
Interpretation:
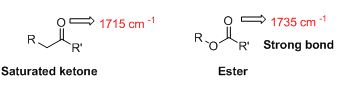
The strongest bond has to be identified from C=O bond in an ester (1735 cm-1) or the C=O bond in a saturated
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy:
It is study of the interaction of matter and
IR frequency (cm-1):
It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations:
It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations:
It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Given information:
The IR value is given below,
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Beer’s Law is A = εbc, where A is absorbance, ε is the molar absorptivity (which is specific to the compound and wavelength in the measurement), and c is concentration. The absorbance of a 2.31 × 10-5 M solution of a compound is 0.822 at a wavelength of 266 nm in a 1.00-cm cell. Calculate the molar absorptivity at 266 nm.arrow_forwardHow to calculate % of unknown solution using line of best fit y=0.1227x + 0.0292 (y=2.244)arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, state the (condensed) formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forward
- Complete the following acid-base reactions and predict the direction of equilibrium for each. Justify your prediction by citing pK values for the acid and conjugate acid in each equilibrium. (a) (b) NHs (c) O₂N NH NH OH H₁PO₁arrow_forward23.34 Show how to convert each starting material into isobutylamine in good yield. ཅ ནད ཀྱི (b) Br OEt (c) (d) (e) (f) Harrow_forwardPlease help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forward
- Propose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forwardSelect the stronger base from each pair of compounds. (a) H₂CNH₂ or EtzN (b) CI or NH2 NH2 (c) .Q or EtzN (d) or (e) N or (f) H or Harrow_forward4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for each of the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. 2. 1. LDA 3. H3O+ HOarrow_forward
- b. H3C CH3 H3O+ ✓ H OHarrow_forward2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward

 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


