
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given alloy, an artificial age-hardening heat treatment needs to be recommended.
Concept Introduction:
The mixture of magnesium with other elements is known as magnesium alloy. The other elements include Zinc, Manganese, Aluminum and Copper.
Solidification takes place after complete mixing. It gets phase transformation to Liquid phase and there is no diffusion in the solid phase. With a decrease in the temperature of aluminum, the solubility of aluminium in magnesium also decreases.
If temperature is increased above,
Answer to Problem 12.30P
For artificial aging, the temperatures of solvus and eutectic point is determined. For this the curve between the percentage of weight of magnesium and the temperature needs to be drawn.
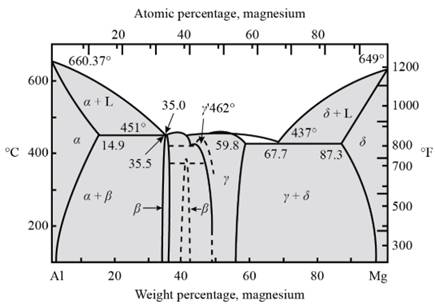
Fig. 1- Phase diagram of Al-Mg system
Explanation of Solution
Form the above graph, one gets to know all the temperatures for artificial age hardening of Magnesium-Aluminium alloy
| Temperature | Al- Mg | Al- Mg | Al- Mg |
| Treat at | Quenching | Quenching | Quenching |
| Age at | Temperature below | Temperature below | Temperature below |
Table No.
Thus, artificial age hardening depends on temperature of solid solubility and the eutectic point. Precipitation treat hardening is done by the help of quenching process.
(b)
Interpretation:
The amount of beta precipitates in all weight percentage of magnesium needs to be compared.
Concept Introduction:
The mixture of magnesium with other elements is known as magnesium alloy. The other elements include Zinc, Manganese, aluminum and Copper.
Solidification takes place after complete mixing. It gets phase transformation to Liquid phase and there is no diffusion in the solid phase. With a decrease in the temperature of aluminum, the solubility of aluminum in magnesium also decreases.
If temperature is increased above,
Answer to Problem 12.30P
The amount of beta precipitates in Al-
Explanation of Solution
Consider,
Aging temperature -
Tie line is passing through weight percentage of Mg as -
Hence, now one can calculate beta precipitate as −
For Al-
For Al-
And for Al-
From calculations, one can observe that if the weight percentage of magnesium in aluminum alloy increases then the amount of beta precipitate also increases.
(c)
Interpretation:
The requirement which is not satisfied in age hardening needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
The mixture of magnesium with other elements is known as magnesium alloy. The other elements include Zinc, Manganese, Aluminum and Copper.
Solidification takes place after complete mixing. It gets phase transformation to Liquid phase and there is no diffusion in the solid phase. With a decrease in the temperature of aluminum, the solubility of aluminum in magnesium also decreases.
If temperature is increased above,
Answer to Problem 12.30P
After the heat treatment, it can be observed that there is a little strengthening remains because the coherent precipitation is not formed.
Explanation of Solution
Age hardening is used to increase the yield strength of malleable metals like as −
- Aluminium
- Magnesium
- Nickel
- Titanium
The hardening depends on the temperature and its solubility in solid phase which results into pure or fine particles with the removal of the impurity phase. For precipitation, sometimes the alloy is kept at the elevated temperature for hours. This process of time delay is known as Aging.
After testing of the alloys with heat treatment, some amount of strengthening is observed. At this stage there is no formation of coherent precipitation. There is only simple dispersion strength as compared to the age hardening.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
- PROBLEM 2.50 1.8 m The concrete post (E-25 GPa and a = 9.9 x 10°/°C) is reinforced with six steel bars, each of 22-mm diameter (E, = 200 GPa and a, = 11.7 x 10°/°C). Determine the normal stresses induced in the steel and in the concrete by a temperature rise of 35°C. 6c " 0.391 MPa 240 mm 240 mm 6₁ = -9.47 MPaarrow_forwardI need help on this question. step by step calculations and answers.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- jan G(f) f Sketch the spectrum of g(t), which has a maximum frequency of 5 kHz, if it is sampled at the following sampling frequencies: 7 kHz, 10 kHz and 15 kHz. Indicate if and how the signal can be recovered at each sampling frequency.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer i will report your answerarrow_forwardA single tone is modulated using FM transmitter. The SNR, at the input of the demodulator 20 dB. If the maximum frequency of the modulating signal is 4 kHz, and the maximum equency deviation is 12 kHz, find the SNR, and the bandwidth (using Carson rule) at the ollowing conditions: . For the given values of fm and Af. !. If the amplitude of the modulating signal is increased by 80%. 3. If the amplitude of the modulating signal is decreased by 50%, and frequency of modulating signal is increased by 50%.arrow_forward
- The circuit shown below on the left has the following parameters: V₁ = 5 V. R₁ = 40, R₂ = 40, α = 0.1. This circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit shown below on the right such that the voltage and current received by an arbitrary load resistor RL, are identical when connected to either circuits. Determine the value of the resistor R (in ) in the equivalent circuit. R₁ Rx R2 R₁ Vx R₁ Vi απ. barrow_forwardLab 07: Java Graphics (Bonus lab) In this lab, we'll be practicing what we learned about GUIs, and Mouse events. You will need to implement the following: ➤ A GUI with a drawing panel. We can click in this panel, and you will capture those clicks as a Point (see java.awt.Point) in a PointCollection class (you need to build this). о The points need to be represented by circles. Below the drawing panel, you will need 5 buttons: о An input button to register your mouse to the drawing panel. ○ о о A show button to paint the points in your collection on the drawing panel. A button to shift all the points to the left by 50 pixels. The x position of the points is not allowed to go below zero. Another button to shift all the points to the right 50 pixels. The x position of the points cannot go further than the You can implement this GUI in any way you choose. I suggest using the BorderLayout for a panel containing the buttons, and a GridLayout to hold the drawing panel and button panels.…arrow_forwardK/S 46. (O المهمات الجديدة 0 المنتهية 12 المغـ ۱۱:۰۹ search ليس لديك اي مهمات ☐ ○ ☑arrow_forward
- the answer should be: V2= -(P0-PL/2μL)(dx-x^)+Ux/darrow_forwardFor some viscoelastic polymers that are subjected to stress relaxation tests, the stress decays with time according to a(t) = a(0) exp(-4) (15.10) where σ(t) and o(0) represent the time-dependent and initial (i.e., time = 0) stresses, respectively, and t and T denote elapsed time and the relaxation time, respectively; T is a time-independent constant characteristic of the material. A specimen of a viscoelastic polymer whose stress relaxation obeys Equation 15.10 was suddenly pulled in tension to a measured strain of 0.5; the stress necessary to maintain this constant strain was measured as a function of time. Determine E (10) for this material if the initial stress level was 3.5 MPa (500 psi), which dropped to 0.5 MPa (70 psi) after 30 s.arrow_forward1. Consider the following a unity feedback control system. R(s) + E(s) 500(s+2)(s+5)(s+6) s(s+8)(s+10)(s+12) -Y(s) Find the followings: a) Type of the system b) Static position error constant Kp, Static velocity error constant Ry and Static acceleration error constant Ka c) Find the steady-state error of the system for (i) step input 1(t), (ii) ramp input t 1(t), (iii) parabolic input t² 1(t). 2. Repeat the above problem for the following system. R(s) + E(s) 500(s + 2)(s + 5) (s+8)(s+ 10)(s+12) Y(s) 3. Repeat the above problem for the following system. R(s) + E(s) 500(s+2)(s+4)(s+5)(s+6)(s+7) s²(s+8)(s+10)(s+12) Y(s)arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





