
Essential University Physics: Volume 1; Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780134197319
Author: Richard Wolfson
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 14E
In Fig. 12.11 the forces shown all have the same magnitude F. For each case shown, is it possible to place a third force so as to meet both conditions for static equilibrium? If so, specify the force and a suitable application point. If not, why not?
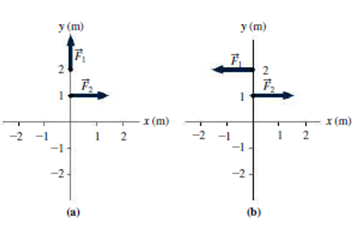
FIGURE 12.11 Exercise 14
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
need help part e
Critical damping is the case where the mass never actually crosses over equilibrium position, but reaches equilibrium as fast as possible. Experiment with changing c to find the critical damping constant. Use the same initial conditions as in the last problem. Zoom in a bit to make sure you don't allow any oscillations to take place - even small ones.
NASA's KC-135 Reduced Gravity Research aircraft, affectionately known as the "Vomit Comet," is used in training astronauts and testing equipment for microgravity environments. During a typical mission, the aircraft makes approximately 30 to 40 parabolic arcs. During each arc, the aircraft and objects inside it are in free-fall, and
passengers float freely in apparent "weightlessness."
The figure below shows the altitude of the aircraft during a typical mission. It climbs from 24,000 ft to 30,850 ft, where it begins a parabolic arc with a velocity of 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-high and exits with velocity 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-low.
31 000
45° nose high
45° nose low
24 000
Zero g
65
Maneuver time (s)
(a) What is the aircraft's speed (in m/s) at the top of the parabolic arc?
110.0
m/s
(b) What is the aircraft's altitude (in ft) at the top of the parabolic arc?
2.04e+04
What is the initial height at the start of the parabolic arc? What is the initial velocity at this point? What is the final…
Chapter 12 Solutions
Essential University Physics: Volume 1; Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Ch. 12.1 - The figure shows three pairs of forces acting on...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.2GICh. 12.3 - The figure shows a person in static equilibrium...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 12.4GICh. 12 - Give an example of an object on which the net...Ch. 12 - Give an example of an object on which the net...Ch. 12 - Prob. 3FTDCh. 12 - Pregnant women often assume a posture with their...Ch. 12 - When you carry a bucket of water with one hand,...Ch. 12 - Is a ladder more likely to slip when you stand...
Ch. 12 - How does a heavy keel help keep a boat from...Ch. 12 - Does choosing a pivot point in an equilibrium...Ch. 12 - If you take the pivot point at the application...Ch. 12 - A short dog and a tall person are standing on a...Ch. 12 - Prob. 11FTDCh. 12 - A body is subject to three forces; F1=1i+2jN,...Ch. 12 - To demonstrate that the choice of pivot point...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12.11 the forces shown all have the same...Ch. 12 - Figure 12.12a shows a thin, uniform square plate...Ch. 12 - Repeat the preceding problem for the equilateral...Ch. 12 - A 23-m-long log of irregular cross section lies...Ch. 12 - A 60-kg uniform board 2.4 m long is supported by a...Ch. 12 - Where should the child in Fig. 12.14 sit if the...Ch. 12 - A 4.2-m-long beam is supported by a cable at its...Ch. 12 - Figure 12.15 shows how a scale with a capacity of...Ch. 12 - A portion of a roller-coaster track is described...Ch. 12 - Prob. 23ECh. 12 - Youre a highway safety engineer, and youre asked...Ch. 12 - Figure 12.17a shows an outstretched arm with mass...Ch. 12 - A uniform sphere of radius R is supported by a...Ch. 12 - You work for a garden equipment company, and youre...Ch. 12 - Figure 12.20 shows the fool and lower leg of a...Ch. 12 - A uniform 5.0-kg ladder is leaning against a...Ch. 12 - The boom in the crane of Fig. 12.21 is free to...Ch. 12 - A uniform board of length L and weight W is...Ch. 12 - Figure 12.23 shows a 1250-kg car that has slipped...Ch. 12 - Repeat Example 12.2, now assuming that the...Ch. 12 - You are headwaiter at a new restaurant, and your...Ch. 12 - Climbers attempting to cross a stream place a...Ch. 12 - A crane in a marble quarry is mounted on the...Ch. 12 - A rectangular block measures w w L, where L is...Ch. 12 - The potential energy as a function of position for...Ch. 12 - A rectangular block of mass m measures w w L,...Ch. 12 - A 160-kg highway sign of uniform density is 2.3 m...Ch. 12 - A 5.0-m-long ladder has mass 9.5 kg and is leaning...Ch. 12 - Prob. 42PCh. 12 - A uniform, solid cube of mass m and side s is in...Ch. 12 - An isosceles triangular block of mass m and height...Ch. 12 - Youre investigating ladder safety for the Consumer...Ch. 12 - A 2.0-m-long rod has density in kilograms per...Ch. 12 - What horizontal force applied at its highest point...Ch. 12 - A rectangular block twice as high as it is wide is...Ch. 12 - What condition on the coefficient of friction in...Ch. 12 - A uniform solid cone of height h and base diameter...Ch. 12 - Prove the statement in Section 12.1 that the...Ch. 12 - Three identical books of length L are stacked over...Ch. 12 - A uniform pole of mass M is at rest on an incline...Ch. 12 - For what angle does the situation in Problem 53...Ch. 12 - Figure 12.31 shows a popular system for mounting...Ch. 12 - The nuchal ligament is a thick, cordlike structure...Ch. 12 - A 4.2-kg plant hangs from the bracket shown in...Ch. 12 - The wheel in Fig. 12.34 has mass M and is weighted...Ch. 12 - An interstellar spacecraft from an advanced...Ch. 12 - Youre called to testify in a product liability...Ch. 12 - Youre designing a vacation cabin at a ski resort....Ch. 12 - Prob. 62PCh. 12 - Engineers designing a new semiconductor device...Ch. 12 - Youve been hired by your states environmental...Ch. 12 - Youve been hired by your states environmental...Ch. 12 - Youve been hired by your states environmental...Ch. 12 - Youve been hired by your states environmental...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What are the two types of bone marrow, and what are their functions?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
All of the following terms can appropriately describe humans except: a. primary consumer b. autotroph c. hetero...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
With the initial appearance of the feature we call Now Solve This, a short introduction is in order. The featur...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 12. What could we conclude if a system has a phase trajectory that sweeps out larger and larger area as time goes by?arrow_forwardneed help part darrow_forwardA cab driver heads south with a steady speed of v₁ = 20.0 m/s for t₁ = 3.00 min, then makes a right turn and travels at v₂ = 25.0 m/s for t₂ = 2.80 min, and then drives northwest at v3 = 30.0 m/s for t3 = 1.00 min. For this 6.80-min trip, calculate the following. Assume +x is in the eastward direction. (a) total vector displacement (Enter the magnitude in m and the direction in degrees south of west.) magnitude direction For each straight-line movement, model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the starting point be the origin of your coordinate system. Use the relationship speed = distance/time to find the distances traveled during each segment. Write the displacement vector, and calculate its magnitude and direction. Don't forget to convert min to s! m Model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the…arrow_forward
- î A proton is projected in the positive x direction into a region of uniform electric field E = (-5.50 x 105) i N/C at t = 0. The proton travels 7.20 cm as it comes to rest. (a) Determine the acceleration of the proton. magnitude 5.27e13 direction -X m/s² (b) Determine the initial speed of the proton. 8.71e-6 magnitude The electric field is constant, so the force is constant, which means the acceleration will be constant. m/s direction +X (c) Determine the time interval over which the proton comes to rest. 1.65e-7 Review you equations for constant accelerated motion. sarrow_forwardThree charged particles are at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure below. (Let q = 2.00 μC, and L = 0.750 m.) y 7.00 με 60.0° L 9 -4.00 μC x (a) Calculate the electric field at the position of charge q due to the 7.00-μC and -4.00-μC charges. 112 Once you calculate the magnitude of the field contribution from each charge you need to add these as vectors. KN/CI + 64 × Think carefully about the direction of the field due to the 7.00-μC charge. KN/Cĵ (b) Use your answer to part (a) to determine the force on charge q. 240.0 If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mN Î + 194.0 × If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mNarrow_forwardIn the Donkey Kong Country video games you often get around by shooting yourself out of barrel cannons. Donkey Kong wants to launch out of one barrel and land in a different one that is a distance in x of 9.28 m away. To do so he launches himself at a velocity of 22.6 m/s at an angle of 30.0°. At what height does the 2nd barrel need to be for Donkey Kong to land in it? (measure from the height of barrel 1, aka y0=0)arrow_forward
- For which value of θ is the range of a projectile fired from ground level a maximum? 90° above the horizontal 45° above the horizontal 55° above the horizontal 30° above the horizontal 60° above the horizontalarrow_forwardA map from The Legend of Zelda: The Breath of the Wild shows that Zora's Domain is 7.55 km in a direction 25.0° north of east from Gerudo Town. The same map shows that the Korok Forest is 3.13 km in a direction 55.0° west of north from Zora's Domain. The figure below shows the location of these three places. Modeling Hyrule as flat, use this information to find the displacement from Gerudo Town to Korok Forest. What is the magnitude of the displacement? Find the angle of the displacement. Measure the angle in degrees north of east of Gerudo Town.arrow_forwardRace car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? c) If the driver’s average rate of acceleration is -9.5 m/s2 as he slows down, how long does it take him to come to a stop (use information about his speed of 28.9 m/s but do NOT use his reaction and movement time in this computation)? Please answer parts a-c. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.arrow_forward
- Below you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Answer questions a-d. a) What was the total race time for each team, in seconds? b) Which team won the race? What was the difference in the teams’ times? c) What was the average speed for each team for the whole race? (provide answer to 3 decimal places). d) Calculate the average speed for each swimmer and report the results in a table like the one above. Remember to show the calculation steps. (provide answer to 3 decimal places). PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK AND STEPS.arrow_forwardNeed complete solution Pleasearrow_forwardBelow you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Fill out the chart below. Calculate average speed per split (m/s). Show all work.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Static Equilibrium: concept; Author: Jennifer Cash;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0BIgFKVnlBU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY