
Concept explainers
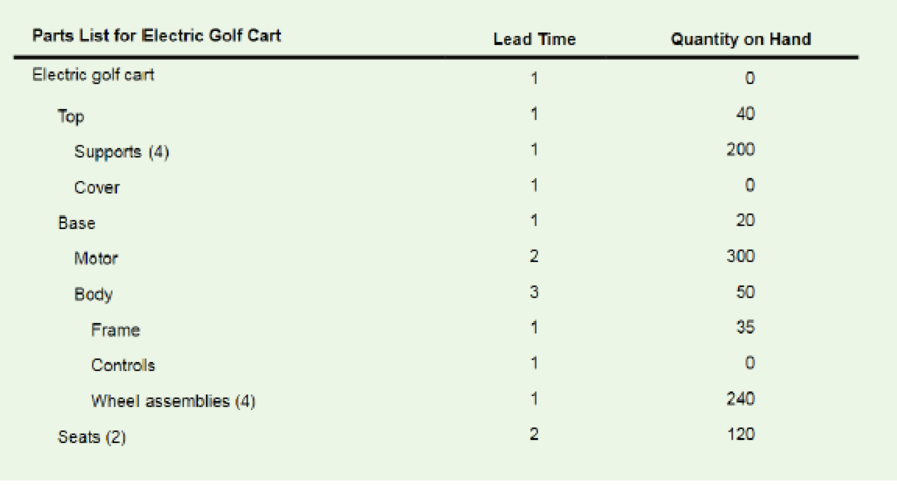
A firm that produces electric golf carts has just received an order for 200 carts, which must be ready for delivery at the start of week 8. Information concerning the product structure, lead times, and quantities on hand is shown in the following table. Use this information to do each of the following:
a. Construct a product tree.
b. Construct an assembly time chart.
c. Develop a material requirements plan that will provide 200 golf carts by week 8 assuming lot-for-lot ordering.
a)
To construct: A product tree
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which can be used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
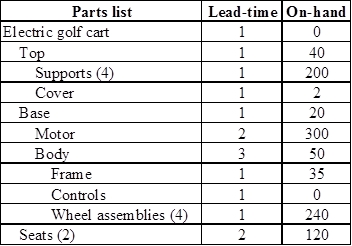
Construct a product tree:
b)
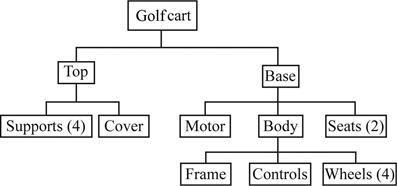
To construct: An assembly time chart
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which can be used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:

Construct an assembly time chart:
c)
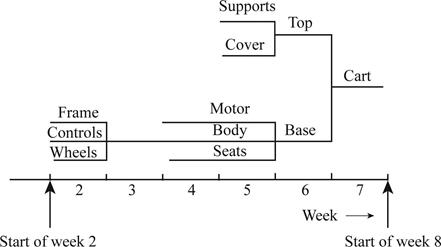
To prepare: Materials Requirement planning using the provided information.
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which can be used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The company needs to provide 200 golf carts by week 8.

Develop a material requirement planning for golf cart:
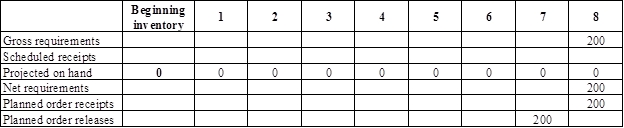
- It is given that the company needs to provide 200 golf carts by week 8.
- Beginning inventory is 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 200 units in week 8 (200-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 200 units in the beginning of Week 8. Hence, they need to order for 200 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 7.
Develop a material requirement planning for top:
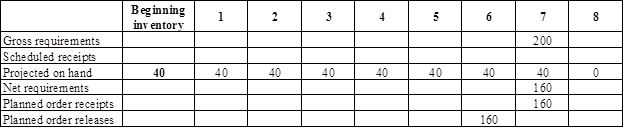
- Golf cart is the parent for top. Hence, the planned order release of the golf cart would be the gross requirement of the top. As number of units required is 1 for top, the planned order release row of golf cart should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of top.
- Beginning inventory is 40 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 160 units in week 7 (200-40).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 160 units in the beginning of Week 7. Hence, they need to order for 160 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 6.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 8 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for supports (4):
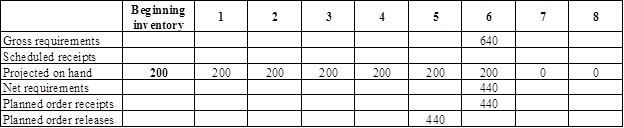
- Top is the parent for supports. Hence, the planned order release of the top would be the gross requirement of the supports. As number of units required is 4 for supports, the planned order release row of top should be multiplied with 4 to attain the gross requirement column of support.
- Beginning inventory is 200 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 440 units in week 6 (640-200).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 440 units in the beginning of Week 6. Hence, they need to order for 440 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 5.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 7 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for cover:
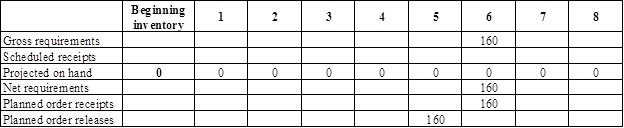
- Top is the parent for cover. Hence, the planned order release of the top would be the gross requirement of the cover. As number of units required is 1 for cover, the planned order release row of top should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of cover.
- Beginning inventory is 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 160 units in week 6 (160-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 160 units in the beginning of Week 6. Hence, they need to order for 160 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 5.
Develop a material requirement planning for base:
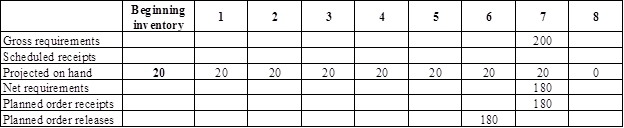
- Golf cart is the parent for base. Hence, the planned order release of the golf cart would be the gross requirement of the base. As number of units required is 1 for base, the planned order release row of golf cart should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of base.
- Beginning inventory is 20 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 180 units in week 7 (200-20).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 180 units in the beginning of Week 7. Hence, they need to order for 180 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 6.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 8 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for motor:
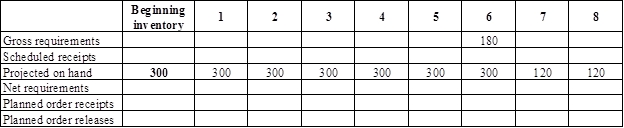
- Base is the parent for motor. Hence, the planned order release of the base would be the gross requirement of the motor. As number of units required is 1 for motor, the planned order release row of base should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of motor.
- Beginning inventory is 300 units.
- Gross requirement for week 6 is 180 units. As the beginning inventory is sufficient to satisfy the demand, there is no necessary to place an order.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 7 is 120 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for body:
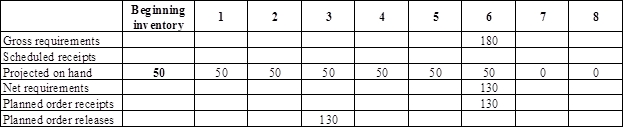
- Base is the parent for body. Hence, the planned order release of the base would be the gross requirement of the body. As number of units required is 1 for body, the planned order release row of base should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of body.
- Beginning inventory is 50 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 130 units in week 6 (180-50).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 3 weeks. Company requires 130 units in the beginning of Week 6. Hence, they need to order for 130 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) before three weeks (as the lead-time is 3 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 7 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for seats (2):
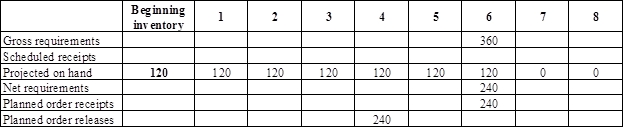
- Base is the parent for seats. Hence, the planned order release of the base would be the gross requirement of the seats. As number of units required is 1 for seats, the planned order release row of base should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of seats.
