
Concept explainers
At what approximate positions might the following compounds show IR absorptions?
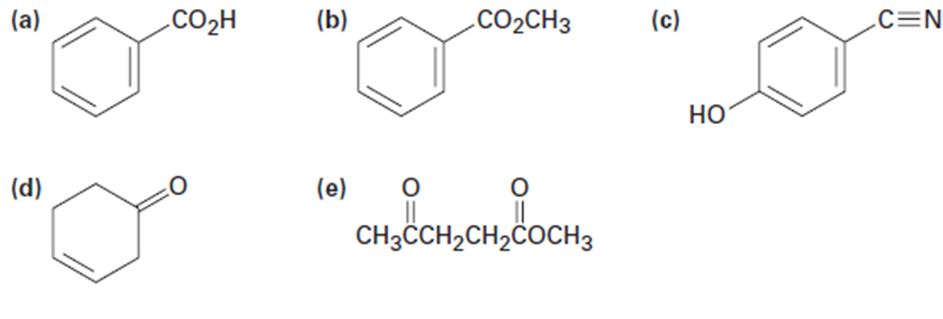
a)
Interpretation:
The approximate absorption frequency has to be given for compound.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 1710-1760 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 2500-3100 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
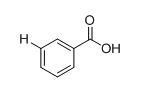
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 1710-1760 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 2500-3100 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
The approximate absorption frequency is given for compound.
b)
Interpretation:
The approximate absorption frequency has to be given for compound.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 1710-1760 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 2500-3100 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
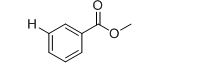
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 1710-1760 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 2500-3100 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
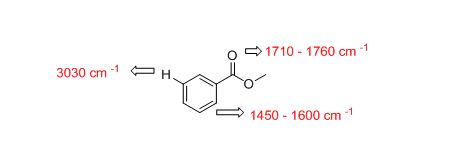
The difference between given pairs of isomers is explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
c)
Interpretation:
The difference between given pairs of isomer has to be explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 2210-2260 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 3400-3650 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 2210-2260 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 3400-3650 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
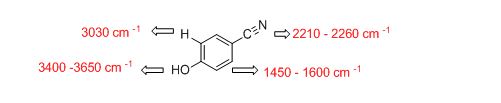
The difference between given pairs of isomers is explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
d)
Interpretation:
The difference between given pairs of isomer has to be explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
The IR absorptions values at 1640-1680 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3020-3100 cm-1 is for vinylic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency and 1715 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
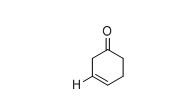
The IR absorptions values at 1640-1680 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3020-3100 cm-1 is for vinylic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency and 1715 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
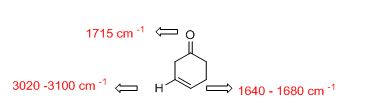
The difference between given pairs of isomers is explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
e)
Interpretation:
The difference between given pairs of isomer has to be explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
The IR absorptions values at 1715 cm-1 is for carbonyl (ketone) stretching frequency and 1735 cm-1 is for carbonyl ester frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
The IR absorptions values at 1715 cm-1 is for carbonyl (ketone) stretching frequency and 1735 cm-1 is for carbonyl ester frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
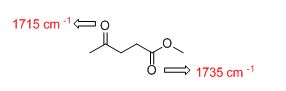
The difference between given pairs of isomers is explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 5.arrow_forward9arrow_forwardalekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward
- 0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forwardx + LEKS: Using a phase diagram a X n/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/10_u-IgNsikr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpw ○ States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.1 atm. pressure (atm) 16 08- solid liquid- 0 200 400 gas 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 25 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. × 5arrow_forwardS: Using a phase diagram leksogi/x/sl.exe/1ou-IgNs kr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZdHYU+80XL-5alyVp O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure se the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the boiling point of X when the pressure on the liquid is 1.6 atm. pressure (atm) 32- 16- solid liquid 0. gas 100 200 temperature (K) 300 Note: your answer must be within 12.5 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. 10 Explanation Check § Q Search J 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Researrow_forward
- 151.2 254.8 85.9 199.6 241.4 87.6 242.5 186.4 155.8 257.1 242.9 253.3 256.0 216.6 108.7 239.0 149.7 236.4 152.1 222.7 148.7 278.2 268.7 234.4 262.7 283.2 143.6 QUESTION: Using this group of data on salt reduced tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardResults Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unloc xb Success Confirmation of Q x O Google Pas alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCavJ17dZtpxbFD0Qggd1J O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Gabr 3/5 he pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at 101. °C is lowered. At what pressure will the sample sublime? Use the phase diagram of X below to nd your answer. pressure (atm) 24- 12 solid liquid gas 200 400 temperature (K) 600 ote: your answer must be within 0.15 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. atm Thanation Check © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center I Q Search L³ ملةarrow_forward301.7 348.9 193.7 308.6 339.5 160.6 337.7 464.7 223.5 370.5 326.6 327.5 336.1 317.9 203.8 329.8 221.9 331.7 211.7 309.6 223.4 353.7 334.6 305.6 340.0 304.3 244.7 QUESTION: Using this group of data on regular tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forward
- Search Results Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unlo x b Success Confirmation of Q aleks.com/alekscgi/x/sl.exe/10_u-lgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTIOHz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCav States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the temperature at which X turns to a gas, if the pressure above the solid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 0. 32- 16 solid liquid gas 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. Дос Xarrow_forwardConsider the reaction below to answer the following questions: Acetoacetic ester can be prepared by the Claisen self-condensation reaction of ethyl acetate. 1. NaOEt, EtOH H&C OCH CH3 2 H30 H3C CH2 OCH2CH3 A. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures. B. Ethyl acetate can be prepared from ethanol as the only organic starting material. Show all reagents and structures for all intermediates in this preparation. C. Give the structures of the ester precursors for the following Claisen condensation product and formulate the reaction. OEtarrow_forwardUse the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the temperature at which X turns to a gas, if the pressure above the solid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 32 16 solid liquid gas 0 0 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. Шос ☑ كarrow_forward

 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


