
a
To calculate: To find the number of wild-type bacteria that mutates using the given information
a
Answer to Problem 32E
The number of wild-type bacteria that mutate is
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Suppose that a fraction 0.2 of wild-type mutate each generation, but that each wild-type individual produces 2.0 offspring while each mutant produces only 1.0 offspring.
Calculation:
Initially, let there be
Now a fraction 0.2 of wild-type mutate each generation.
Therefore, the number of wild-type bacteria that mutate is
b
To calculate: To find the number of wild-type bacteria and the number of mutants after mutation using the given information
b
Answer to Problem 32E
The number of mutants after mutation is given by
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Suppose that a fraction 0.2 of wild-type mutate each generation, but that each wild-type individual produces 2.0 offspring while each mutant produces only 1.0 offspring.
Calculation:
Now the number of wild type bacteria after mutation is given by
Also, the number of mutants after mutation is given by
c
To calculate: To find the number of wild-type bacteria and the number of mutants after reproduction using the given information
c
Answer to Problem 32E
Therefore, the number of mutants after reproduction shall be
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Suppose that a fraction 0.2 of wild-type mutate each generation, but that each wild-type individual produces 2.0 offspring while each mutant produces only 1.0 offspring.
Calculation:
Now, each wild-type individual produces 2.0 offspring.
Therefore, the number of wild-type bacteria after reproduction is given by
Also, each mutant produces only 1.5 offspring.
Therefore, the number of mutants after reproduction shall be
d
To calculate: To find the total number of bacteria after mutation and reproduction using the given information
d
Answer to Problem 32E
The total number of bacteria after mutation and reproduction is given by
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Suppose that a fraction 0.2 of wild-type mutate each generation, but that each wild-type individual produces 2.0 offspring while each mutant produces only 1.0 offspring.
Calculation:
The total number of bacteria after mutation and reproduction is given by
e
To calculate: To find the fraction of mutants after mutation and reproduction using the given information
e
Answer to Problem 32E
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Suppose that a fraction 0.2 of wild-type mutate each generation, but that each wild-type individual produces 2.0 offspring while each mutant produces only 1.0 offspring.
Calculation:
To find the fraction of mutants after mutation and reproduction, divide the discrete-time dynamical system for
Therefore, we have
f
To calculate: To find the equilibrium using the obtained values
f
Answer to Problem 32E
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Suppose that a fraction 0.2 of wild-type mutate each generation, but that each wild-type individual produces 2.0 offspring while each mutant produces only 1.0 offspring.
Calculation:
Let
To find the equilibrium consider,
Solving the above equation gives,
Therefore,
g
To calculate: To determine and to find whether the equilibrium is stable or not using the obtained information
g
Answer to Problem 32E
The fraction of mutants will end up at about 33.33 percent.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Suppose that a fraction 0.2 of wild-type mutate each generation, but that each wild-type individual produces 2.0 offspring while each mutant produces only 1.0 offspring.
Calculation:
The cobweb starting from the initial condition is as shown below:
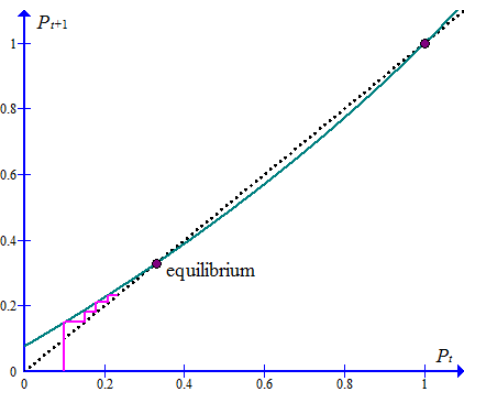
The equilibrium at l/ 3 seems to be stable. The fraction of mutants will end up at about 33.33 percent.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Modeling the Dynamics of Life: Calculus and Probability for Life Scientists
- Golden Ratio search Method f(x) = 2x^3 - 3x^2 - 12x + 1 Golden ratio search rules 1.If f(x) < f(x2): 1. Eliminate all x values less than x2 2. X2 becomes the new a 3. x, becomes the new x2 4. no change in b If f(x) > f(x2): 1. Eliminate all x values greater than x 2. x, becomes the new b 3. x2 becomes the new x 4. no change in aquesion=Narrow the interval in which the minimizer of the function f is located using the golden search method, starting with the initial interval (0,6], until its width is less than 2. Then, accept the midpoint of this interval as an approximate value of the minimizer of the function fand determine it. (ф=0.62)According to the question above, fill in the table below using the algorithm until the appropriate place.please write every step by step in a verry comprehensive wayarrow_forwardIn preparing for the upcoming holiday season, Fresh Toy Company (FTC) designed a new doll called The Dougie that teaches children how to dance. The fixed cost to produce the doll is $100,000. The variable cost, which includes material, labor, and shipping costs, is $31 per doll. During the holiday selling season, FTC will sell the dolls for $39 each. If FTC overproduces the dolls, the excess dolls will be sold in January through a distributor who has agreed to pay FTC $10 per doll. Demand for new toys during the holiday selling season is extremely uncertain. Forecasts are for expected sales of 60,000 dolls with a standard deviation of 15,000. The normal probability distribution is assumed to be a good description of the demand. FTC has tentatively decided to produce 60,000 units (the same as average demand), but it wants to conduct an analysis regarding this production quantity before finalizing the decision. (a) Determine the equation for computing FTC's profit for given values of the…arrow_forwardFor all integers a and b, (a + b)^4 ≡ a^4 + b^4 (mod 4).arrow_forward
- Let Χ be a real-valued character (mod k). Let k S = Σnx(n). n=1 If (a, k) = 1, ax(a)S = S (mod k). (iii) Write k = 2ºq where q is odd. Show that there is an integer a with (a, k) = 1 such that a = 3 (mod 2ª) and a = 2 (mod q). Deduce that 12S = 0 (mod k).arrow_forwardProve that (1) Σσς (α) μ(η/α) = n d/n (ii) Σσς(d) = η Σσο(α)/d d❘n d❘n (iii) σ (d) σ (n/d) = Σ d³oo(d) σo(n/d). d|n dnarrow_forwardhow to do part b,carrow_forward
- If p = 5 (mod 8), where p is prime, show that p|2 (P-1)/2 + 1. State and prove the corresponding result when p = 7 (mod 8). Deduce that 250 + 1 and 251 1 are composite. -arrow_forwardWhy the character no change for my remark?arrow_forwardIn preparing for the upcoming holiday season, Fresh Toy Company (FTC) designed a new doll called The Dougie that teaches children how to dance. The fixed cost to produce the doll is $100,000. The variable cost, which includes material, labor, and shipping costs, is $31 per doll. During the holiday selling season, FTC will sell the dolls for $39 each. If FTC overproduces the dolls, the excess dolls will be sold in January through a distributor who has agreed to pay FTC $10 per doll. Demand for new toys during the holiday selling season is extremely uncertain. Forecasts are for expected sales of 60,000 dolls with a standard deviation of 15,000. The normal probability distribution is assumed to be a good description of the demand. FTC has tentatively decided to produce 60,000 units (the same as average demand), but it wants to conduct an analysis regarding this production quantity before finalizing the decision. (a) Determine the equation for computing FTC's profit for given values of the…arrow_forward
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning

