
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. bromination of allylicc carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid which leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.
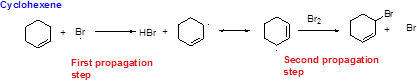
Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reaction with bromine molecule and forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
(a)
Answer to Problem 26P
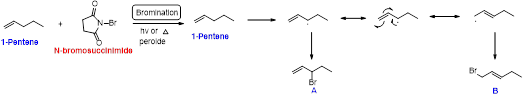
1-pentene undergoes bromination using N-bromosuccinamide and yields brominated compound A and B which is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. Bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid

Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid which leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.

Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reaction with bromine molecule forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
(b)
Answer to Problem 26P
2-methyl-2-pentene undergoes bromination using N-bromo succinamide and yields brominated compound A, B as a major product and C, D as minor product which is shown below.
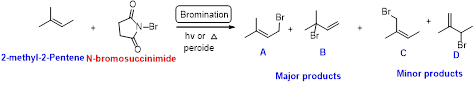
Explanation of Solution
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. bromination of allylicc carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid
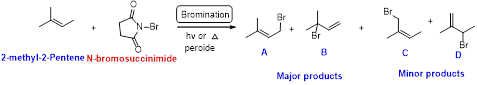
Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
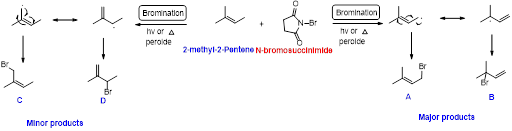
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present. (bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
Bromination will occur on tertiary radical than the secondary than primary radical, tertiary radical is more stable radical than the other radicals.
(c)
Answer to Problem 26P
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane which is shown below
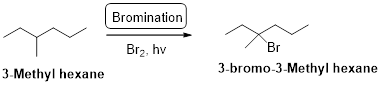
Explanation of Solution
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane which is shown below
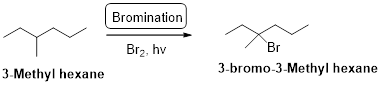
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
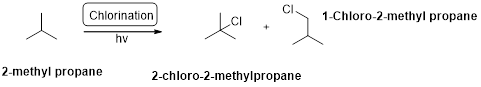
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
(d)
Answer to Problem 26P
Cyclohexane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 1-chloro cyclohexane which is shown below
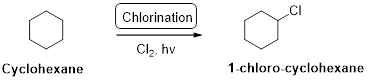
Explanation of Solution
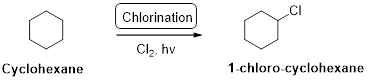
Cyclohexane undergoes radical chlorination, all the carbons in cyclohexane are secondary. Therefore, it yields the 1-chloro cyclohexane which is shown above.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
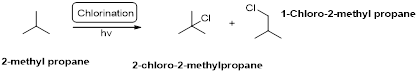
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
(e)
Answer to Problem 26P
Cyclopentane has no reaction with chlorine in dichloromethane which is shown below

Explanation of Solution
Cyclopentane has no reaction with chlorine in dichloromethane, because the reaction will not go without light or heat which is shown below

(f)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
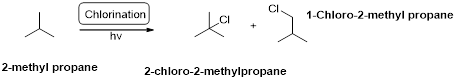
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
(f)
Answer to Problem 26P
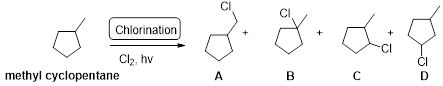
Explanation of Solution
Methyl cyclopentane undergoes radical chlorination, the carbons in cyclopentane are secondary and primary. Therefore, it yields the four types of chlorocyclopentane which is shown below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-W/S.G+SOLN.MANUAL
- if the answer is no reaction than state that and please hand draw!arrow_forward"I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardreciprocal lattices rotates along with the real space lattices of the crystal. true or false?arrow_forwardDeducing the reactants of a Diels-Alder reaction vn the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ O If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Product can't be made in one step. Explanation Checkarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Larrow_forward> Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accesarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: O O + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. eserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center >arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





