
(a)
Interpretation: The major product of the given reaction has to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Major product in the reaction of
General scheme:
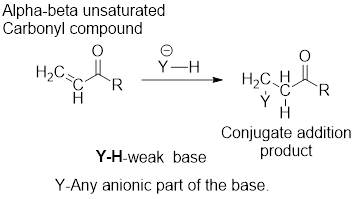
It can be observed that the conjugate addition product has been formed by the addition of basic anion to the beta-carbon atom and that of hydrogen atom to the alpha-carbon carbon atom.
The examples for the weak bases are:
(b)
Interpretation: The major product of the given reaction has to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Major product in the reaction of
General scheme:

It can be observed that the conjugate addition product has been formed by the addition of basic anion to the beta-carbon atom and that of hydrogen atom to the alpha-carbon carbon atom.
The examples for the weak bases are:
(c)
Interpretation: The major product of the given reaction has to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Major product in the reaction of
General scheme:

It can be observed that the conjugate addition product has been formed by the addition of basic anion to the beta-carbon atom and that of hydrogen atom to the alpha-carbon carbon atom.
The examples for the weak bases are:
Major product in the reaction of
General scheme:
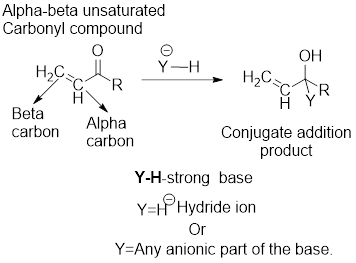
It can be observed that the direct addition product has been formed from the direct reaction of the strong base with the carbonyl
The examples for the strong bases are:
(d)
Interpretation: The major product of the given reaction has to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Major product in the reaction of
General scheme:

It can be observed that the conjugate addition product has been formed by the addition of basic anion to the beta-carbon atom and that of hydrogen atom to the alpha-carbon carbon atom.
The examples for the weak bases are:
Major product in the reaction of
General scheme:

It can be observed that the direct addition product has been formed from the direct reaction of the strong base with the carbonyl functional group of the
The examples for the strong bases are:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry Study Guide & Solution Manual, Books a la Carte Edition
- Nonearrow_forward3. A molecular form of "dicarbon", C2, can be generated in gas phase. Its bond dissociation energy has been determined at 599 kJ/mol. Use molecular orbital theory to explain why energy of dissociation for C₂+ is 513 kJ/mol, and that for C2² is 818 kJ/mol. (10 points)arrow_forward9.73 g of lead(IV) chloride contains enough Cl- ions to make ____ g of magnesium chloride.arrow_forward
- 6. a) C2's. Phosphorus pentafluoride PF5 belongs to D3h symmetry group. Draw the structure of the molecule, identify principal axis of rotation and perpendicular (4 points) b) assume that the principal axis of rotation is aligned with z axis, assign symmetry labels (such as a1, b2, etc.) to the following atomic orbitals of the P atom. (character table for this group is included in the Supplemental material). 3s 3pz (6 points) 3dz²arrow_forward2. Construct Lewis-dot structures, and draw VESPR models for the ions listed below. a) SiF5 (4 points) b) IOF4 (4 points)arrow_forward5. Complex anion [AuCl2]¯ belongs to Doh symmetry point group. What is the shape of this ion? (4 points)arrow_forward
- 4. Assign the following molecules to proper point groups: Pyridine N 1,3,5-triazine N Narrow_forward7. a) Under normal conditions (room temperature & atmospheric pressure) potassium assumes bcc lattice. Atomic radius for 12-coordinate K atom is listed as 235 pm. What is the radius of potassium atom under normal conditions? (3 points) b) Titanium metal crystallyzes in hcp lattice. Under proper conditions nitrogen can be absorbed into the lattice of titanium resulting in an alloy of stoichiometry TiNo.2. Is this compound likely to be a substitutional or an interstitial alloy? (Radius of Ti (12-coordinate) is 147 pm; radius of N atom is 75 pm. (3 points)arrow_forwardcan someone answer the questions and draw out the complete mechanismarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
