
Concept explainers
The solid-state structure of silicon is shown below.
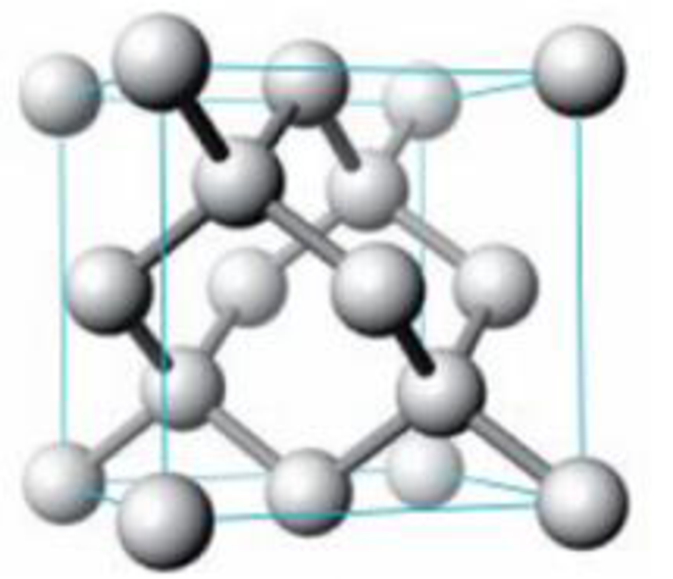
Unit cell for silicon
- (a) Describe this crystal as pc, bcc, or fcc.
- (b) What type of holes are occupied in the lattice?
- (c) How many Si atoms are there per unit cell?
- (d) Calculate the density of silicon in g/cm3 (given that the cube edge has a length of 543.1 pm).
- (e) Estimate the radius of the silicon atom. (Note: The Si atoms on the edges do not touch one another.)
(a)
Interpretation:
Given silicon crystal has to be described for PC, BCC or FCC.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contributions, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
The types of the lattice is face center cubic crystal
Explanation of Solution
The types of the lattice is face center cubic crystal, because It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
(b)
Interpretation:
The types of holes that are occupied in the lattice has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
Silicon atoms are located in one half of the tetrahedral holes
Explanation of Solution
Silicon atoms are located in one half of the tetrahedral holes.
(c)
Interpretation:
Number of silicon atoms per unit cell has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
Totally eight atoms in the unit cell
Explanation of Solution
Silicon atoms are located in one half of the tetrahedral holes.
(d)
Interpretation:
The density of the silicon atom has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
Density is
Explanation of Solution
The density of the silicon atom is given below,
(e)
Interpretation:
The radius of the silicon atom has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
Radius is
Explanation of Solution
The radius of silicon atom can be calculated as,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- ME EX1) Prblm #19-20 I'm so confused with these problems. Can you please help me solve them and explain them? Problems number 19-20, and thanks! step by step and in detail for me please helparrow_forwardCalculate the flux of oxygen between the ocean and the atmosphere, given that: Temp = 18°C Salinity = 35 ppt Density = 1025 kg/m3 Oxygen concentration measured in bulk water = 263.84 mmol/m3 Wind speed = 7.4 m/s Oxygen is observed to be about 10% initially supersaturatedarrow_forward( ME EX1) Prblm 27-28: Can you explain to me both prblms in detail and for prblm 28 what do you mean bi conjugated bi ponds and those structures I'm confused...arrow_forward
- A. Determine the number of electrons in a system of cyclic conjugation (zero if no cyclic conjugation). B. Specify whether the species is "a"-aromatic, "aa"-anti-aromatic, or "na"-non-aromatic (neither aromatic nor anti-aromatic). (Presume rings to be planar unless structure obviously prevents planarity. If there is more than one conjugated ring, count electrons in the largest.) 1. A.Electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. 18 B.The compound is (a, aa, or na) a 2. A.Electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. 10 B.The compound is (a, aa, or na) naarrow_forwardWater is boiling at 1 atm pressure in a stainless steel pan on an electric range. It is observed that 2 kg of liquid water evaporates in 30 min. Find the rate of heat transfer to the water (kW).arrow_forwardCould you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the resonance structures that were given please.arrow_forward
- Could you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the question.arrow_forwardplease solve. If the answer is "no error" and it asks me to type something, and i typed a-helix, its always wrong.arrow_forwardCan you please solve and explain this for me in a simple way? I cant seem to comprehend this problem.arrow_forward
- Part I. Problem solving. Include all necessary calculations 13 provide plots and graphs. Complexation wl diphenyl carbazide (OPC) in acidic media is another type of sensitive photometric method used for the analysis of aqueous. hexavalent chromium. At 540nm the cherry-red complex as a result of DPC reaction w/ chromium can be photometrically measured. at this wavelength. - a 25mL The UV-vis analysis for the determination of nexavalent chromium in ground water sample is given below. The experiment was based on external calibration method w/ each measurement sample prepared are as follows lab sample analysis contained the standard 100 ppb croy cor groundwater sample, volumes used as indicated below), 12.50 mL of 0.02 M H2Soy and 5.50 ml of 100 ppm DPC (wi water to adjust final volume to 25-ml). The main stripping method was square wave voltammetry, following the conditions set in the main ASV experiment. Standard 100 Volumetric Groundwater H2SO4 0.20 M, flask Sample, mL ppb CrO4*, 100…arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardPredict the products of the following reactions. Draw mechanism arrows for each step for a, b, and c. a.) HBr b.) HI H₂O H2SO4 d.) C12 HO H2SO4 1.) BH3 2.) H2O2, NaOHarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning



