
Concept explainers
a.
Use the regression feature of a graphing utility to find a model of the form
a.
Answer to Problem 12PS
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The heat exchanger of a heating system has a heat probe attached to it. The temperature
Use the regression feature of a graphing utility to find a model of the form
Calculation:
Consider the following data
To find the quadratic regression model using the graphing utility
Press stat. The display will be
Now press edit. The display will be
Now type in data provided. The display will be
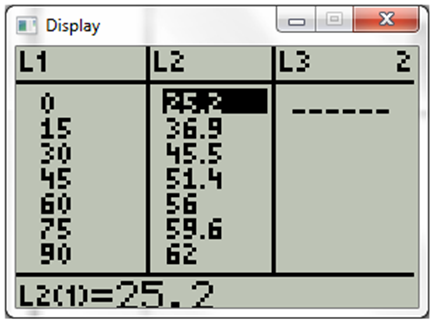
Now press stat and choose calc. The display will be
Now press QuadReg. The display will be
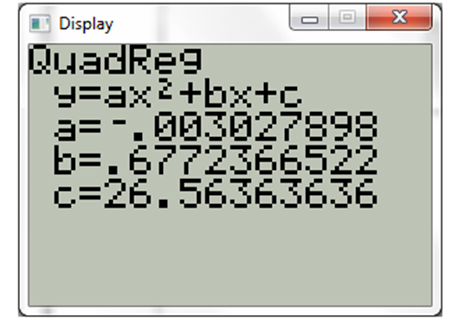
Hence, the quadratic regression model of the baove data is
b.
Verify that the model fit according to the data.
b.
Answer to Problem 12PS
The model fits the data well with least devition.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The heat exchanger of a heating system has a heat probe attached to it. The temperature
Use the graphing utility to graph
Calculation:
Consider the following data
To plot the function, proceed as follows.
Press 2nd
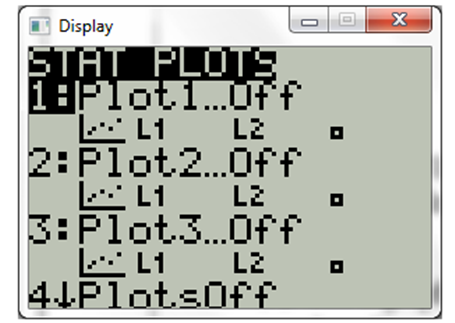
Now select on under plot
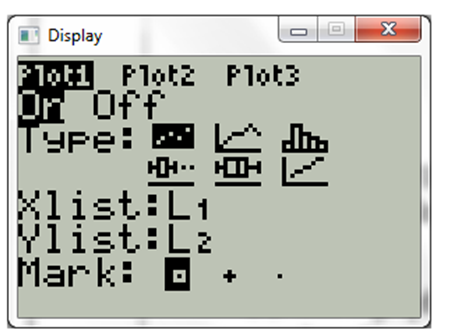
Now choose window and choose the proper scale. The display will be
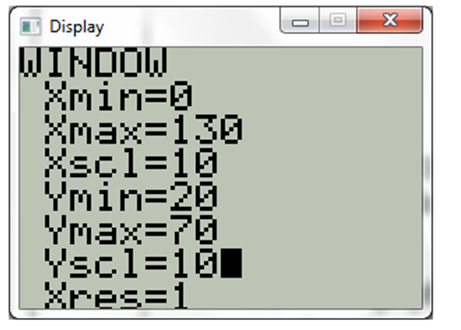
Now choose
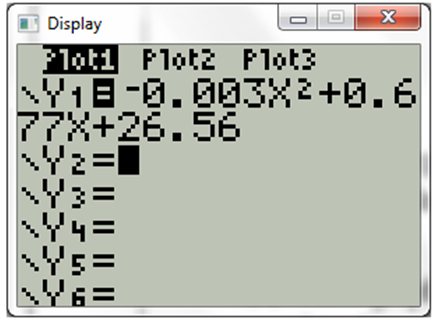
Now press graph. The display will be
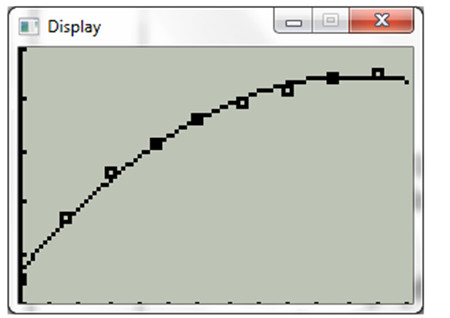
The derivation between the scatter plot of the points and the equation obtained from regression model is minimal.
Hence, the model fits the data well with least devition.
c.
Verify that the model fit according to the data.
c.
