
Concept explainers
You’ve been hired by your state’s environmental agency to monitor carbon dioxide levels just above rivers, with the goal of understanding whether river water acts as a source or sink of CO2. You’ve constructed the apparatus shown in Fig. 12.38, consisting of a boom mounted on a pivot, a vertical support, and a rope with pulley for raising and lowering the boom so its end can extend different distances over the river. In addition, there's a separate rope and pulley for dropping the sampling apparatus so it’s just above the river.
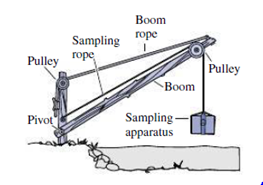
FIGURE 12.38 Passage Problem 64–67
If you secure the boom at a fixed angle and lower the sampling apparatus at constant speed, the boom rope tension will
- a. increase.
- b. decrease.
- c. remain the same.
- d. increase only if the sampling apparatus is more massive than the boom.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
- The force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE DO NOT USE LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forward
- ་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- A spiral transition curve is used on railroads to connect a straight portion of the track with a curved portion. (Figure 1) Part A v = v₁ft/s 600 ft y = (106) x³ If the spiral is defined by the equation y = (106)³, where x and y are in feet, determine the magnitude of the acceleration of a train engine moving with a constant speed of v₁ = 30 ft/s when it is at point x = 600 ft. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forwardsolve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





