
Characterize a system at
a. the rates of the forward and reverse reactions
b. the overall composition of the reaction mixture For a general reaction
Interpretation: The given systems at equilibrium are to be characterized. For the given reaction, the required plot is to be shown. The plot that illustrates the rate of forward reaction and rate of reverse reaction is to be sketched.
Concept introduction: Chemical equilibrium is a state of a system in which the rate of forward reaction and that of the backward reaction is equal. It is affected by various factors such as concentration of reactants or products, temperature, pressure.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Answer
- a) Rate of the forward and reverse reactions are equal at equilibrium.
- b) The overall composition remains constant at equilibrium.
The plot of concentrations of A,B and C versus time is shown in Figure 1.
The plot illustrating the rate of forward reaction and rate of reverse reaction versus time is shown in Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
(I)
(a)
To determine: The characterization of the given system at equilibrium.
The rate of the forward and reverse reactions is equal at equilibrium.
At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products do not change. When equilibrium is attained by a system, equilibrium rate of forward reaction will be equal to rate of backward reaction.
(b)
To determine: The characterization of the given system at equilibrium.
The overall composition remains constant at equilibrium.
The forward and backward reaction at equilibrium proceeds with same rate, hence the concentration of reactants and products do not change. Therefore, the overall composition remains constant at equilibrium.
(II)
To determine: The plot of concentrations of A,B and C versus time and the plot illustrating the rate of forward reaction and rate of reverse reaction versus time.
The plot of concentrations of A, B and C versus time is shown in Figure 1.
The given reaction is,
If one starts with only reactants present, then the plot of concentrations of A,B and C versus time will be like,
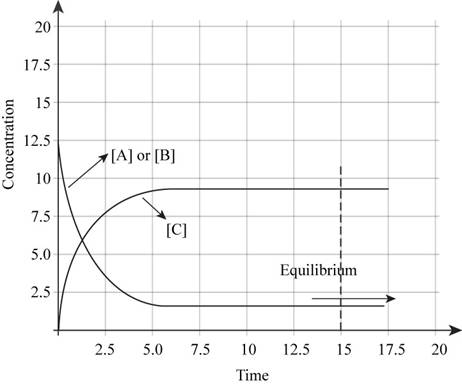
Figure 1
In the beginning of the reaction, the concentration of reactants is more. As the time proceeds, the concentration of reactants decreases and the concentration of products increases. At equilibrium, there is no change in the concentrations of reactants and products.
The plot illustrating the rate of forward reaction and rate of reverse reaction versus time is shown in Figure 2.
In the beginning of the reaction, the concentration of reactants is more. Therefore, rate of forward reaction is high. But as the reaction proceeds further, the reactants are consumed to form products. Hence rate of forward reaction decreases and rate of backward reaction increases. At equilibrium, both the rates are equal. Therefore, plot illustrating the rate of forward reaction and rate of reverse reaction versus time will be like,
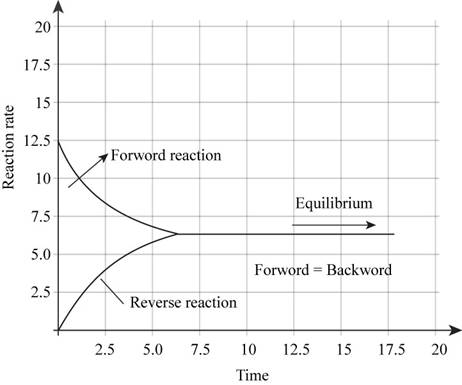
Figure 2
Conclusion
- a) Rate of the forward and reverse reactions are equal at equilibrium.
- b) The overall composition remains constant at equilibrium.
The plot of concentrations of A, B and C versus time is shown in Figure 1.
The plot illustrating the rate of forward reaction and rate of reverse reaction versus time is shown in Figure 2
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY: AN ATOMS FIRST APPROACH
- 2. Use Hess's law to calculate the AH (in kJ) for: rxn CIF(g) + F2(g) → CIF 3 (1) using the following information: 2CIF(g) + O2(g) → Cl₂O(g) + OF 2(g) AH = 167.5 kJ ΔΗ 2F2 (g) + O2(g) → 2 OF 2(g) 2C1F3 (1) + 202(g) → Cl₂O(g) + 3 OF 2(g) о = = -43.5 kJ AH = 394.1kJarrow_forwardci Draw the major product(s) of the following reactions: (3 pts) CH3 HNO3/H2SO4 HNO3/ H2SO4 OCH3 (1 pts)arrow_forwardProvide the product for the reactionarrow_forward
- What is the net ionic equation for the reaction between tin(IV) sulfide and nitric acid?arrow_forwardThe combustion of 28.8 g of NH3 consumes exactly _____ g of O2. 4 NH3 + 7 O2 ----> 4 NO2 + 6 H2Oarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular formula of the bond-line structure shown below OH HO ○ C14H12O2 ○ C16H14O2 ○ C16H12O2 O C14H14O2arrow_forward
- Check all molecules that are acids on the list below. H2CO3 HC2H3O2 C6H5NH2 HNO3 NH3arrow_forwardFrom the given compound, choose the proton that best fits each given description. a CH2 CH 2 Cl b с CH2 F Most shielded: (Choose one) Least shielded: (Choose one) Highest chemical shift: (Choose one) Lowest chemical shift: (Choose one) ×arrow_forwardConsider this molecule: How many H atoms are in this molecule? How many different signals could be found in its 1H NMR spectrum? Note: A multiplet is considered one signal.arrow_forward
- For each of the given mass spectrum data, identify whether the compound contains chlorine, bromine, or neither. Compound m/z of M* peak m/z of M + 2 peak ratio of M+ : M + 2 peak Which element is present? A 122 no M + 2 peak not applicable (Choose one) B 78 80 3:1 (Choose one) C 227 229 1:1 (Choose one)arrow_forwardShow transformation from reactant to product, step by step. *see imagearrow_forwardCheck the box if the molecule contains the listed item. *See imagearrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





