
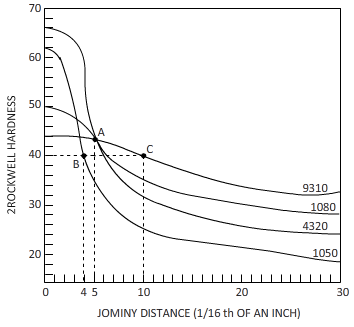
(a)
Interpretation:
The hardness of
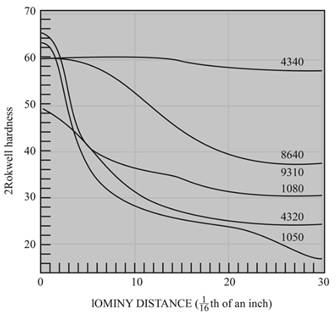
Figure
Concept Introduction:
Hardness is a material property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is a material property to resistance to twisting, scraping or cutting. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.33P
The hardness of
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
| Jominy distance | Cooling rate ( |
Calculations:
From the given diagram and table, the
(b)
Interpretation:
The cooling rate and distance to hardness of
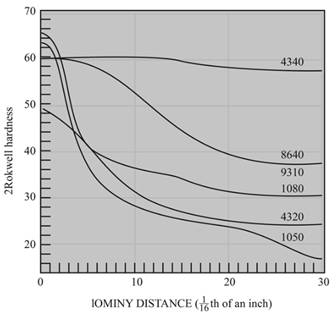
Figure
Concept Introduction:
Hardness is a material property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is a material property to resistance to twisting, scraping or cutting. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.33P
Hardness level ranges from
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
| Jominy distance | Cooling rate ( |
Calculations:
Figure
The equation byjominy is
By using the Jominy table, the cooling rate obtained is
(c)
Interpretation:
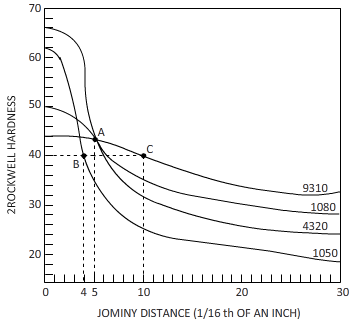
The cooling rate and distance to the hardness of
Figure
Concept Introduction:
Hardness is a material property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is a material property to resistance to twisting, scraping or cutting. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.33P
The distance to the hardness of
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
| Jominy distance | Cooling rate ( |
Calculations:
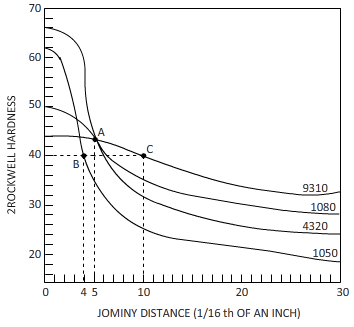
Figure
The equation byjominy is
By using the Jominy table, the cooling rate obtained is
(d)
Interpretation:
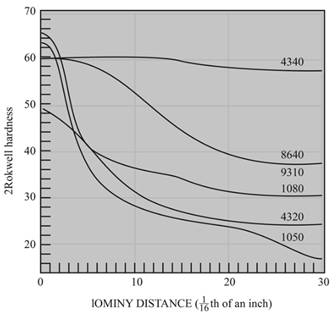
The cooling rate and distance tothehardness of
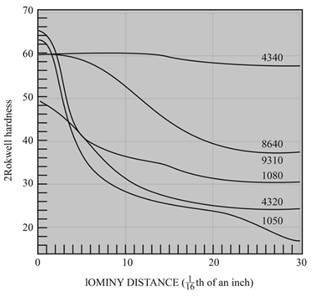
Figure
Concept Introduction:
Hardness is a material property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is a material property to resistance to twisting, scraping or cutting. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.33P
The distance to the hardness of
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
| Jominy distance | Cooling rate ( |
Calculations:
Figure
The equation byjominy is,
By using the Jominy table, the cooling rate obtained is
(e)
Interpretation:
The cooling rate and distance tothehardness of
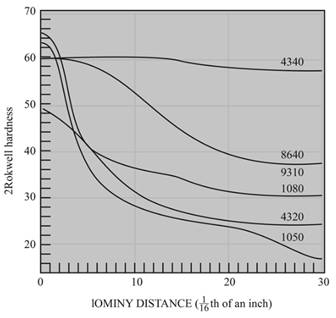
Figure
Concept Introduction:
Hardness is a material property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is a material property to resistance to twisting, scraping or cutting. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.33P
The distance to the hardness of
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
| Jominy distance | Cooling rate ( |
Calculations:
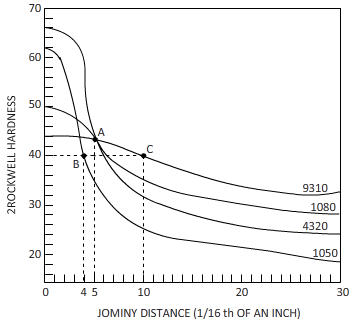
Figure
The equation byjominy is,
By using the Jominy table, the cooling rate obtained is
(f)
Interpretation:
The cooling rate and distance to hardness of
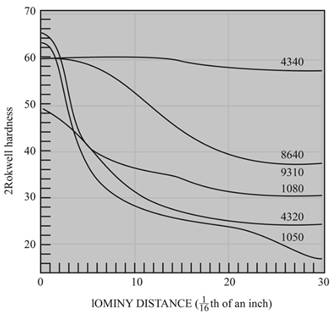
Figure
Concept Introduction:
Hardness is a material property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is a material property to resistance to twisting, scraping or cutting. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.33P
The distance tothehardness of
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
| Jominy distance | Cooling rate ( |
Calculations:
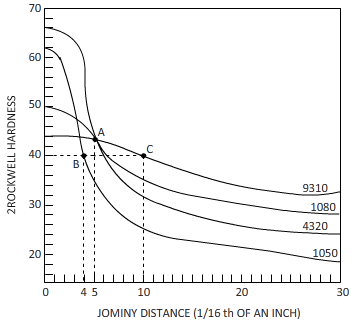
Figure
The equation byjominy is,
By using the Jominy table, the cooling rate obtained is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
