
(a)
Interpretation:
The heat treatment for
Concept Introduction:
Material hardness is the property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is the property of any material due to which it resist to bend, scratch or any other deformation. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.16P
Heating to
Explanation of Solution
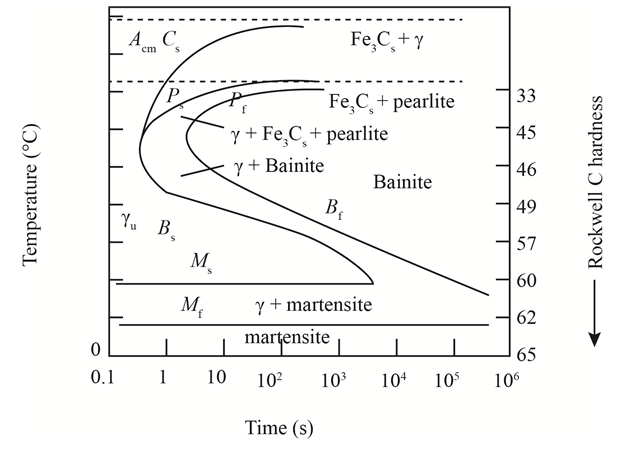
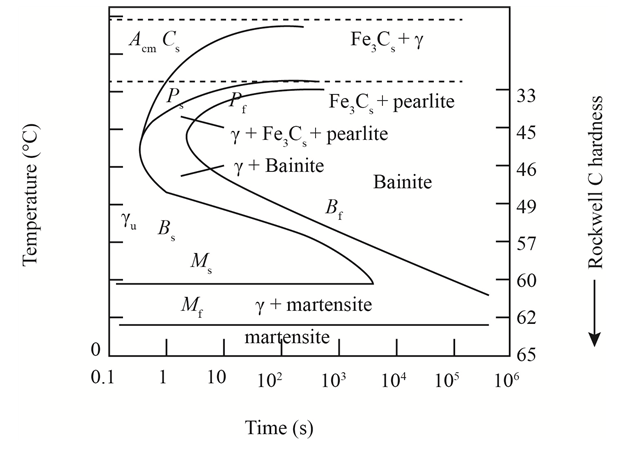
The given diagram is a TTT diagram which gases a relation between composition and temperature with time.
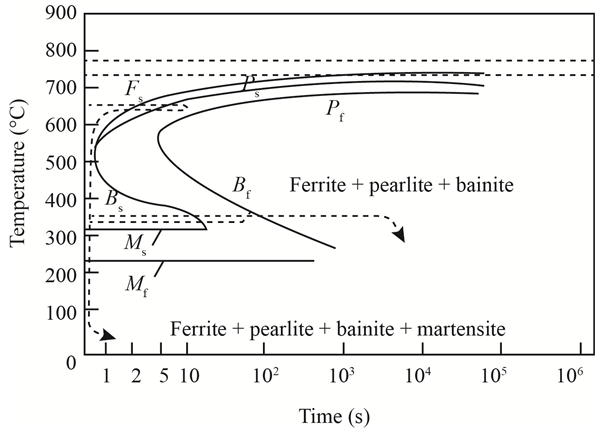
The given image shows temperature and time for ferrite, pearlite, bainite, and martensite following are the steps to obtain appropriate isothermal heat treatment.
For isothermally annealed
1) Step1: Heat the steel to
2) Step2: Quench it to
3) Step3: Quench again it to
(b)
Interpretation:
The heat treatment for
Concept Introduction:
Material hardness is the property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is the property of any material due to which it resist to bend, scratch or any other deformation. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.16P
Heating to
Explanation of Solution
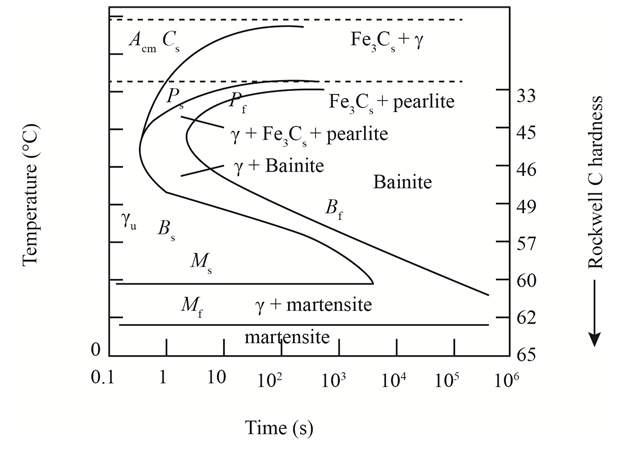
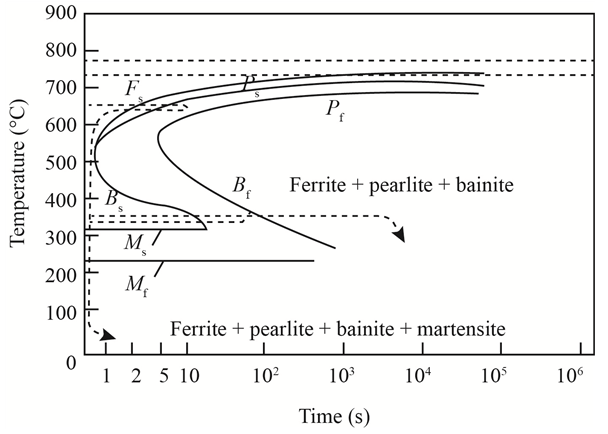
The given diagram is a TTT diagram which gases a relation between composition and temperature with time.