- Beginning inventory is 120 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 240 units in week 6 (360-120).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. Company requires 240 units in the beginning of Week 6. Hence, they need to order for 240 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) before two weeks (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 4.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 7 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for frame:
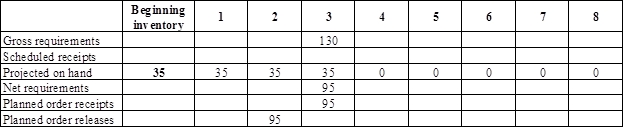
- Body is the parent for frame. Hence, the planned order release of the body would be the gross requirement of the frame. As number of units required is 1 for frame, the planned order release row of body should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of frame.
- Beginning inventory is 35 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 95 units in week 3 (130-35).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 95 units in the beginning of Week 3. Hence, they need to order for 95 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 2.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for controls:
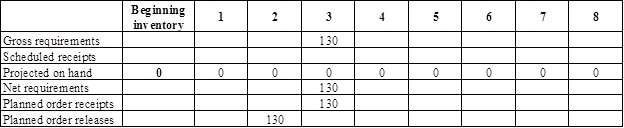
- Body is the parent for controls. Hence, the planned order release of the body would be the gross requirement of the controls. As number of units required is 1 for controls, the planned order release row of body should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of controls.
- Beginning inventory is 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 130 units in week 3 (130-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 130 units in the beginning of Week 3. Hence, they need to order for 130 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 2.
Develop a material requirement planning for wheel assemblies (4):
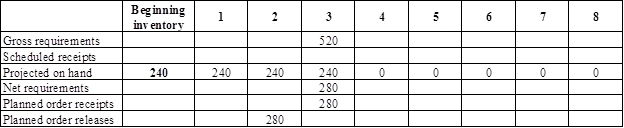
- Body is the parent for wheel assemblies. Hence, the planned order release of the body would be the gross requirement of the wheel assemblies. As number of units required is 4 for wheel assemblies, the planned order release row of body should be multiplied with 4 to attain the gross requirement column of wheel assemblies.
- Beginning inventory is 240 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 280 units in week 3 (520-240).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 280 units in the beginning of Week 3. Hence, they need to order for 280 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 2.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Operations Management
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 8th Edition
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Essentials of MIS (13th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
- 7. Wireless Infrastructure in the Cloud Wireless devices have changed the way organisations and their customers interact. Wireless enabled devices have driven the mindset that wireless networks must be ubiquitous, fast, and constantly available. These are demands that have traditionally put organisations and their user communities in direct conflict with their IT departments, as constructing and maintaining wireless infrastructures are typically time-consuming, complex, and costly endeavours.arrow_forwardIM.54 A growing online retailer sells thousands of items yet has has one specialty product category with just 30 items. They want to classify these thirty items according to the annual dollar volume (revenue) generated by each item. The table below lists each item number, Annual Sales (in units), and Price per unit: Item # Annual Sales Price 1 221 $25.85 2 446 $14.15 3 8,940 $168.19 4 2,965 $15.99 5 1,322 $29.37 6 2,575 $12.77 7 767 $28.43 8 5,803 $163.01 9 2,673 $20.51 10 642 $14.71 11 4,168 $54.53 12 1,881 $22.55 13 2,417 $29.63 14 5,207 $36.41 15 1,381 $20.55 16 9,635 $173.69 17 17,406 $27.07 18 1,573 $25.99 19 6,471 $64.99 20 6,047 $29.83 21 433 $20.89 22 2,279 $53.59 23 15,532 $106.91 24 1,585 $4.09 25 5,376 $65.23 26 2,965 $37.93 27 2,048 $28.51 28 1,174 $22.99 29 381 $5.57 30 2,930 $3.43 Which item in the table above has the highest annual dollar volume? In the answer field below, write the ITEM # that…arrow_forwardIM.84 An outdoor equipment manufacturer sells a rugged water bottle to complement its product line. They sell this item to a variety of sporting goods stores and other retailers. The manufacturer offers quantity discounts per the following discount schedule: Option Plan Quantity Price A 1 - 2,199 $5.00 B 2,200 - 3,699 $4.55 C 3,700+ $3.90 A large big-box retailer expects to sell 9,200 units this year. This retailer estimates that it incurs an internal administrative cost of $235 each time it places an order with the manufacturer. Holding cost for the retailer is $60 per case per year. (There are 52 units or water bottles per case.)Based on this information, and not taking into account any quantity discount offers, what is the calculated EOQ (in units)? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) Based on this information, sort each quantity discount plan from left to right by dragging the MOST preferred option plan to the left, and the LEAST preferred option…arrow_forward
- Please provide detailed solutions to the following problems/exercises (4 problems/exercises x 9 points each): 1) View the video ON Unveils ‘Lightspray’ Technology (4.55 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), and The Secret of Lightspray (8.27 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), answer the following questions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjmeaC-wlZs a) What is new about the design of ON’s shoes? b) How will ON’s new manufacturing technique affect location planning for footwear firms? c) How does ON focus on it sustainability strategy? Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs for each of the questions. 2) Unimed Hospital currently processes patient admissions through three admitting clerks who are set up to work in series, with respective reliabilities of 0.96, 0.95, and 0.90 (see figure below). a) Find the reliability of the current admission process. Due to rising patient complaints, the hospital administrator, Chimeg…arrow_forward3) A startup firm, Pocket International, has come up with a tiny programmable computer, NerdCom Mini Air, that sells for $49.99. The firm estimates that the programmable computers have an expected life that is exponential, with a mean of 24 months. The firm wants to estimate the probability that the NerdCom Mini Air will have a life that ends: a) after the initial 24 months of service. b) before the 24 months of service is completed. c) not before 48 months of service. Note: You could work out the problem by hand or use excel; in chapter 4S, section 4S.2 of the Stevenson text, reliability (finding the probability of functioning for a specified length of time) is covered with examples; chapters 4 & 4S Stevenson lecture power point slides 33 to 38 (chapters 4 & 4S lecture: 32.30 mins to 38.56 mins) cover reliability over time with examples.arrow_forwardDiscuss how training and development programs can be best presented to ultimately change the behavior of employees, often without their knowledge or awareness.arrow_forward
- Doctor Earrow_forwardConsidering contemporary challenges in business, analyze a real-world case where a company successfully navigated a major shift in its marketing strategy to adapt to changing market dynamics. Discussion Question and Prompt: Identify the key factors that contributed to the success of their marketing strategy in the face of contemporary issues. How can businesses draw insights from this case to inform their own marketing strategies amid current business challenges?arrow_forward1) View the video Service Processing at BuyCostumes (10.41 minutes, Ctrl+Click on the link); what are your key takeaways (tie to one or more of the topics discussed in Chapter 3) after watching this video. (viddler.com/embed/a6b7054c) Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs. 2) Orkhon Foods makes hand-held pies (among other products). The firm’s weekly sales of hand-held pies over the past seven weeks are given in the table. The firm’s operations manager, Amarjargal, wants to forecast sales for week 8. Weeks Sales of hand-held pies(000s) 1 19 2 18 3 17 4 20 5 18 6 22 7 20 Forecast the week 8 sales using the following approaches: a) Naïve approach b) 5-month moving average c) 3-month weighted moving average using the following weights: 0.50 for week 7, 0.30 for week 6, and 0.20 for week 5. d) Exponential smoothing using a smoothing constant of 0.30, assume a…arrow_forward
- Answer all parts to question 4 and show all workingarrow_forward1) View the video Service Processing at BuyCostumes (10.41 minutes, Ctrl+Click on the link); what are your key takeaways (tie to one or more of the topics discussed in Chapter 3) after watching this video. (viddler.com/embed/a6b7054c) Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs. 2) Orkhon Foods makes hand-held pies (among other products). The firm’s weekly sales of hand-held pies over the past seven weeks are given in the table. The firm’s operations manager, Amarjargal, wants to forecast sales for week 8. Weeks Sales of hand-held pies(000s) 1 19 2 18 3 17 4 20 5 18 6 22 7 20 Forecast the week 8 sales using the following approaches: a) Naïve approach b) 5-month moving average c) 3-month weighted moving average using the following weights: 0.50 for week 7, 0.30 for week 6, and 0.20 for week 5. d) Exponential smoothing using a smoothing constant of 0.30, assume a week 2…arrow_forwardWhat area of emotional intelligence refers to the ability to manage your emotions, particularly in stressful situations, and maintain a positive outlook despite setbacks? relationship management self awareness social awareness self managementarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning





