of neighboring protons
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the spectrum represents the number of protons giving rise to the signal.
To find:
The structure of the compound to be identified for the given molecular formula and 1HNMR spectrum.
Answer to Problem 55GP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI value:
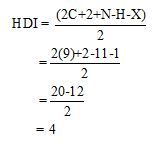
The HDI calculation confirms the presence of an aliphatic ring and double bond
Adjust the relative integration with the number of protons from the molecular formula.
The total number of protons in the molecular formula C9H11Br is 11.
Interpret the given information.
Given information:
Three signals with multiplicity and integration values.
2.15ppm(2H, quintet, J=7HZ)
2.75ppm(2H, triplet, J=7HZ)
3.38ppm(2H, triplet, J=7HZ)
7.22ppm(5H, singlet)
The HDI value confirms the compound has either a ring or a double bond (four level of unsaturation). The total integration value (2+2+2+5=11 protons) is also an exact value with the protons of the molecular formula.
A signal at 2.15ppm with integration of 2H’s represents three methyl groups which are chemically equivalent having one neighboring proton indicates the characteristic pattern of alkyl group.
A signal with integration of 2H’s represent benzylic appears at 2.75ppm which present at aromatic group
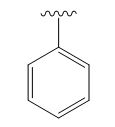
A signal with integration of 5H’s represent benzylic appears at 7.30ppm which present at aromatic group and accounts for the four degree of unsaturation.
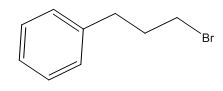
The overall predicted structure is:

The methyl groups can be interchanged via reflectional symmetry and the compound gives rise to totally four signals in spectrum.
The structure of the compound is identified using the details of 1HNMR spectrum and DHI calculation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
- 0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward9arrow_forward
- alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forwardx + LEKS: Using a phase diagram a X n/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/10_u-IgNsikr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpw ○ States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.1 atm. pressure (atm) 16 08- solid liquid- 0 200 400 gas 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 25 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. × 5arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

