
Concept explainers
a.
Toinvestigate : Right and oblique cylinders.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given information : To draw right cylinder and oblique cylinder with a height of
Graph :
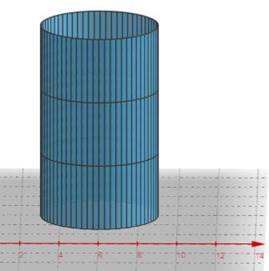 Fig. 1: Right Cylinder
Fig. 1: Right Cylinder
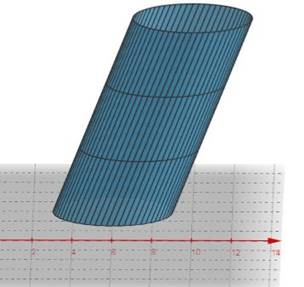 Fig. 2: Oblique Cylinder
Fig. 2: Oblique Cylinder
Interpretation : The sides of the oblique cylinder are not perpendicular to the base. While the sides of the right cylinder are perpendicular to the base.
b.
Tofind: If the volume of the square prism is less than, greater than, or equal to the volume of the cylinder.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Given information : Square prism with a height of
Formula used : The volume of the square prism is
Calculation : Calculate the volume of each shape.
Interpretation : The volume of the square prism is greater than the volume of the cylinder.
c.
To explain: the change which affects the volume of the cylinder more: multiplying the height by x or multiplying the radius by x .
c.
Explanation of Solution
The volume of a cylinder is
If we multiply by height by x , the volume becomes
And, if we multiply the radius by x, the volume becomes
We can see
So, the volume of the cylinder will be more, if we multiply the radius by x .
Chapter 12 Solutions
Geometry, Student Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- If AB = 10 and AC = 13, what is AD? B A D C Write your answer as a whole number or as a decimal rounded to the nearest hundredth.arrow_forwardHeight = 1 Width=1 How much is the shaded area in the chart above?arrow_forwardLauris Online Back to Subject 不 4 ப 12 2 points T 35° 25° R M 4 N P 6Q 5 What is m/MNT? 120 T 12 What is the length of MR? 120 units 167:02:04 Time Remaining Yama is designing a company logo. The company president requested for the logo to be made of triangles. Yama is proposing the design shown. C 64°F Clear Q Search L 13 Ide dia des You scre Edi 12 L Tarrow_forward
- Classwork for Geometry 1st X S Savvas Realize * MARYIA DASHUTSINA-Ba → CA savvasrealize.com/dashboard/classes/49ec9fc00d8f48ec9a4b05b30c9ee0ba A > SIS © = =Wauconda Middle S... 31 WMS 8th Grade Tea... SIS Grades and Attenda.... esc GEOMETRY 1ST < Study Guide T6 K 18 L 63° 9 N M Quadrilateral JKLM is a parallelogram. What is the m ZKJN? mZKJN = Review Progress acerarrow_forwardWhy is this proof incorrect? State what statement and/or reason is incorrect and why. Given: Overline OR is congruent to overline OQ, angle N is congruent to angle PProve: Angle 3 is congruent to angle 5 Why is this proof incorrect? Statements Reasons 1. Overline OR is congruent to overline OQ, angle N is congruent to angle P 1. Given 2. Overline ON is congruent to overline OP 2. Converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem 3. Triangle ONR is congruent to triangle OPQ 3. SAS 4. Angle 3 is congruent to angle 5 4. CPCTCarrow_forwardGiven: AABE ~ ACDE. Prove: AC bisects BD. Note: quadrilateral properties are not permitted in this proof. Step Statement Reason AABE ACDE Given 2 ZDEC ZAEB Vertical angles are congruent try Type of Statement A E B D Carrow_forward
- 2) Based on the given information and the diagram, a. Which congruence statements can be proven? Select all that apply.Given: Overline OR is congruent to overline OQ, angle N is congruent to angle PProve: angle 3 is congruent to angle 5A. Overline ON is congruent to overline OPB. Angle 1 is congruent to angle 2C. Overline ON is congruent to overline OR and overline OP is congruent to overine OQD. angle 1 is congruent to angle 3 and angle 2 is congruent to angle 5There are more than one correct answerarrow_forwardnt/Ray Skew Lines/ J K # H L 艹 G C D E F Diagrams m Three Points th a Protractor Answer Attempt 3 out of 3 el 1 is congruent to Submit Answer 103 Log Out REE Young the → C # $arrow_forward4:54 PM Thu Jan 16 cdn.assess.prod.mheducation.com Question 3 The angle bisectors of APQR are PZ, QZ, and RZ. They meet at a single point Z. (In other words, Z is the incenter of APQR.) Suppose YZ = 22, QZ = 23, mz WPY 38°, and mzXQZ = 54°. Find the following measures. Note that the figure is not drawn to scale. P W Z X R Y mzXQW WZ = = 0 mz XRZ = 0°arrow_forward
- Ja дх dx dx Q3: Define the linear functional J: H()-R by تاریخ (v) = ½a(v, v) - (v) == Let u be the unique weak solution to a(u,v) = L(v) in H₁(2) and suppose that a(...) is a symmetric bilinear form on H() prove that a Buy v) = 1- u is minimizer. 2- u is unique. 3- The minimizer J(u,) can be rewritten under J(u)=u' Au-ub, algebraic form Where A, b are repictively the stiffence matrix and the load vector Q4: A) Answer only 1-show that thelation to -Auf in N, u = 0 on a satisfies the stability Vulf and show that V(u-u,)||² = ||vu||2 - ||vu||2 lu-ulls Chu||2 2- Prove that Where =1 ||ul|= a(u, u) = Vu. Vu dx + fu. uds B) Consider the bilinear form a(u, v) = (Au, Av) + (Vu, Vv) + (Vu, v) + (u, v) Show that a(u, v) continues and V- elliptic on H(2) (3) (0.0), (3.0)arrow_forwardQ1: A) fill the following: 1- The number of triangular in a triangular region with 5 nodes is quadrilateral with n=5 and m=6 nodés is 2- The complex shape function in 1-D 3- dim(P4(K))=- (7M --- and in the and multiplex shape function in 2-D is 4- The trial space and test space for problem -Auf, u = go on and B) Define the energy norm and prove that the solution u, defined by Galerkin orthogonal satisfies the best approximation. Q2: A) Find the varitional form for the problem 1330 (b(x)) - x²=0, 0arrow_forwardcould you help?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

