
Concept explainers
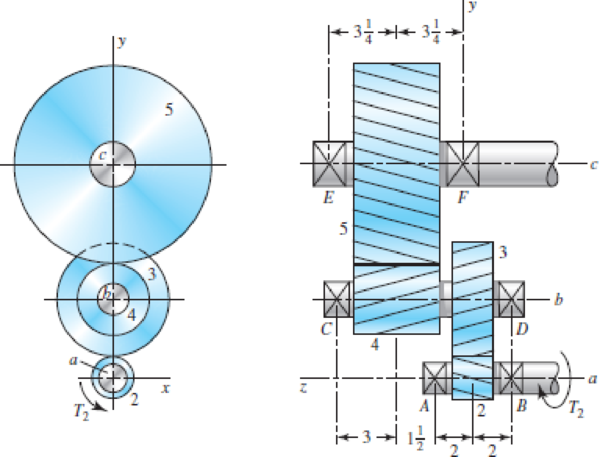
The figure shows a double-reduction helical gearset. Pinion 2 is the driver, and it receives a torque of 1200 lbf · in from its shaft in the direction shown. Pinion 2 has a normal diametral pitch of 8 teeth/in, 14 teeth, and a normal pressure angle of 20° and is cut right-handed with a helix angle of 30°. The mating gear 3 on shaft b has 36 teeth. Gear 4, which is the driver for the second pair of gears in the train, has a normal diametral pitch of 5 teeth/in, 15 teeth, and a normal pressure angle of 20° and is cut left-handed with a helix angle of 15°. Mating gear 5 has 45 teeth. Find the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the bearings C and D on shaft b if bearing C can take only a radial load while bearing D is mounted to take both radial and thrust loads.
Problem 13–50
Dimensions in inches.
The magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the bearing
The magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the bearing
Answer to Problem 50P
The magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the bearing
The magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the bearing
Explanation of Solution
The figure below shows the forces acting on the assembly of gears on the shaft
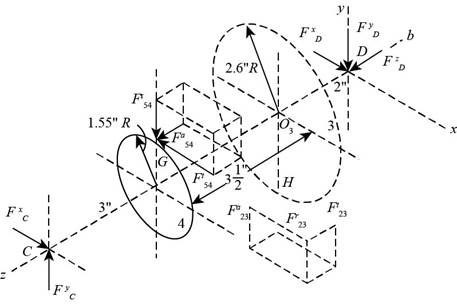
Figure-(1)
The center of the gear 3 is
Write the expression for the diameter of the gear 2.
Here, the number of teeth on the gear 2 is
Write the expression for the diameter of the gear 4.
Here, the number of teeth on the gear 2 is
Write the expression for the diameter of the gear 3.
Here, the number of teeth on the gear 3 is
Write the expression for the diameter of the gear 5.
Here, the number of teeth on the gear 5 is
Write the expression for the transverse pressure angle for gears 2.
Here, the normal pressure angle is
The transverse pressure angle for gears 2 and 3 are same.
Write the expression for the transverse pressure angle for gears 4.
Here, the normal pressure angle is
Write the expression for the tangential force on the gear 3.
Here, the torque on the gear 2 is
Write the expression for the radial force on the gear 3.
Write the expression for the axial force on the gear 3.
Calculate the tangential load on the gear 4.
Write the expression for the radial force on the gear 4.
Write the expression for the axial force on the gear 4.
Write the expression for the position vector for
Here, the length of
Write the expression for the position vector for
Here, the length of
Write the expression for the position vector for
Here, the length of
Write the expression for the force
Write the expression for the force
Write the expression for the force on the bearing
Write the expression for the force on the bearing
Write the expression for the moment at
Substitute
Write the expression for the force balance equation.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Further simplification,
Compare the
Compare the
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Further simplification.
Compare the
Compare the
Compare the
Substitute
Thus, the force in the bearing
Substitute
Thus, the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the bearing
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design (McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering)
- Using method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. A E 6 m D 600 N 4 m B 4 m 900 Narrow_forwardQuestion 5. The diagram below shows a mass suspended from a tie supported by two horizontal braces of equal length. The tie forms an angle "a" of 60° to the horizontal plane, the braces form an angle 0 of 50° to the vertical plane. If the mass suspended is 10 tonnes, and the braces are 10m long, find: a) the force in the tie; & b) the force in the braces Horizontal Braces, Tie Massarrow_forward= MMB 241 Tutorial 2.pdf 1 / 3 75% + + Tutorial z Topic: Kinematics of Particles:-. QUESTIONS 1. Use the chain-rule and find y and ŷ in terms of x, x and x if a) y=4x² b) y=3e c) y = 6 sin x 2. The particle travels from A to B. Identify the three unknowns, and write the three equations needed to solve for them. 8 m 10 m/s 30° B x 3. The particle travels from A to B. Identify the three unknowns, and write the three equations needed to solve for them. A 40 m/s 20 m B 1arrow_forward
- 3 m³/s- 1 md 45° V 1.8 mr 2mrarrow_forward= MMB 241 Tutorial 2.pdf 3/3 75% + + 6. A particle is traveling along the parabolic path y = 0.25 x². If x = 8 m, vx=8 m/s, and ax= 4 m/s² when t = 2 s, determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity and acceleration at this instant. y = 0.25x² -x 7. Determine the speed at which the basketball at A must be thrown at the angle of 30° so that it makes it to the basket at B. 30° -x 1.5 m B 3 m -10 m- 8. The basketball passed through the hoop even though it barely cleared the hands of the player B who attempted to block it. Neglecting the size of the ball, determine the 2arrow_forwardAdhesives distribute loads across the interface, whereas fasteners create areas of localized stresses. True or Falsearrow_forward
- A continuous column flash system is separating 100 kmol/h of a saturated liquid feed that is 45 mol% methanol and 55 mol% water at 1.0 atm. Operate with L/V = 1.5 and the outlet bottoms at xN = 0.28. Find the values of FL, FV, y1, and the number of equilibrium stages required. Find the value of Q used to vaporize FV. For a normal flash with the same feed and the same V/F, find the values of x and y.arrow_forwardA beer still is being used to separate ethanol from water at 1.0 atm. The saturated liquid feed flow rate is F = 840.0 kmol/h. The feed is 44.0 mol% ethanol. The saturated vapor steam is pure water with ratio of steam flow rate S to feed rate, S/F = 2/3. We desire a bottoms product that is 4.0 mol% ethanol. CMO is valid. Find the mole fraction of ethanol in the distillate vapor, yD,E. Find the number of equilibrium stages required. If the feed is unchanged and the S/F ratio is unchanged, but the number of stages is increased to a very large number, what is the lowest bottoms mole fraction of ethanol that can be obtained?arrow_forward3.1 Convert the following base-2 numbers to base-10: (a) 1011001, (b) 110.0101, and (c) 0.01011.arrow_forward
- Consider the forces acting on the handle of the wrench in (Figure 1). a) Determine the moment of force F1={−F1={−2i+i+ 4 jj −−8k}lbk}lb about the zz axis. Express your answer in pound-inches to three significant figures. b) Determine the moment of force F2={F2={3i+i+ 7 jj −−6k}lbk}lb about the zz axis. Express your answer in pound-inches to three significant figures.arrow_forwardI need you to explain each and every step (Use paper)arrow_forwardCalculate the Moment About the Point A -20"- 5 lb 40 N D 1.5 m 40 N 4.5 m A 15 lb. 150 mm 52 N 5 12 100 mm 15 lb. 26 lb. 12 5 34 lb. 13 8 15 77777 36 lb.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





