
Concept explainers
Suppose Fruit, Apple, Orange, GoldenDelicious, and McIntosh are defined in the following inheritance hierarchy:
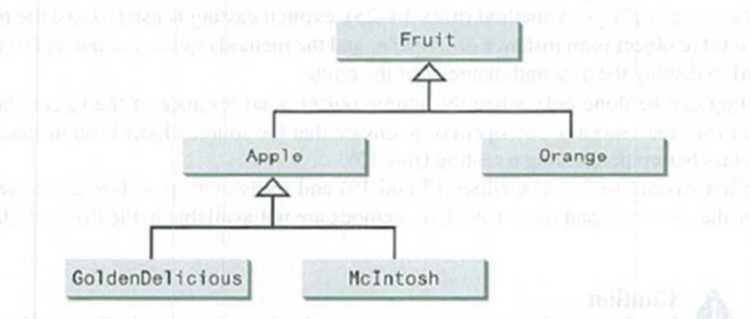
Assume the following code is given:
Fruit fruit = new GoldenDelicious();
Orange orange = new Orange();
Answer the following questions:
a. Is fruit instanceof Fruit?
b. Is fruit instanceof Orange?
c. Is fruit instanceof Apple?
d. Is fruit instanceof GoldenDelicious?
e. Is fruit instanceof McIntosh?
f. Is orange instanceof Orange?
g. Is orange instanceof Fruit?
h. Is orange instanceof Apple?
i. Suppose the method makeAppleCider is defined in the Apple class. Can Fruit invoke this method? Can orange invoke this method?
j. Suppose the method makeOrangeJuice is defined in the Orange class. Can orange invoke this method? Can Fruit invoke this method?
k. Is the statement Orange p = new Apple() legal?
l. Is the statement McIntosh p = new Apple() legal?
m. Is the statement Apple p = new McIntosh() legal?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Introduction to Java Programming and Data Structures: Brief Version (11th Global Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
- 2:21 m Ο 21% AlmaNet WE ARE HIRING Experienced Freshers Salesforce Platform Developer APPLY NOW SEND YOUR CV: Email: hr.almanet@gmail.com Contact: +91 6264643660 Visit: www.almanet.in Locations: India, USA, UK, Vietnam (Remote & Hybrid Options Available)arrow_forwardProvide a detailed explanation of the architecture on the diagramarrow_forwardhello please explain the architecture in the diagram below. thanks youarrow_forward
- Complete the JavaScript function addPixels () to calculate the sum of pixelAmount and the given element's cssProperty value, and return the new "px" value. Ex: If helloElem's width is 150px, then calling addPixels (hello Elem, "width", 50) should return 150px + 50px = "200px". SHOW EXPECTED HTML JavaScript 1 function addPixels (element, cssProperty, pixelAmount) { 2 3 /* Your solution goes here *1 4 } 5 6 const helloElem = document.querySelector("# helloMessage"); 7 const newVal = addPixels (helloElem, "width", 50); 8 helloElem.style.setProperty("width", newVal); [arrow_forwardSolve in MATLABarrow_forwardHello please look at the attached picture. I need an detailed explanation of the architecturearrow_forward
- Information Security Risk and Vulnerability Assessment 1- Which TCP/IP protocol is used to convert the IP address to the Mac address? Explain 2-What popular switch feature allows you to create communication boundaries between systems connected to the switch3- what types of vulnerability directly related to the programmer of the software?4- Who ensures the entity implements appropriate security controls to protect an asset? Please do not use AI and add refrencearrow_forwardFind the voltage V0 across the 4K resistor using the mesh method or nodal analysis. Note: I have already simulated it and the value it should give is -1.714Varrow_forwardResolver por superposicionarrow_forward
- Describe three (3) Multiplexing techniques common for fiber optic linksarrow_forwardCould you help me to know features of the following concepts: - commercial CA - memory integrity - WMI filterarrow_forwardBriefly describe the issues involved in using ATM technology in Local Area Networksarrow_forward
- Programming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT  Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr




