
(a)
Interpretation:
The microstructure present in
Concept Introduction:
Heat treatment is a process used to change the material's physical and chemical properties. Metallurgical is the most frequent applications. Heat treatment is used in the production of many products such as glass. Heat treatment includes heating or cooling to achieve the required outcome, usually at extreme temperatures.
Answer to Problem 13.14P
The microstructure that is present after going through the various processes, is ferrite and pearlite.
Explanation of Solution
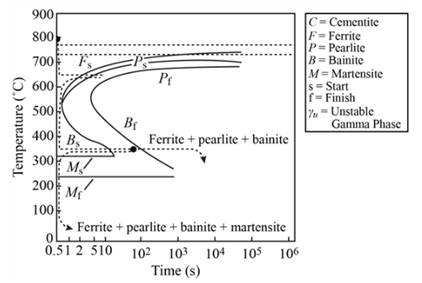
When
(b)
Interpretation:
The microstructure present in steel heated at
Concept Introduction:
Heat treatment is a process used to change the material'sphysical and chemical properties. Metallurgical is the most frequent applications. Heat treatment is used in the production of many products such as glass. Heat treatment includes heating or cooling to achieve the required outcome, usually at extreme temperatures.
Answer to Problem 13.14P
Bainite remains as microstructure after going through the heating and quenching process.
Explanation of Solution
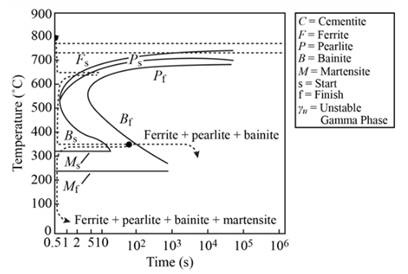
When
Thus, bainite microstructure remains after going through heating and quenching.
(c)
Interpretation:
The microstructure present in steel after being heated at
Concept Introduction:
Heat treatment is a process used to change the material's physical and chemical properties. Metallurgical is the most frequent applications. Heat treatment is used in the production of many products such as glass. Heat treatment includes heating or cooling to achieve the required outcome, usually at extreme temperatures.
Answer to Problem 13.14P
Martensite remains as microstructure after heated at
Explanation of Solution
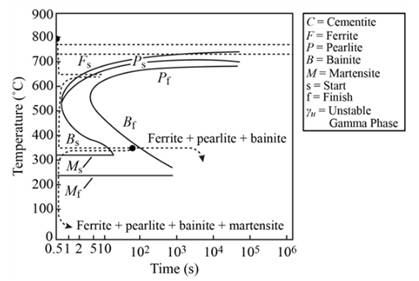
When
(d)
Interpretation:
The microstructure present in
Concept Introduction:
Heat treatment is a process used to change the materials physical and chemical properties. Metallurgical is the most frequent applications. Heat treatment is used in the production of many other products such as glass. Heat treatment includes heating or cooling to achieve the required outcome, usually at extreme temperatures.
Answer to Problem 13.14P
Ferrite and martensite remain as microstructure after heated at
Explanation of Solution
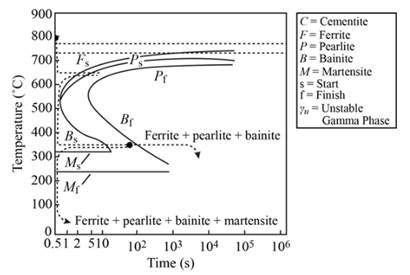
When
(e)
Interpretation:
The microstructure present in
Concept Introduction:
Heat treatment is a process used to change the material's physical and chemical properties. Metallurgical is the most frequent applications. Heat treatment is used in the production of many products such as glass. Heat treatment includes heating or cooling to achieve the required outcome, usually at extreme temperatures.
Answer to Problem 13.14P
Ferrite and bainite remain as microstructure.
Explanation of Solution
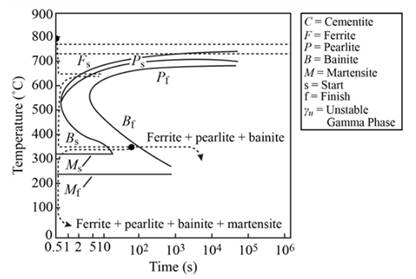
When the
(f)
Interpretation:
The microstructure present in
Concept Introduction:
Heat treatment is a process used to change the material's physical and chemical properties. Metallurgical is the most frequent applications. Heat treatment is used in the production of many products such as glass. Heat treatment includes heating or cooling to achieve the required outcome, usually at extreme temperatures.
Answer to Problem 13.14P
Ferrite, bainite, and martensite remain as microstructure.
Explanation of Solution
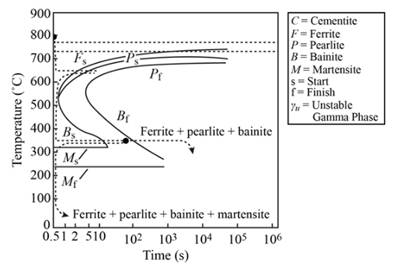
When
(g)
Interpretation:
The microstructure in
Concept Introduction:
Heat treatment is a process used to change the material's physical and chemical properties. Metallurgical is the most frequent applications. Heat treatment is used in the production of many products such as glass. Heat treatment includes heating or cooling to achieve the required outcome, usually at extreme temperatures.
Answer to Problem 13.14P
Tempered martensite is the only microstructures that remain in
Explanation of Solution
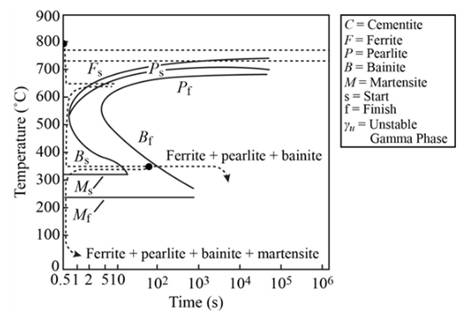
When
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering, SI Edition
- For tixed inlet state and exit pressure, use a cold-air standard analysis to show that the pressure ratio across the two compressor stages that gives nunimum work input is:=)) k/(k-1) when Ta Ti, where Ta is the temperature of the air entering the second stage compressor and Pi is the intercooler pressure. Put the suitable assumptionsarrow_forwardb) The joint probability function for the random variables X and Y is given in Table below. Find a) the marginal probability function of X and Y. P(Y/X) and P(X/Y). c) P(X ≥ 2, Y ≤ 2) y 1 2 3 10.05 0.05 0.1 P(X, Y) = X 20.05 0.1 0.35 3 0 0.2 0.1arrow_forwardHow can construction project managers find a balance between speeding up schedules and the risks of making more mistakes and needing rework, especially when using methods like fast tracking?arrow_forward
- Derive the equation below ah ap ax 12μ ax, +( ah ap ay 12μ ay Where P P (x, y) is the oil film pressure. 1..ah 2 axarrow_forwardWord File Edit View Insert Format Tools Table Window Help PEPSI AutoSave 5-Marca, Christopher Read-Only Compatibility Mode - Saved to my Mac Insert Draw Design Layout References Mailings Review View Picture Format X Aptos (Body) ▾ 10 A A Aa Po BIU x, x A DA EvE E1INT AaBbCcl Pleading 2 Lalacoder AaBbCcl AalibGDdEe AaBbCcDr Abde ABC Normal Title No Spacing Heading 3 Heading 3 Subtitie Suble B d Only To save a copy of this document, click Duplicate. Problem 10) For the Boolean.expression, which is the correct MSOP expression? I Y = wxyz+xy+w Expression A. I Y = wxyz+y 663 words Expression B. English (United States) Accessibility: Investigate A APR LO M O stv Iarrow_forwardCan you determine the eignevalues by hand?arrow_forward
- Monthly exam 13 2021-2022 Power plant Time: 1.5 Hrs Q1. A The gas-turbine cycle shown in Fig. is used as an automotive engine. In the first turbine, the gas expands to pressure Ps, just low enough for this turbine to drive the compressor. The gas is then expanded through the second turbine connected to the drive wheels. The data for the engine are shown in the figure, and assume that all processes are ideal. Determine the intermediate pressure Ps, the net specific work output of the engine, and the mass flow rate through the engine. Find also the air temperature entering the burner T3 and the thermal efficiency of the engine. Exhaust Air intake Φ www Regenerator www Bumer Compressor Turbine Power turbine et 150 kW Wompressor P₁ = 100 kPa T₁ = 300 K PP₁ =60 P-100 kPa T₁ = 1600 K Q2. On the basis of a cold air-standard analysis, show that the thermal efficiency of an ideal regenerative gas turbine can be expressed as 77 = 1- where - () () гp is the compressor pressure ratio, and T₁ and…arrow_forwardI need to find m in R = mD from the image given. Do you really need to know what R and D is to find R. I was thinking geometrically we can find a relationship between R and D. D = R*cos(30). Then R = mD becomes m = R/D = 1/cos(30) = 1.1547. Is that correct?arrow_forwardQ1] B/ (16 Marks) To produce a lightweight epoxy part to provide thermal insulation. The available material are hollow glass beads for which the outside diameter is 1.6 mm and the wall thickness is 0.04 mm. Determine the weight and number of beads that must be added to the epoxy to produce a 0.5 kg of composite with a density of 0.65 g/cm³. The density of the glass is 2.5 g/cm³ and that of the epoxy is 1.25 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- Suppose a random variable X as pmf / Px (x) = { %, x = 1, 2, 3, 0, otherwise. find constand c ①P(X = 1), P(X 7,2), PC1 3) C CDFarrow_forwardGiven the following request to an AI chatbot, which response is better? Prompt Write a love poem about someone longing for a sandwich. Make it a sonnet, and give it a tone that straddles a serious love poem and whimsy appropriate for a poem about a sandwich.arrow_forwardHelp i keep getting the wrong answer. So I must be doing something wrong.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





