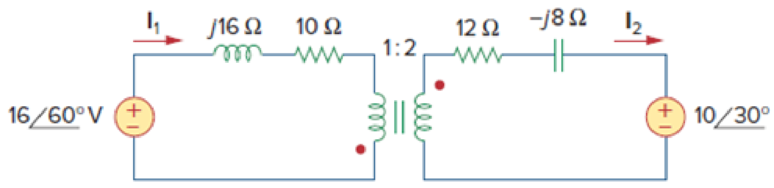
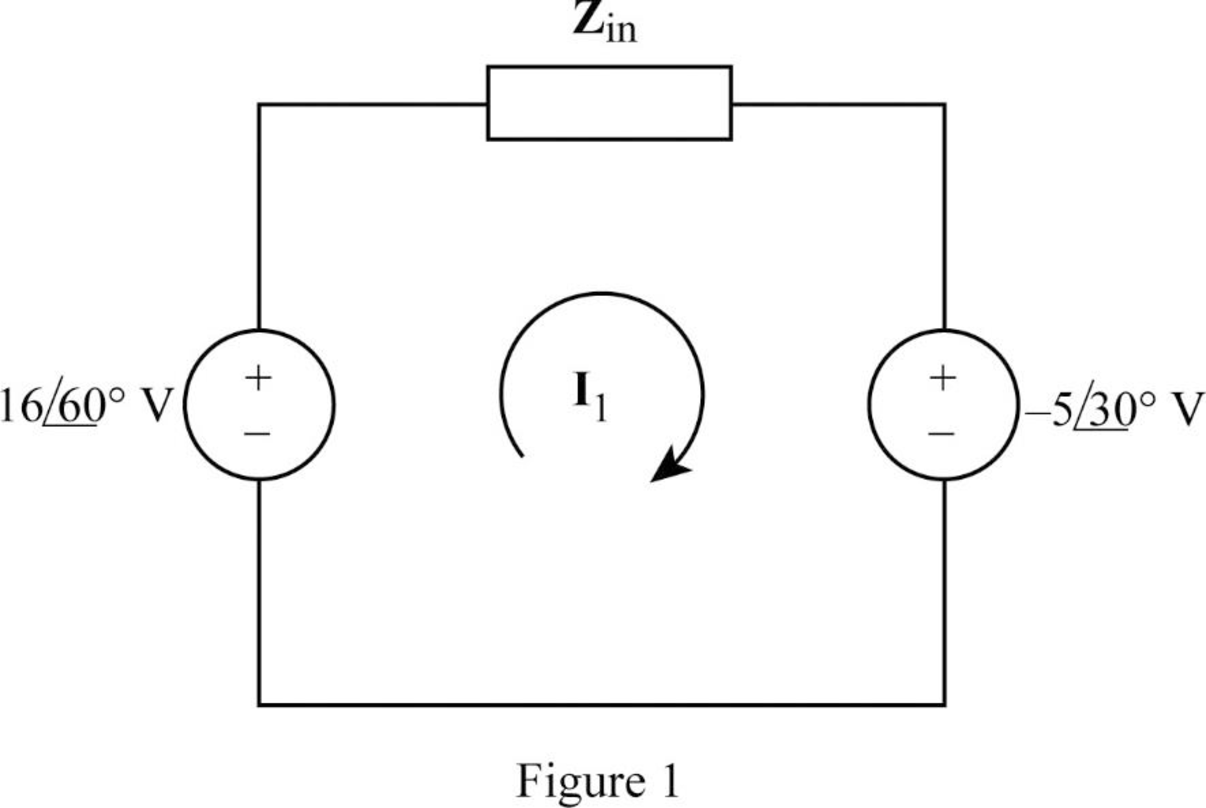
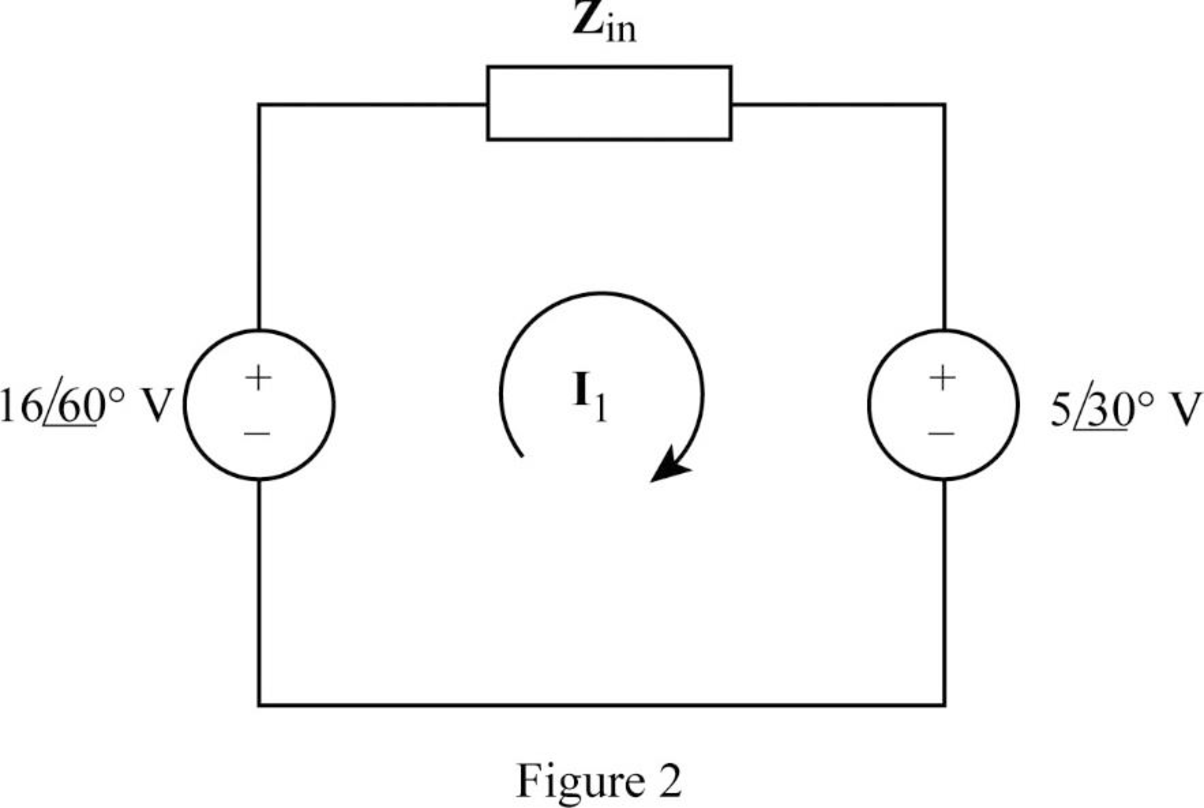
Problem 1RQ: Refer to the two magnetically coupled coils of Fig. 13.69(a). The polarity of the mutual voltage is:... Problem 2RQ Problem 3RQ Problem 4RQ Problem 5RQ: The ideal transformer in Fig. 13.70(a) has N2/N1 = 10. The ratio V2/V1 is: (a) 10 (b) 0.1 (c) 0.1... Problem 6RQ Problem 7RQ: A three-winding transformer is connected as portrayed in Fig. 13.71(a). The value of the output... Problem 8RQ Problem 9RQ Problem 10RQ Problem 1P: For the three coupled coils in Fig. 13.72, calculate the total inductance. Figure 13.72 For Prob.... Problem 2P: Using Fig. 13.73, design a problem to help other students better understand mutual inductance.... Problem 3P: Two coils connected in series-aiding fashion have a total inductance of 500 mH. When connected in a... Problem 4P: (a) For the coupled coils in Fig. 13.74(a), show that Leq = L1 + L2 + 2M (b) For the coupled coils... Problem 5P: Two coils are mutually coupled, with L1 = 50 mH, L2 = 120 mH, and k = 0.5. Calculate the maximum... Problem 6P: Given the circuit shown in Fig. 13.75, determine the value of V1 and I2. Figure 13.75 Problem 7P: For the circuit in Fig. 13.76, find Vo. Figure 13.76 For Prob. 13.7. Problem 8P: Find v(t) for the circuit in Fig. 13.77. Problem 9P Problem 10P: Find vo in the circuit of Fig. 13.79. Figure 13.79 For Prob. 13.10. Problem 11P: Use mesh analysis to find ix in Fig. 13.80, where is = 4 cos(600t) A and vs = 110 cos(600t + 30) Problem 12P: Determine the equivalent Leq in the circuit of Fig. 13.81. Figure 13.81 For Prob. 13.12. Problem 13P: For the circuit in Fig. 13.82, determine the impedance seen by the source. Figure 13.82 Problem 14P: Obtain the Thevenin equivalent circuit for the circuit in Fig. 13.83 at terminals a-b. Problem 15P: Find the Norton equivalent for the circuit in Fig. 13.84 at terminals a-b. Problem 16P: Obtain the Norton equivalent at terminals a-b of the circuit in Fig. 13.85. Problem 17P: In the circuit of Fig. 13.86, ZL is a 15-mH inductor having an impedance of j40 . Determine Zin when... Problem 18P: Find the Thevenin equivalent to the left of the load Z in the circuit of Fig. 13.87. Problem 19P: Determine an equivalent T-section that can be used to replace the transformer in Fig. 13.88. Figure... Problem 20P: Determine currents I1, I2, and I3 in the circuit of Fig. 13.89. Find the energy stored in the... Problem 21P Problem 22P: Find current Io in the circuit of Fig. 13.91. Problem 23P: Let is = 5 cos (100t) A. Calculate the voltage across the capacitor, vc. Also calculate the value of... Problem 24P: In the circuit of Fig. 13.93, (a) find the coupling coefficient, (b) calculate vo, (c) determine the... Problem 25P Problem 26P: Find Io in the circuit of Fig. 13.95. Switch the dot on the winding on the right and calculate Io... Problem 27P: Find the average power delivered to the 50- resistor in the circuit of Fig. 13.96. Problem 28P: In the circuit of Fig. 13.97, find the value of X that will give maximum power transfer to the 20-... Problem 29P Problem 30P: (a) Find the input impedance of the circuit in Fig. 13.99 using the concept of reflected impedance.... Problem 31P: Using Fig. 13.100, design a problem to help other students better understand linear transformers and... Problem 32P: Two linear transformers are cascaded as shown in Fig. 13.101. Show that... Problem 33P: Determine the input impedance of the air-core transformer circuit of Fig. 13.102. Figure 13.102 For... Problem 34P: Using Fig. 13.103, design a problem to help other students better understand how to find the input... Problem 35P: Find currents I1, I2, and I3 in the circuit of Fig. 13.104. Figure 13.104 For Prob. 13.35. Problem 36P: As done in Fig. 13.33, obtain the relationships between terminal voltages and currents for each of... Problem 37P: A 2402,400-V rms step-up ideal transformer delivers 50 kW to a resistive load. Calculate: (a) the... Problem 38P: Design a problem to help other students better understand ideal transformers. Problem 39P: A 1,200240-V rms transformer has impedance on the high-voltage side. If the transformer is connected... Problem 40P: The primary of an ideal transformer with a turns ratio of 5 is connected to a voltage source with... Problem 41P: Given I2 = 2 A, determine the value of Is in Fig. 13.106. Figure 13.106 For Prob. 13.41. Problem 42P: For the circuit in Fig. 13.107, determine the power absorbed by the 2- resistor. Assume the 120 V is... Problem 43P: Obtain V1 and V2 in the ideal transformer circuit of Fig. 13.108. Figure 13.108 For Prob. 13.43. Problem 44P: In the ideal transformer circuit of Fig. 13.109, find i1(t) and i2(t). Problem 45P: For the circuit in Fig. 13.110, find the value of the average power absorbed by the 8- resistor. Problem 