Answer to Problem 12PS
The model fits the data well with least deviation.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The heat exchanger of a heating system has a heat probe attached to it. The temperature
A rational model for the data is given by
Use the graphing utility to graph
Calculation:
Consider the following data
Consider the rational model of the data
To graph the model using the graphing utility with original values of
Press stat and choose edit. The display will be
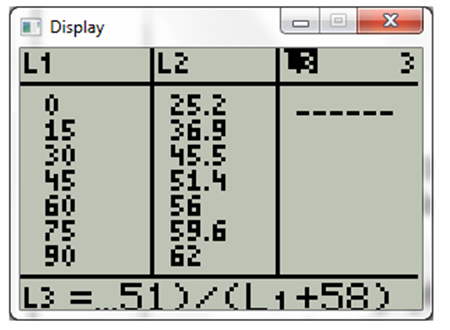
Now type in the function and display will be
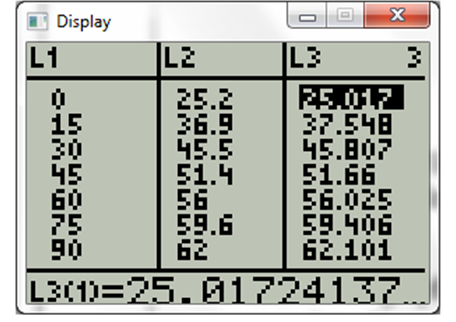
Now choose 2nd
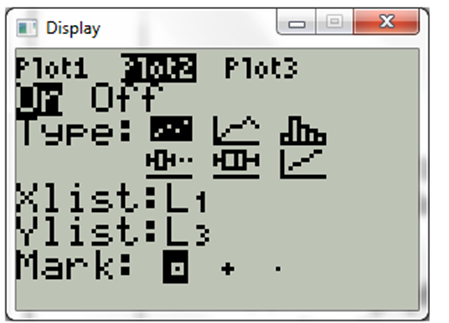
Now press graph. The display will be
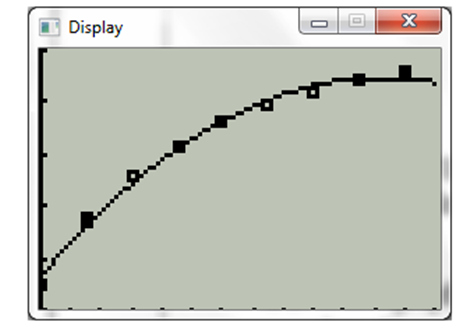
The deviation between the scatter plot of the points, the equation obtained from the regression model and the data evaluated for
Hence, the model fits the data well with least deviation.
d.
Evaluate
d.
Answer to Problem 12PS
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The heat exchanger of a heating system has a heat probe attached to it. The temperature
Evaluate
Calculation:
Consider the following data
Now move up the arrow key to obtain the value of
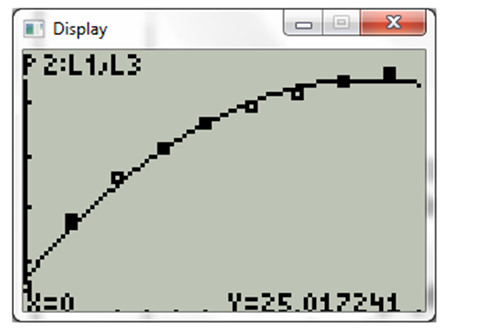
Hence, the value
e.
Find the
e.
Answer to Problem 12PS
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The heat exchanger of a heating system has a heat probe attached to it. The temperature
Find
Calculation:
Consider the following data
Now consider the limit of the function
To determine the limit of the function, proceed as follows.
Divide both numerator and denominator by
f.
Explain your reasoning.
f.
Answer to Problem 12PS
The functional relationship between temperature and time is discrete in nature.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The heat exchanger of a heating system has a heat probe attached to it. The temperature
Interpret the result of part (e) in the context of the problem. Is it possible to perform this type of analysis using
Calculation:
Consider the following data
The time
This type of analysis is not possible using the data provided for
Hence, the functional relationship between temperature and time is discrete in nature.
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- f'(x)arrow_forwardA body of mass m at the top of a 100 m high tower is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. Assume that the air resistance FD acting on the body is proportional to the velocity V, so that FD=kV. Taking g = 9.75 m/s2 and k/m = 5 s, determine: a) what height the body will reach at the top of the tower, b) how long it will take the body to touch the ground, and c) the velocity of the body when it touches the ground.arrow_forwardA chemical reaction involving the interaction of two substances A and B to form a new compound X is called a second order reaction. In such cases it is observed that the rate of reaction (or the rate at which the new compound is formed) is proportional to the product of the remaining amounts of the two original substances. If a molecule of A and a molecule of B combine to form a molecule of X (i.e., the reaction equation is A + B ⮕ X), then the differential equation describing this specific reaction can be expressed as: dx/dt = k(a-x)(b-x) where k is a positive constant, a and b are the initial concentrations of the reactants A and B, respectively, and x(t) is the concentration of the new compound at any time t. Assuming that no amount of compound X is present at the start, obtain a relationship for x(t). What happens when t ⮕∞?arrow_forwardConsider a body of mass m dropped from rest at t = 0. The body falls under the influence of gravity, and the air resistance FD opposing the motion is assumed to be proportional to the square of the velocity, so that FD = kV2. Call x the vertical distance and take the positive direction of the x-axis downward, with origin at the initial position of the body. Obtain relationships for the velocity and position of the body as a function of time t.arrow_forwardAssuming that the rate of change of the price P of a certain commodity is proportional to the difference between demand D and supply S at any time t, the differential equations describing the price fluctuations with respect to time can be expressed as: dP/dt = k(D - s) where k is the proportionality constant whose value depends on the specific commodity. Solve the above differential equation by expressing supply and demand as simply linear functions of price in the form S = aP - b and D = e - fParrow_forwardFind the area of the surface obtained by rotating the circle x² + y² = r² about the line y = r.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





