
Concept explainers
Joe Henry’s machine shop uses 2,500 brackets during the course of a year. These brackets are purchased from a supplier 90 miles away. The following information a known about the brackets:
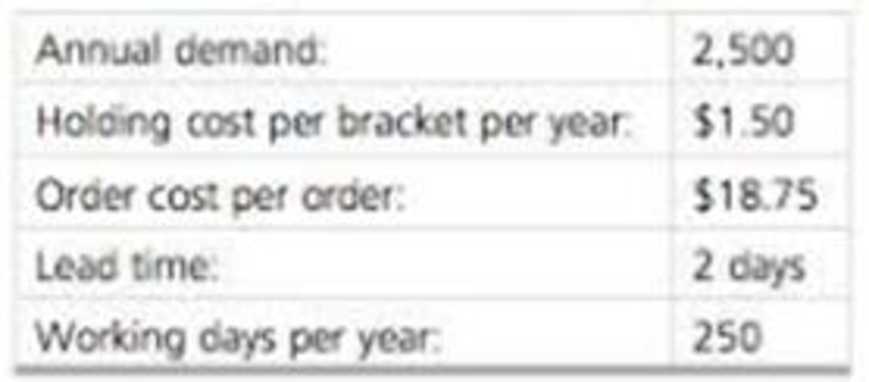
a) Given the above information, what would be the economic order quantity (EOQ)?
b) Given the EOQ, what would be the average inventory? What would be the annual inventory holding cost?
c) Given the EOQ, how many orders would be made each year? What would be the annual order cost?
d) Given the EOQ, what is the total annual cost of managing the inventory?
e) What is the time between orders?
f) What is the reorder point (ROP)?
a)
To calculate: The economic order quantity (EOQ).
Introduction:
Economic order quantity (EOQ):
EOQ is the quantity of units a company must add to its inventory so as to minimize the total inventory costs. It will determine the ideal order quantity which will decrease the inventory management costs.
Answer to Problem 15P
The economic order quantity (EOQ) is 250 brackets.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate EOQ:
Calculation of EOQ:
Hence, the economic order quantity (EOQ) is 250 brackets.
b)
To calculate: The average inventory and annual holding cost at EOQ.
Answer to Problem 15P
The average inventory is 125 units and the annual holding cost is $187.50.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate average inventory:
Formula to calculate annual holding cost:
Calculation of average inventory:
Hence, the average inventory is 125 units.
Calculation of annual holding cost:
Hence, the annual holding cost is $187.50.
c)
To determine: The optimal number of orders per year and annual ordering cost.
Answer to Problem 15P
The optimal number of orders per year is 10 orders and annual ordering cost is $187.50.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate optimal number of orders:
Formula to calculate annual order cost:
Calculation of optimal number of orders:
Hence, the optimal number of orders per year is 10 orders.
Calculation of annual ordering cost:
Hence, the annual ordering cost is $187.50 and annual ordering cost is $187.50.
d)
To determine: The total annual cost of managing the inventory.
Introduction:
Total cost of inventory:
The total cost involved in ordering and carrying an inventory and the costs associated with the management and handling of associated activities.
Answer to Problem 15P
The total annual cost of managing the inventory is $375 per year.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the total cost of inventory:
Calculation of total cost:
Hence, the total annual cost of managing the inventory is $375 per year
e)
To determine: The time between any two orders.
Introduction:
Optimal number of orders:
The optimal number of orders is the number of orders a firm has to make such that the overall inventory cost is minimized.
Answer to Problem 15P
The time between any two orders is 25days.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate time between any two orders:
Calculation of optimal number of orders:
Hence, the time between any two orders is 25 days.
f)
To calculate: The reorder point.
Introduction:
Reorder point (ROP):
The reorder point is the level of the firm’s inventory which triggers the firm to act and replenish the stock of the particular item. It will be the minimum quantity of the item; the firm must hold in its stock.
Answer to Problem 15P
The reorder point is 20 units.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Annual demand= 2,500 units / year
Order cost= $18.75 / order
Holding cost = $1.50 / bracket / year
Number of days = 250 / year
Lead time = 2 days
Formula to calculate reorder point (ROP):
Calculation of reorder point (ROP):
Hence, the reorder point is 20 units.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- EXPLAIN Human Resource Information System (HRIS)arrow_forwardRead the mini-case study below and answer the following questions.With an enormous amount of data stored in databases and data warehouses, it is increasinglyimportant to develop powerful tools for analysis of such data and mining interestingknowledge from it. Data mining is a process of inferring knowledge from such huge data. Themain problem related to the retrieval of information from the World Wide Web is theenormous number of unstructured documents and resources, i.e., the difficulty of locating andtracking appropriate sources.Briefly explain any five (5) types of information you can get from data mining.arrow_forwardProblem 1: Practice Problems Chapter 6 Managing Quality The accounts receivable department has documented the following defects over a 30-day period: Category Frequency Invoice amount does not agree with the check amount 108 Invoice not on record (not found) 24 No formal invoice issued Check (payment) not received on time 18 30 Check not signed 8 Invoice number and invoice referenced do not agree 12 What techniques would you use and what conclusions can you draw about defects in the accounts receivable department? Problem 2: Prepare a flow chart for purchasing a Big Mac at the drive-through window at McDonalds. Problem 3: Draw a fishbone chart detailing reasons why a part might not be correctly machined.arrow_forward
- Problem 5: Development of a new deluxe version of a particular software product is being considered. The activities necessary for the completion of this project are listed in the table below along with their costs and completion times in weeks. Activity Normal Crash Normal Crash Immediate Time Time Cost Cost Predecessor A 4 3 2,000 2,600 B 2 1 2,200 2,800 A C 3 3 500 500 A D 8 4 2,300 2,600 A E 6 3 900 1,200 B, D F 3 2 3,000 4,200 C, E G 4 2 1,400 2,000 F a. What is the project expected completion date? b. What is the total cost required for completing this project on normal time? c. If you wish to reduce the time required to complete this project by 1 week, which activity should be crashed, and how much will this increase the total cost?arrow_forwardI need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.with diagramarrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- provide scholarly reseach and references for the following 1. explain operational risks and examples of such risk faced by management at financial institutions 2. discuss the importance of establishing an effective risk management policy at financial institutions to manage operational risk, giving example of a risk management strategy used by financial institutions to mitigate such risk. 3. what is the rold of the core principles of effective bank supervision as it relates to operational risk, in the effective management of financial institutions.arrow_forwardPlease show all units, work, and steps needed to solve this problem I need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.arrow_forwardIM.82 A distributor of industrial equipment purchases specialized compressors for use in air conditioners. The regular price is $50, however, the manufacturer of this compressor offers quantity discounts per the following discount schedule: Option Plan Quantity Discount A 1 - 299 0% B 300 - 1,199 0.50% C 1,200+ 1.50% The distributor pays $56 each time it places an order with the manufacturer. Holding costs are negligible (none) but they do earn 10% annual interest on all cash balances (meaning there will be a financial opportunity cost when they put cash into inventory). Annual demand is expected to be 10,750 units. When there is no quantity discount (Option Plan A, the first row of the schedule listed above), what is the adjusted order quantity? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) 491 Based on your answer to the previous question, and based on the annual demand as stated above, what will be the annual ordering costs? (Display your answer to the…arrow_forward
- Excel Please. The workload of many areas of banking operations varies considerably based on time of day. A variable capacity can be achieved effectively by employing part-time personnel. Because part-timers are not entitled to all the fringe benefits, they are often more economical than full-time employees. Other considerations, however, may limit the extent to which part-time people can be hired in a given department. The problem is to find an optimal workforce schedule that would meet personnel requirements at any given time and also be economical. Some of the factors affecting personnel assignments are listed here: The bank is open from 9:00am to 7:00pm. Full-time employees work for 8 hours (1 hour for lunch included) per day. They do not necessarily have to start their shift when the bank opens. Part-time employees work for at least 4 hours per day, but less than 8 hours per day and do not get a lunch break. By corporate policy, total part-time personnel hours is limited…arrow_forwardIM.84 An outdoor equipment manufacturer sells a rugged water bottle to complement its product line. They sell this item to a variety of sporting goods stores and other retailers. The manufacturer offers quantity discounts per the following discount schedule: Option Plan Quantity Price A 1 - 2,399 $5.50 B 2,400 - 3,999 $5.20 C 4,000+ $4.50 A large big-box retailer expects to sell 9,700 units this year. This retailer estimates that it incurs an internal administrative cost of $225 each time it places an order with the manufacturer. Holding cost for the retailer is $55 per case per year. (There are 40 units or water bottles per case.) Based on this information, and not taking into account any quantity discount offers, what is the calculated EOQ (in units)? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) Number Based on this information, sort each quantity discount plan from left to right by dragging the MOST preferred option plan to the left, and the LEAST preferred…arrow_forwardIn less than 150 words, what is an example of what your reflection of core values means to you and your work: Commitment, Perseverance, Community, Service, Pride?arrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing