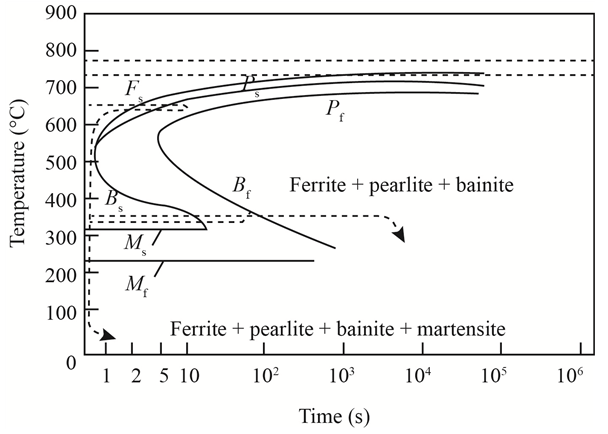
The given image shows temperature and time for ferrite, pearlite, bainite, and martensite following are the steps to obtain appropriate isothermal heat treatment.
For isothermally annealed
1) Step1: Heat the steel to
2) Step2: Quench it to yy
3) Step3: Quench again it toyyy
(c)
Interpretation:
The heat treatment for yyyyy
Concept Introduction:
Material hardness is the property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is the property of any material due to which it resist to bend, scratch or any other deformation. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.16P
Heating to
Explanation of Solution
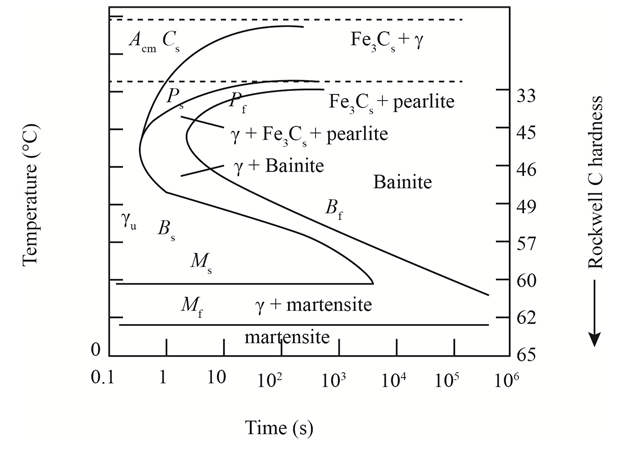
The given diagram is a TTT diagram which gases a relation between composition and temperature with time.
The given image shows temperature and time for ferrite, pearlite, bainite, and martensite following are the steps to obtain appropriate isothermal heat treatment.
For isothermally annealed
1) Step1: Heat the steel to
2) Step2: Quench it to
3) Step3: Quench again it to
(d)
Interpretation:
The heat treatment for
Concept Introduction:
Material hardness is the property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is the property of any material due to which it resist to bend, scratch or any other deformation. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.16P
Heating to
Explanation of Solution
The given diagram is a TTT diagram which gases a relation between composition and temperature with time.
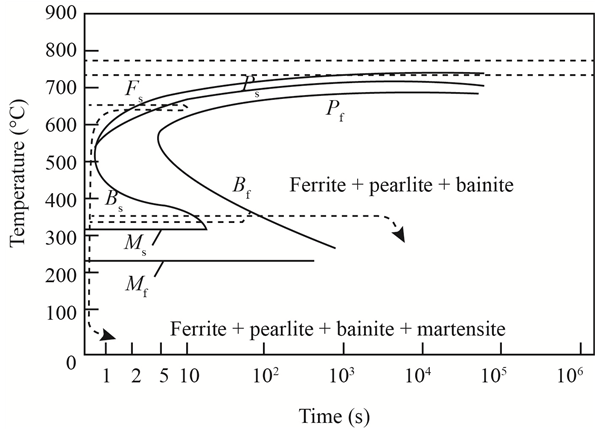
The given image shows temperature and time for ferrite, pearlite, bainite, and martensite following are the steps to obtain appropriate isothermal heat treatment.
For isothermally annealed 1050 steel with HRC 40 is:-
1) Step1: Heat the steel to
2) Step2: Quench it to
3) Step3: Quench again it to
(e)
Interpretation:
The heat treatment for
Concept Introduction:
Material hardness is the property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is the property of any material due to which it resist to bend, scratch or any other deformation. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.16P
Heating to
Explanation of Solution
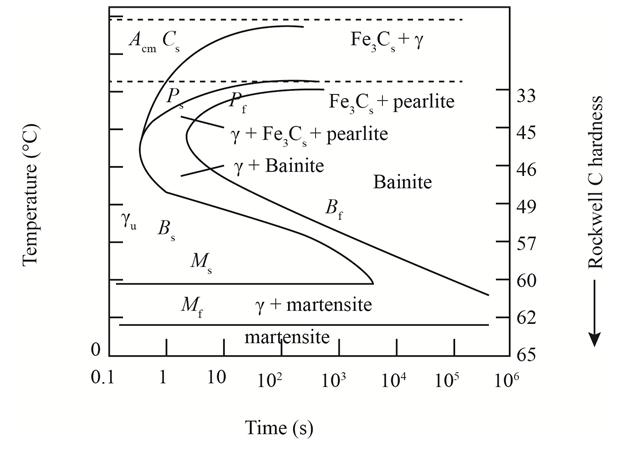
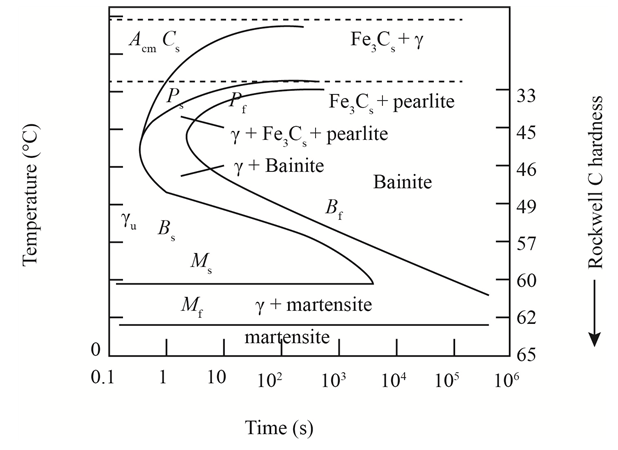
The given diagram is a TTT diagram which gases a relation between composition and temperature with time.
The given image shows temperature and time for ferrite, pearlite, bainite, and martensite following are the steps to obtain appropriate isothermal heat treatment.
For isothermally annealed 10110 steel with HRC 55is:-
1) Step1: Heat the steel to
2) Step2: Quench it to
3) Step3: Quench again it to
(f)
Interpretation:
The heat treatment for
Concept Introduction:
Material hardness is the property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic reformation. Plastic reformation means material reformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is the property of any material due to which it resist to bend, scratch or any other deformation. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal, material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 13.16P
Heating to
Explanation of Solution
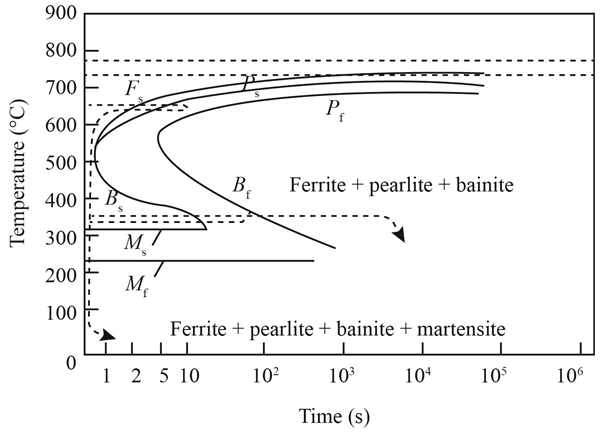
The given diagram is a TTT diagram which gases a relation between composition and temperature with time.
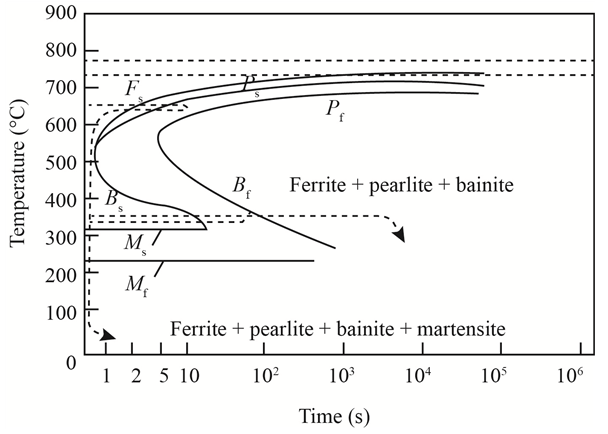
The given image shows temperature and time for ferrite, pearlite, bainite, and martensite following are the steps to obtain appropriate isothermal heat treatment.
For isothermally annealed
1) Step1: Heat the steel to
2) Step2: Quench it to
3) Step3: Quench again it to
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
- the answer should be: V2= -(P0-PL/2μL)(dx-x^)+Ux/darrow_forwardFor some viscoelastic polymers that are subjected to stress relaxation tests, the stress decays with time according to a(t) = a(0) exp(-4) (15.10) where σ(t) and o(0) represent the time-dependent and initial (i.e., time = 0) stresses, respectively, and t and T denote elapsed time and the relaxation time, respectively; T is a time-independent constant characteristic of the material. A specimen of a viscoelastic polymer whose stress relaxation obeys Equation 15.10 was suddenly pulled in tension to a measured strain of 0.5; the stress necessary to maintain this constant strain was measured as a function of time. Determine E (10) for this material if the initial stress level was 3.5 MPa (500 psi), which dropped to 0.5 MPa (70 psi) after 30 s.arrow_forward1. Consider the following a unity feedback control system. R(s) + E(s) 500(s+2)(s+5)(s+6) s(s+8)(s+10)(s+12) -Y(s) Find the followings: a) Type of the system b) Static position error constant Kp, Static velocity error constant Ry and Static acceleration error constant Ka c) Find the steady-state error of the system for (i) step input 1(t), (ii) ramp input t 1(t), (iii) parabolic input t² 1(t). 2. Repeat the above problem for the following system. R(s) + E(s) 500(s + 2)(s + 5) (s+8)(s+ 10)(s+12) Y(s) 3. Repeat the above problem for the following system. R(s) + E(s) 500(s+2)(s+4)(s+5)(s+6)(s+7) s²(s+8)(s+10)(s+12) Y(s)arrow_forward
- For the flows in Examples 11.1 and 11.2, calculate the magnitudes of the Δ V2 / 2 terms omitted in B.E., and compare these with the magnitude of the ℱ terms.arrow_forward4. Consider a unity (negative) feedback control system whose open-loop transfer function is given by the following. 2 G(s) = s³ (s + 2) Find the steady-state error of the system for each of the following inputs. = a) u(t) (t²+8t+5) 1(t) b) u(t) = 3t³ 1(t) c) u(t) (t+5t² - 1) 1(t) =arrow_forward1 2. For the following closed-loop system, G(s) = and H(s) = ½ (s+4)(s+6) a. Please draw the root locus by hand and mark the root locus with arrows. Calculate the origin and angle for asymptotes. b. Use Matlab to draw the root locus to verify your sketch. Input R(s) Output C(s) KG(s) H(s)arrow_forward
- 5. Consider following feedback system. R(s) + 100 S+4 +1 Find the steady-state error for (i) step input and (ii) ramp input.arrow_forward6. Find (i) settling time (Ts), (ii) rise time (Tr), (iii) peak time (Tp), and (iv) percent overshoot (% OS) for each of the following systems whose transfer functions are given by: a) H(s) = 5 s²+12s+20 5 b) H(s) = s²+6s+25 c) H(s) = (s+2) (s²+12s+20) (s²+4s+13) Use dominant pole approximation if needed.arrow_forwardCalculate ℛP.M. in Example 11.2.arrow_forward
- For spherical sand particles with Dp = 0.03 and ρparticles = 150 lbm / ft3 estimate the minimum fluidizing velocity for air and for water. Assume ε = 0.3. In the case of the water we must rederive Eq. 11.42, taking into account the buoyant force on the particles. Below are the provide answers. Please show all work to get to the correct answers.arrow_forward7. Answer the following questions. Take help from ChatGPT to answer these questions (if you need). But write the answers briefly using your own words with no more than two sentences and make sure you check whether ChatGPT is giving you the appropriate answers in the context of class. a) Why do we need transient performance metrics? Name a few of such metrics. b) Define (i) settling time, (ii) rise time, (iii) peak time and (iv) percent overshoot. c) What is damping ratio? How does overshoot change with the change of damping ratio? When do we have zero overshoot? d) What is the criterion for selecting dominant pole in higher order systems? When dominant pole approximation is not valid? How will you calculate the transient performance metrics for the case when dominant pole approximation does not hold?arrow_forwardCan you help me with this problemarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