46P: (a) Find I1 and I2 in the circuit of Fig. 13.111 below. (b) Switch the dot on one of the windings.... Problem 47P Problem 48P: Using Fig. 13.113, design a problem to help other students better understand how ideal transformers... Problem 49P: Find current ix in the ideal transformer circuit shown in Fig. 13.114. Problem 50P Problem 51P: Use the concept of reflected impedance to find the input impedance and current I1 in Fig. 13.116.... Problem 52P: For the circuit in Fig. 13.117, determine the turns ratio n that will cause maximum average power... Problem 53P: Refer to the network in Fig. 13.118. (a) Find n for maximum power supplied to the 200- load. (b)... Problem 54P: A transformer is used to match an amplifier with an 8- load as shown in Fig. 13.119. The Thevenin... Problem 55P: For the circuit in Fig. 13.120, calculate the equivalent resistance. Problem 56P: Find the power absorbed by the 100- resistor in the ideal transformer circuit of Fig. 13.121. Problem 57P: For the ideal transformer circuit of Fig. 13.122 below, find: (a) I1 and I2, (b) V1, V2, and Vo, (c)... Problem 58P: Determine the average power absorbed by each resistor in the circuit of Fig. 13.123. Problem 59P: In the circuit of Fig. 13.124, let vs = 165 sin(1,000t) V. Find the average power delivered to each... Problem 60P: Refer to the circuit in Fig. 13.125 on the following page. (a) Find currents I1, I2, and I3. (b)... Problem 61P: For the circuit in Fig. 13.126, find Il, I2, and Vo. Problem 62P: For the network in Fig. 13.127, find: (a) the complex power supplied by the source, (b) the average... Problem 63P: Find the mesh currents in th circuit of Fig. 13.128 Problem 64P: For the circuit in Fig. 13.129. find the turns ratio so that the maximum power is delivered to the... Problem 65P: Calculate the average power dissipated by the 20- resistor in Fig. 13.130. Problem 66P: Design a problem to help other students better understand how the ideal autotransformer works. Problem 67P: An autotransformer with a 40 percent tap is supplied by an 880-V, 60-Hz source and is used for... Problem 68P: In the ideal autotransformer of Fig. 13.131, calculate Il, I2, and Io. Find the average power... Problem 69P: In the circuit of Fig. 13.131, N1 = 190 turns and N2 = 10 turns. Determine the Thevenin equivalent... Problem 70P: In the ideal transformer circuit shown in Fig. 13.133, determine the average power delivered to the... Problem 71P: When individuals travel, their electrical appliances need to have converters to match the voltages... Problem 72P: In order to meet an emergency, three single-phase transformers with 12,4707,200 V rms are connected... Problem 73P: Figure 13.135 on the next page shows a three-phase transformer that supplies a Y-connected load. (a)... Problem 74P: Consider the three-phase transformer shown in Fig. 13.136. The primary is fed by a three-phase... Problem 75P: A balanced three-phase transformer bank with the -Y connection depicted in Fig. 13.137 is used to... Problem 76P: Using Fig. 13.138, design a problem to help other students better understand a Y-, three-phase... Problem 77P: The three-phase system of a town distributes power with a line voltage of 13.2 kV. A pole... Problem 78P: Use PSpice or MultiSim to determine the mesh currents in the circuit of Fig. 13.140. Take = 1... Problem 79P: Use PSpice or MultiSim to find I1, I2, and I3 in the circuit of Fig. 13.141. Problem 80P Problem 81P: Use PSpice or MultiSim to find I1, I2, and I3 in the circuit of Fig. 13.142. Problem 85P: A stereo amplifier circuit with ail output impedance of 7.2 k is to be matched to a speaker with an... Problem 86P: A transformer having 2,400 turns on the primary and 48 turns on the secondary is used as an... Problem 87P: A radio receiver has an input resistance of 300 . When it is connected directly to an antenna system... Problem 88P: A step-down power transformer with a turns ratio of n = 0.1 supplies 12.6 V rms to a resistive load.... Problem 89P: A 240120-V rms power transformer is rated at 10 kVA. Determine the turns ratio, the primary current,... Problem 90P: A 4-kVA, 2,400240-V rms transformer has 250 turns on the primary side. Calculate: (a) the turns... Problem 91P: A 25,000240-V rms distribution transformer has a primary current rating of 75 A. (a) Find the... Problem 92P: A 4,800-V rms transmission line feeds a distribution transformer with 1,200 turns on the primary and... Problem 93CP: A four-winding transformer (Fig. 13.146) is often used in equipment (e.g., PCs, VCRs) that may be... Problem 94CP: A 440/110-V ideal transformer can be connected to become a 550/440-V ideal autotransformer. There... Problem 95CP: Ten bulbs in parallel are supplied by a 7,200120-V transformer as shown in Fig. 13.147, where the... format_list_bulleted

 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,




