
EBK CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST
3rd Edition
ISBN: 8220103675505
Author: Burdge
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.2, Problem 1PPC
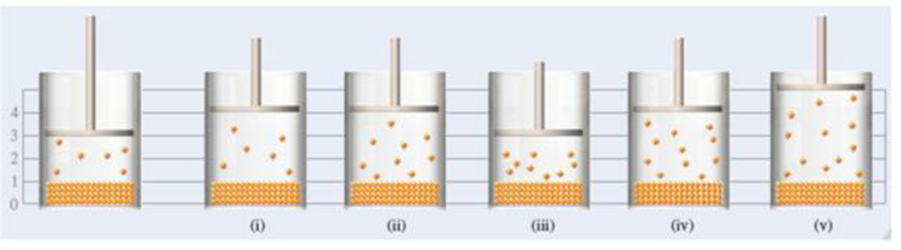
The diagram on the left depicts a system at room temperature. (The space above the liquid contains air and the vapor of the liquid in the container, and is sealed with a movable piston, making the pressure inside the vessel equal to atmospheric pressure.) Which of the diagrams [(i)–(v)] could represent the same system at a higher temperature?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Show work. Don't give Ai generated solution
In the video, we looked at the absorbance of a certain substance and how it varies
depending on what wavelength of light we are looking at. Below is a similar scan of a
different substance. What color BEST describes how this substance will appear?
Absorbance (AU)
Violet
Blue
Green
Orange
1.2
1.0-
0.8-
0.6-
0.4-
0.2
0.0
450
500
550
600
650
700
Wavelength (nm)
violet
indigo
blue
green
yellow orange
red
Red
O Cannot tell from this information
In the above graph, what causes -450 nm wavelength of light to have a higher
absorbance than light with a -550 nm wavelength? Check all that are true.
The distance the light travels is different
The different data points are for different substances
The concentration is different at different times in the experiment
Epsilon (molar absortivity) is different at different wavelengths
5. a. Data were collected for Trial 1 to determine the molar mass of a nonvolatile solid solute when dissolved in cyclo-
hexane. Complete the table for the analysis (See Report Sheet). Record calculated values with the correct number
of significant figures.
B. Freezing Point of Cyclohexane plus
Calculation Zone
Unknown Solute
2. Mass of cyclohexane (g)
10.14
Part C.4
3. Mass of added solute (g)
0.255
C. Calculations
1. k; for cyclohexane (°C⚫ kg/mol)
20.0
2. Freezing point change, AT, (°C)
3.04
Part C.6
3. Mass of cyclohexane in solution (kg)
4. Moles of solute, total (mol)
Show calculation.
5. Mass of solute in solution, total (g)
6. Molar mass of solute (g/mol)
Show calculation.
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST
Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.1WECh. 12.2 - Prob. 1PPACh. 12.2 - Prob. 1PPBCh. 12.2 - The diagram on the left depicts a system at room...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.2.1SRCh. 12.2 - Given the following information for C6F6,...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.2.3SRCh. 12.2 - Using the result from question 12.2.3 and another...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.2WECh. 12.3 - When silver crystallizes, it forms face-centered...
Ch. 12.3 - The density of sodium metal is 0.971 g/cm3 and the...Ch. 12.3 - Nickel has a face-centered cubic unit cell with an...Ch. 12.3 - A metal crystallizes in a body-centered cubic unit...Ch. 12.4 - How many of each ion are contained within a unit...Ch. 12.4 - Referring to Figure 12.23, determine how many of...Ch. 12.4 - Referring to Figure 12.23, determine how many of...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 3PPCCh. 12.4 - The edge length of the NaCl unit cell is 564 pm....Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 4PPACh. 12.4 - NiO also adopts the face-centered cubic...Ch. 12.4 - The metal iridium (Ir) crystallizes with a...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 5PPACh. 12.4 - Copper crystallizes in a face-centered cubic...Ch. 12.4 - Given that the diameter and average mass of a...Ch. 12.5 - (a) Calculate the amount of heat deposited oil the...Ch. 12.5 - Calculate the amount of energy (in kilojoules)...Ch. 12.5 - Determine the final state and temperature of 100 g...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 6PPCCh. 12.5 - How much energy (in kilojoules) is required to...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.5.2SRCh. 12.6 - Using the following phase diagram, (a) determine...Ch. 12.6 - Use the following phase diagram to (a) determine...Ch. 12.6 - Prob. 7PPBCh. 12.6 - Prob. 7PPCCh. 12.6 - Prob. 12.6.1SRCh. 12.6 - Prob. 12.6.2SRCh. 12 - Prob. 12.1KSPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.2KSPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.3KSPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.4KSPCh. 12 - Explain why liquids, unlike gases, are virtually...Ch. 12 - What is surface tension? What is the relationship...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.3QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.4QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.5QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.6QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.7QPCh. 12 - Why does the viscosity of a liquid decrease with...Ch. 12 - Why is ice less dense than water?Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.10QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.11QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.12QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.13QPCh. 12 - Predict which of the following liquids has greater...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.15QPCh. 12 - Vapor pressure measurements at several different...Ch. 12 - The vapor pressure of liquid X is lower than that...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.18QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.19QPCh. 12 - Define the following terms: crystalline solid,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.21QPCh. 12 - Classify the solid states in terms of crystal...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.23QPCh. 12 - Define X-ray diffraction. What are the typical...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.25QPCh. 12 - What is the coordination number of each sphere in...Ch. 12 - Calculate the number of spheres that would be...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.28QPCh. 12 - Barium metal crystallizes in a body-centered cubic...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.30QPCh. 12 - Europium crystallizes in a body-centered cubic...Ch. 12 - Crystalline silicon has a cubic structure. The...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.33QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.34QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.35QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.36QPCh. 12 - Shown here is a zinc oxide unit cell. What is the...Ch. 12 - Describe and give examples of the following types...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.39QPCh. 12 - A solid is hard, brittle, and electrically...Ch. 12 - A solid is soft and has a low melting point (below...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.42QPCh. 12 - Which of the following are molecular solids and...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.44QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.45QPCh. 12 - What is a phase change? Name all possible changes...Ch. 12 - What is the equilibrium vapor pressure of a...Ch. 12 - Use any one of the phase changes to explain what...Ch. 12 - Define the following terms: (a) molar heat of...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.50QPCh. 12 - What can we learn about the intermolecular forces...Ch. 12 - The greater the molar heat of vaporization of a...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.53QPCh. 12 - A closed container of liquid pentane (bp = 36.1C)...Ch. 12 - What is critical temperature? What is the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.56QPCh. 12 - How do the boiling points and melting points of...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.58QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.59QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.60QPCh. 12 - Which of the following phase transitions gives off...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.62QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.63QPCh. 12 - Calculate the amount of heat (in kilo joules)...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.65QPCh. 12 - The molar heats of fusion and sublimation of lead...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.67QPCh. 12 - How is the rate of evaporation of a liquid...Ch. 12 - Explain why steam at 100C causes more serious bums...Ch. 12 - The following compounds, listed with then- boiling...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.71QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.72QPCh. 12 - Explain how waters phase diagram differs from...Ch. 12 - The blades of ice skates are quite thin, so the...Ch. 12 - A length of wire is placed on top of a block of...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.76QPCh. 12 - A phase diagram of water is shown. Label the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.78QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.79QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.80QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.81QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.82QPCh. 12 - The average distance between base pairs measured...Ch. 12 - A CO2 fire extinguisher is located on the outside...Ch. 12 - What is the vapor pressure of mercury at its...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.86QPCh. 12 - The liquid-vapor boundary line in the phase...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.88QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.89QPCh. 12 - A student is given four solid samples labeled W,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.91QPCh. 12 - The diagram shows a kettle of boiling water....Ch. 12 - The south pole of Mars is covered with solid...Ch. 12 - The properties of gases, liquids, and solids...Ch. 12 - The standard enthalpy of formation of gaseous...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.96QPCh. 12 - Under the same conditions of temperature and...Ch. 12 - The distance between Li+ and Cl is 257 pm in solid...Ch. 12 - Heat of hydration, that is, the heat change that...Ch. 12 - The fluorides of the second period elements and...Ch. 12 - Calculate the H for the following processes at...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.102QPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.103QPCh. 12 - Ozone (O3) is a strong oxidizing agent that can...Ch. 12 - A sample of limestone (CaCO3) is heated in a...Ch. 12 - Carbon and silicon belong to Group 4A of the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.107QPCh. 12 - A 1.20-g sample of water is injected into an...Ch. 12 - What are the advantages of cooking the vegetable...Ch. 12 - A quantitative measure of how efficiently spheres...Ch. 12 - The phase diagram of helium is shown. Helium is...Ch. 12 - The phase diagram of sulfur is shown. (a) How many...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.113QPCh. 12 - Argon crystallizes in the face-centered cubic...Ch. 12 - Given the phase diagram of carbon, answer the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.116QPCh. 12 - Swimming coaches sometimes suggest that a drop of...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.118QPCh. 12 - Why do citrus growers spray their trees with water...Ch. 12 - Calcium metal crystallizes in a face-centered...Ch. 12 - A student heated a beaker of cold water (on a...Ch. 12 - The compound diclilorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2) has...Ch. 12 - Iron crystallizes in a body-centered cubic...Ch. 12 - Sketch the cooling curves of water from about 110C...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.125QPCh. 12 - A sampleof water shows the following behavior as...Ch. 12 - A closed vessel of volume 9.6 L contains 2.0 g of...Ch. 12 - The electrical conductance of copper metal...Ch. 12 - Assuming ideal behavior, calculate the density of...Ch. 12 - Explain why drivers are advised to use motor oil...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.131QPCh. 12 - Silicon used in computer chips must have an...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.133QP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw and name the R groups of all 20 amino acids.arrow_forward3. Two solutions are prepared using the same solute: Solution A: 0.14 g of the solute dissolves in 15.4 g of t-butanol Solution B: 0.17 g of the solute dissolves in 12.7 g of cyclohexane Which solution has the greatest freezing point change? Show calculations and explain.arrow_forward2. Give the ground state electron configuration (e.g., 02s² σ*2s² П 2p²) for these molecules and deduce its bond order. Ground State Configuration Bond Order H2+ 02- N2arrow_forward
- 1. This experiment is more about understanding the colligative properties of a solution rather than the determination of the molar mass of a solid. a. Define colligative properties. b. Which of the following solutes has the greatest effect on the colligative properties for a given mass of pure water? Explain. (i) 0.01 mol of CaCl2 (ii) 0.01 mol of KNO3 (iii) 0.01 mol of CO(NH2)2 (an electrolyte) (an electrolyte) (a nonelectrolyte)arrow_forward5. b. For Trials 2 and 3, the molar mass of the solute was 151 g/mol and 143 g/mol respectively. a. What is the average molar mass of the solute ? b. What are the standard deviation and the relative standard deviation (%RSD) for the molar mass of the solute ?arrow_forwardShow work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- 2. Explain why ice cubes formed from water of a glacier freeze at a higher temperature than ice cubes formed from water of an under- ground aquifer. Photodynamic/iStockphotoarrow_forwardShow reaction mechanism. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward7. Draw the Lewis structures and molecular orbital diagrams for CO and NO. What are their bond orders? Are the molecular orbital diagrams similar to their Lewis structures? Explain. CO Lewis Structure NO Lewis Structure CO Bond Order NO Bond Order NO Molecular Orbital Diagram CO Molecular Orbital Diagramarrow_forward
- 5. The existence of compounds of the noble gases was once a great surprise and stimulated a great deal of theoretical work. Label the molecular orbital diagram for XeF (include atom chemical symbol, atomic orbitals, and molecular orbitals) and deduce its ground state electron configuration. Is XeF likely to have a shorter bond length than XeF+? Bond Order XeF XeF+arrow_forward6. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B22+ B22+, B2, C22, B22 and N22+ Molecular Orbital Diagram B2 C22- B22- N22+ Which molecule is paramagnetic?arrow_forward3. Put the following species in order of increasing bond length by using molecular orbital diagrams and calculating their bond orders: F2, F2, F2+ Molecular Orbital Diagram F2 F2 F2+ Bond Order Shortest bond: Longest bondarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning
DISTINCTION BETWEEN ADSORPTION AND ABSORPTION; Author: 7activestudio;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbWRuSk-BhE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Difference Between Absorption and Adsorption - Surface Chemistry - Chemistry Class 11; Author: Ekeeda;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e7Ql2ZElgc0;License: Standard Youtube License