
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula of
Concept introduction:
An electron dot formula is a way of representing the molecular structure in which electrons are represented by a dot. Structural formula is a way in which atoms are linked together through a solid line. This solid line represents the covalent bond. An electron dot structure is known as Lewis structure. Electron dot structure indicates the valence electrons of an atom which are involved in bonding.
Answer to Problem 43E
Electron dot structure and structural formula of
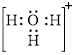
Explanation of Solution
In molecule
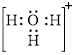
Figure 1

Figure 2
Solid line, in Figure 2, between the oxygen atom and the hydrogen atom is the covalent bond which is made up of two electrons. This bond is formed by sharing of electrons between the atoms present in that bond.
An electron dot structure and structural formula of
(b)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula of
Concept introduction:
An electron dot formula is a way of representing the molecular structure in which electrons are represented by a dot. Structural formula is a way in which atoms are linked together through a solid line. This solid line represents the covalent bond. An electron dot structure is known as Lewis structure. Electron dot structure indicates the valence electrons of an atom which are involved in bonding.
Answer to Problem 43E
Electron dot structure and structural formula of
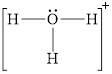
![]()
![]()
Explanation of Solution
In molecule
![]()
Figure 3
![]()
Figure 4
Solid line, in Figure 4, between the oxygen atom and the hydrogen atom shows the covalent bond which is made up of two electrons. This bond is formed by sharing of electrons between the atoms present in that bond.
An electron dot structure and structural formula of
(c)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula of
Concept introduction:
An electron dot formula is a way of representing the molecular structure in which electrons are represented by a dot. Structural formula is a way in which atoms are linked together through a solid line. This solid line represents the covalent bond. An electron dot structure is known as Lewis structure. Electron dot structure indicates the valence electrons of an atom which are involved in bonding.
Answer to Problem 43E
Electron dot structure and structural formula of
![]()
![]()
Explanation of Solution
In molecule
![]()
Figure 5
. ![]()
Figure 6
Solid line, in Figure 6, between the sulfur and hydrogen atom is the covalent bond which is made up of two electrons. This bond is formed by sharing of electrons between the atoms present in that bond.
An electron dot structure and structural formula of
(d)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula of
Concept introduction:
An electron dot formula is a way of representing the molecular structure in which electrons are represented by a dot. Structural formula is a way in which atoms are linked together through a solid line. This solid line represents the covalent bond. An electron dot structure is known as Lewis structure. Electron dot structure indicates the valence electrons of an atom which are involved in bonding.
Answer to Problem 43E
Electron dot structure and structural formula of
![]()
![]()
Explanation of Solution
In molecule
![]()
Figure 7
![]()
Figure 8
Each solid line, in Figure 8, between the carbon and nitrogen atom is the covalent bond which is made up of two electrons. This bond is formed by sharing of electrons between the atoms present in that bond.
An electron dot structure and structural formula of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EP INTRODUCTORY CHEM.-MOD.MASTERINGCHEM
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward13) When solid barium phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of barium ions to phosphate ions would be: a. 1:1 b. 2:3 c. 3:2 d. 2:1 14) The pH of a 0.05 M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is 15) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of KOH at 25°C isarrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward7) The pH of a 0.05M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is a. 1.3 b. 2.3 c. 3.3 d. 12.7arrow_forward
- 11) The Ksp expression for copper (II) sulfate is: a. [Cu2+][SO4²¯] b. [Cu²+]² [SO4²]² c. [Cu²+]²[SO4²] d. [CuSO4] 12) Which of the following is true about a chemical system in equilibrium? a. All chemical reactions have stopped b. The concentration of reactants is equal to the concertation of products c. The forward and reverse reaction rates become equal d. The system will remain at equilibrium regardless of any external factorsarrow_forward21) Explain the difference between the rate of a reaction and the extent of a reaction. Why are both of these concepts important, if you are a chemical engineer that is trying to develop a process to produce a large volume of a specific type of chemical compound?arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