- Q2- What are the parameters and loss that can be determined during open-circuit test of singlephase transformer. Draw the circuit diagram of open-circuit test and explain how can you calculate the Parameters and loss.arrow_forwardQ6- the open circuit and short circuit tests on a 10 KVA, 125/250 v, 50 Hz single phase transformer gave the following results: O.C. Test: 125 V,0.6 A, 50 W ( on L.V.) S.C. Test: 20 V, 40 A, 177.78 W (on H.V. side) Calculate: i) Copper losses on half load ii) Full load efficiency at 0.8 leading p.f. iii) Half load efficiency at 0.8 leading p.f. iv) Regulation at full load at 0.9 leading p.f. Ans: 44.445 W, 97.23%, 97.69%, -1.8015%arrow_forwardQ3-A two-winding transformer has a primary winding with 208 turns and a secondary winding with 6 turns. The primary winding is connected to a 4160V system. What is the secondary voltage at no load? What is the current in the primary winding with a 50-amp load connected to the secondary winding? What is the apparent power flowing in the primary and secondary circuits? Ans. 120 V, 1.44 A, 6000 VAarrow_forward
- Q12- A three phase transformer 3300/400 V,has D/Y connected and working on 50Hz. The line current on the primary side is 12A and secondary has a balanced load at 0.8 lagging p.f. Determine the i) Secondary phase voltage ii) Line current iii) Output power Ans. (230.95 V, 99.11 A, 54.94 kW)arrow_forwardQ1- A single phase transformer consumes 2 A on no load at p.f. 0.208 lagging. The turns ratio is 2/1 (step down). If the loads on the secondary is 25 A at a p.f. 0.866 lagging. Find the primary current and power factor.arrow_forwardQ5-The efficiency of a 200 KVA, single phase transformer is 98% when operating at full load 0.8 lagging p.f. the iron losses in the transformer is 2000 watt. Calculate the i) Full load copper losses ii) half load copper losses and efficiency at half load. Ans: 1265.306 watt, 97.186%arrow_forward
- Q7- A 5 KVA, 500/250 V,50 Hz, single phase transformer gave the following reading: O.C. Test: 250 V,2 A, 50 W (H.V. side open) S.C. Test: 25 V10 A, 60 W (L.V. side shorted) Determine: i) The efficiency on full load, 0.8 lagging p.f. ii) The voltage regulation on full load, 0.8 leading p.f. iii) Draw the equivalent circuit referred to primary and insert all the values it.arrow_forwardQ4- A single phase transformer has 350 primary and secondary 1050 turns. The primary is connected to 400 V,50 Hz a.c. supply. If the net cross sectional area of core is 50 cm2, calculate i) The maximum value of the flux density in the core. ii) The induced e.m.f in the secondary winding. Ans: 1.029 T, 1200Varrow_forwarddesign rectangular sections for the beam and loads, and p values shown. Beam weights are not included in the loads given. Show sketches of cross sections including bar sizes, arrangements, and spacing. Assume concrete weighs 23.5 kN/m'. fy= 420 MPa, and f’c= 21 MPa.Show the shear and moment diagrams as wellarrow_forward
- 4:13 Question • Imagine you have a friend who just finished reading the book "Johnny Chan" by Mitch Raycroft and really enjoyed it. Would "The Wager" by David Grann be a good recommendation for him? Great Recommendation Bad Recommendation In 3-5+ full sentences, please describe why this may or may not be a good recommendation. (The more detailed and well-reasoned explanation you write, the better, since we prioritize high-quality writing.) Oli bartleby.com 1arrow_forward25 mm Brass core E = 105 GPa 0 = 20.9 x 10 °C PROBLEM 2.49 The aluminum shell is fully bonded to the brass core and the assembly is unstressed at a temperature of 15°C. Considering only axial deformations, determine the stress in the aluminum when the temperature reaches 195°C. 60 mm Aluminum shell E = 70 GPa a = 23.6 × 10°Carrow_forwardGiven the following addresses, which two addresses conflict in the cache: The numb of locations in the cache is 2048, the cahche is indexed by address bits 15 to 5 and the tag bits are from 31 to 16. (a) 0x0000 0100 (b) 0x0000 1400 (c) 0x0010 0100 (d) 0x0100 0140arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





