
Concept explainers
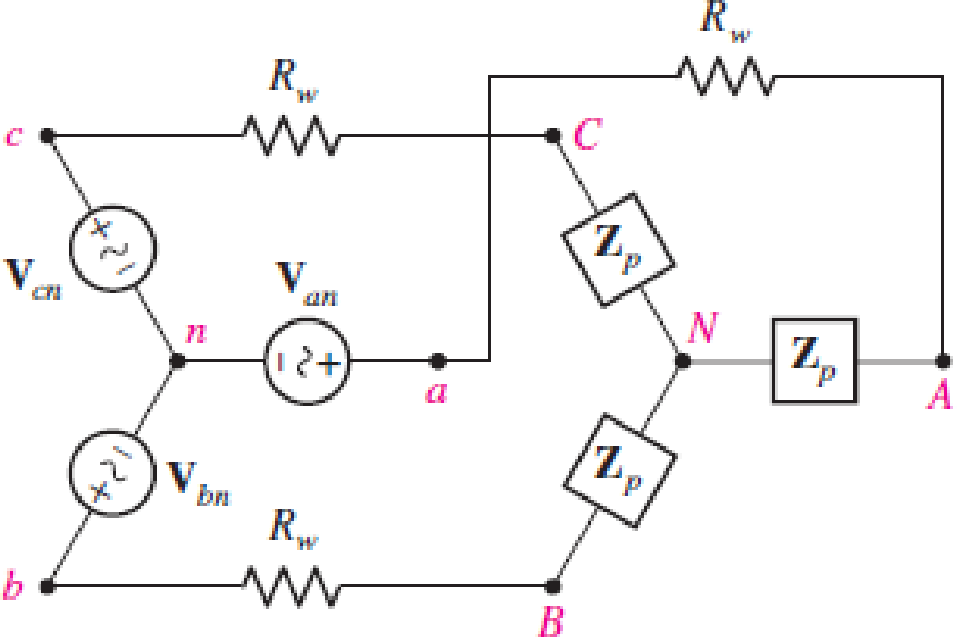
Assume the system shown in Fig. 12.34 is balanced, Rw = 0, 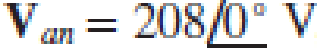 , and a positive phase sequence applies. Calculate all phase and line currents, and all phase and line voltages, if Zp is equal to (a) 1 kΩ; (b) 100 + j48 Ω; (c) 100 − j48 Ω.
, and a positive phase sequence applies. Calculate all phase and line currents, and all phase and line voltages, if Zp is equal to (a) 1 kΩ; (b) 100 + j48 Ω; (c) 100 − j48 Ω.
(a)
All the line and phase currents and all the line and phase voltages for the given load impedance.
Answer to Problem 17E
The line and phase currents in sequence are
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The resistance of the wire
The phase to neutral voltage
The load impedance
Calculation:
The system follows positive sequence hence the phase to neutral voltages will be,
For phase
For phase
The required diagram is shown in Figure 1.
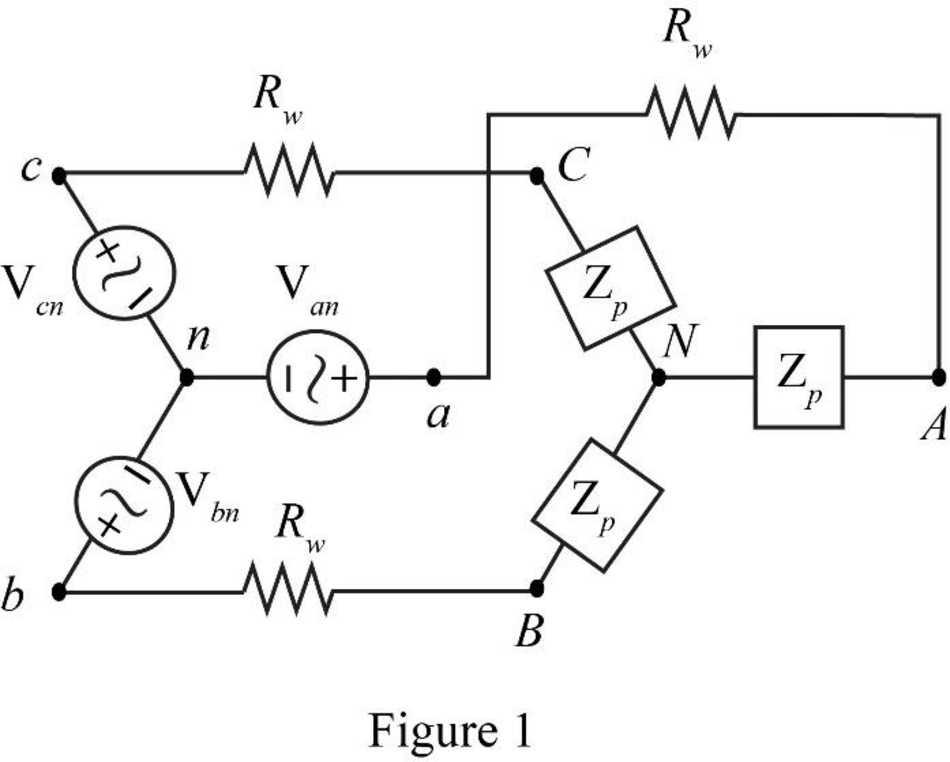
The line voltage between phase
Substitute
The system follows positive sequence hence the line to line voltages will be,
All the phase and line voltages are independent of the impedance value and hence these values will remain same for all the values of load impedance
The conversion from
Hence, the load impedance
Since the given system is a star connected system, the phase currents will be equal to the line currents.
The phase
Here,
The phase
Substitute
The phase
Here,
The phase
Substitute
The phase
Here,
The phase
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the line and phase currents in sequence are
(b)
All the line and phase currents and all the line and phase voltages for the given load impedance.
Answer to Problem 17E
The line and phase currents in sequence are
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The load impedance
Calculation:
All the phase and line voltages are independent of the impedance value and hence these values will remain same for all the values of load impedance
The phase
Here,
The phase
Substitute
The phase
Here,
The phase
Substitute
The phase
Here,
The phase
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the line and phase currents in sequence are
(c)
All the line and phase currents and all the line and phase voltages for the given load impedance.
Answer to Problem 17E
The line and phase currents in sequence are
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The load impedance
Calculation:
All the phase and line voltages are independent of the impedance value and hence these values will remain same for all the values of load impedance
The phase
Here,
The phase
Substitute
The phase
Here,
The phase
Substitute
The phase
Here,
The phase
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the line and phase currents in sequence are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
ENGINEERING CIRCUIT...(LL)>CUSTOM PKG.<
- Fundamentals of Energy Systems HW 4 Q4arrow_forwardFundamentals of Energy Systems HW 4 Q6arrow_forwardConstruct a battery pack to deliver 360V and 450-mile range for a vehicle that consumes 200 Wh/mile, from prismatic cells with 25Ah and 3.6 V. Physical dimensions of the cell are 0.5 cm thickness, 20 cm width and 40 cm length. a) Report configuration of the battery pack. 10-points b) Resistance of each cell is 0.05 Ohm, calculate the total internal resistance of the battery pack. 10-points c) Calculate the voltage drop during discharge when the battery is discharged at 100A. 10-points d) Calculate the amount of anode and cathode to build a prismatic cell with 25Ah capacity. Assume the cell chemistry as: Si anode and [Li(Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3)O2] cathode. Atomic weight of elements: Li=7, Si = 28, Ni=58, Co=59, Mn=55, O=16, 10-points e) Calculate the theoretical specific energy (Wh/kg) and practical energy density (Wh/liter) of the battery pack. 10-points f) Calculate the thickness on anode and cathode coating assuming each electrode has 30%…arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardDesign a battery pack for an electric bike that consumes in average 10Wh/mile and drive 30 miles per charge. The battery state of charge window is 80%. Design the battery by using new commercial cylindrical cells with 20mm diameter and 80mm height. The battery is constructed based on graphite anode C6 and cathode Li(Ni0.8Co0.15Al0,05)O2 that provides 3.75V at the cell level and 10Ah capacity. Density of anode is 2.2 g/cm3 and density of cathode is 4.5 g/cm3. Report on the battery pack configuration if the required battery pack voltage is 75 volts. If the thickness of anode and cathode is limited to 130 microns (130 x 10-4 cm) calculate the total electrode surface area in each cell. Assume the porosity of electrodes are 30%. Calculate the weight of active materials (anode and cathode) in grams and the total current collector’s and electrolyte membrane areas in (cm2).arrow_forwardDO NOT USE AI NEED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION Find total impedance of circuit in polar form and power factor.arrow_forward
- Do NOT WANT AI. need diagram fully labeled pleasearrow_forwardCalculate the current magnitude in the coils e1, e2 of theMagnetic circuit, if:ɸa = 3.00 x 10^-3 Wb, φb = 0.80 x 10^-3 Wb, ɸc = 2.20 x 10^-3 Wb L ab = 0.10 m,A ab = 5.0 cm^2L afeb = L acdb = 0.40 mA afeb = A acdb = 20 cm^2 MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICSH (At/m) 240 350 530 1300 5000 9000B (T) 0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3 1.5 1.6arrow_forwardA toroid magnetic circuit is composed of three sections A, B and C, thesection C has an air gap, section A has an 850 round coil thatconsumes a current of 1.2 A. the physical and magnetic properties of each sectionare: Section A: Length = 80 mm, Cross section = 120 mm^2, μr = 400 Section B: Length = 60 mm, Cross section = 40 mm^2, μr = 250 Section C: Length = 50 mm, Cross section = 200 mm^2, μr = 600 Gap: Length = 1 mm, Cross section = 40 mm^2, μr = 1 Calculate:The magnetic field density in each of the sectionsarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





